Contents

Obesity – a disease in which a person has excess fat deposits in the subcutaneous tissue, as well as in other tissues and organs. This pathology manifests itself in an increase in body weight due to the accumulation of adipose tissue by 20% or more of the average values. Obese people suffer from various sexual disorders, experience psychological and physiological discomfort, over time they develop disorders in the functioning of the joints, spine and internal organs. Excess deposits of adipose tissue increase the risk of cardiovascular pathologies, diabetes, liver and kidney diseases. Accordingly, the risk of death increases. In this regard, obesity requires treatment, which most often consists of three components: dietary nutrition, physical activity, and psychological assistance to the patient.
It has been found that men are twice as likely to be obese as women. The age at which people usually begin to get better is between 30 and 60 years of age. Only in the Russian Federation this disease affects 30% of people of working age. Another 25% of the country’s population is overweight. Scientists all over the world are concerned about the problem of obesity. WHO experts call this disease an epidemic of our time, from which millions of people are already suffering. Moreover, the risks of developing obesity are practically not affected by the social status of a person and his nationality.
To assess the danger of obesity, the following facts should be taken into account in numbers:
Obese people suffer from angina pectoris and coronary artery disease 3-4 times more often than people with normal body weight;
Hypertension is diagnosed in obese people 3 times more often;
Acute respiratory and viral infections, pneumonia and other diseases in obese people are more severe and protracted. They are more likely to experience various complications.
To diagnose obesity in a patient, it is necessary to determine his body mass index (BMI). Calculating this indicator is quite simple. The formula proposed by WHO back in 1997 remains relevant today. So, to determine BMI, you can use the following formula: weight in kilograms divided by a person’s height in meters squared.
The resulting value allows you to calculate the individual BMI of a person, which is characterized by the following values:
If the BMI is less than 18,5, then the person is underweight;
If the value obtained is in the range from 18,5 to 24,9, then the body weight of a person is considered normal;
If the value obtained is in the range from 25,0 to 29,9, then body weight is considered overweight;
The first degree of obesity is diagnosed with a BMI of 30,0 to 34,9;
The second degree of obesity is diagnosed with a BMI in the range between 35,0 and 39,9;
The third and fourth degree of obesity is diagnosed if the BMI is greater than 40.
Moreover, a BMI exceeding 30 indicates that a person already has direct threats to health and needs medical help.
Obesity symptoms
Obesity symptoms may seem obvious to every person – it is the presence of excess body weight. Indeed, this is the most specific symptom indicating a problem. Fat deposits are found on the abdomen, in the back, on the sides, on the shoulders, on the hips. At the same time, the muscles of such people are most often weak and underdeveloped.
Other symptoms of obesity include:
Changes in appearance. People get a second chin, men often suffer from gynecomastia (their mammary glands increase in size). The abdomen is covered with fatty folds that resemble an apron;
Often in overweight people there is an inguinal and umbilical hernia;
Patients get tired faster, drowsy, sweating of such people is increased;
As the disease progresses, shortness of breath joins, as the cardiovascular system suffers;
Due to violations of metabolic processes, failures occur in the digestive system. Nausea often worries, constipation develops;
The joints and spine suffer from excessive load, pain occurs in them;
Obese people are prone to edema;
In women, a violation of the menstrual cycle is possible, in men potency suffers. Sexual desire is reduced;
Folds and excessive sweating cause the development of skin pathologies, including prickly heat, furunculosis, eczema, pyoderma, acne. Stretch marks appear on the abdomen and thighs. Places of increased friction are particularly affected.
Depending on where the fat is deposited, there are three types of obesity. So, if fat is deposited mainly in the upper body, and the figure begins to resemble an apple in shape, then doctors talk about the abdominal type of obesity. This condition is considered very dangerous for health, as it threatens the development of cardiovascular pathologies.
When fat deposits begin to accumulate in the lower part of the body, and the torso itself is shaped like a pear, then experts talk about the femoral-buttock type of obesity. Most often, fat is distributed in this way in female representatives. This type of obesity is dangerous for the development of varicose veins, venous insufficiency and articular pathologies.
As for the third type of obesity, it is called mixed. In this case, fat is distributed evenly throughout the body.
Depending on the type of obesity, the symptoms of the disease will vary. Differences are expressed in the rate at which body weight increases, and also in whether a person has problems with the endocrine and nervous systems.
Based on this, they distinguish:
Symptoms of alimentary type of obesity. There is a gradual weight gain. Fat is distributed evenly, although sometimes it accumulates more on the hips and abdomen. The endocrine system is working normally;
Symptoms of hypothalamic obesity. Body weight increases very quickly. Fat is deposited to a greater extent on the buttocks and thighs, as well as on the abdomen. A person experiences constant hunger, which causes him to overeat. Especially noticeable increase in appetite in the evening. Such people drink a lot of water, as they are constantly thirsty. Patients get up at night to eat. Patients have a tremor of the limbs, they complain of dizziness. Since weight is quickly gained, the skin cannot withstand such loads. It has pink stretch marks. Women often suffer from infertility, facial hair may grow, and the menstrual cycle is disrupted. As for men, their sexual function suffers first of all. From the side of the nervous system, the following pathologies are observed: frequent headaches occur, insomnia appears. Blood pressure in patients is most often elevated;
Symptoms of the endocrine form of obesity. If the work of some endocrine glands is disrupted, the patient may begin to gain body weight. Fat deposits are distributed unevenly throughout the body. Women acquire masculine features, in men, on the contrary, breasts begin to grow, stretch marks appear on the skin. In addition, a person suffers from symptoms associated with a particular disease of the endocrine glands;
Symptoms of lipomatosis. This form of obesity must be considered separately, as body weight increases due to benign hyperplasia of fat cells. Lipomas appear on the human body, which do not hurt, have a symmetrical shape. Men are more susceptible to lipomatosis. A special form of the disease is Derkum’s lipomatosis, in which itchy, painful lipomas appear on the arms, legs, and body.
Causes and factors contributing to obesity

Obesity most often begins to develop due to the fact that there is a violation of the normal balance between energy consumption and the supply of this energy with food. It has been established that the main cause of obesity is overeating. It is this that in 90% of cases contributes to the fact that a person begins to gain weight. The abundance of kilocalories from food cannot be used up by the body by 100%. Therefore, the excess turns into fat and is deposited in the so-called fat “depot”. Such depots are mainly subcutaneous fat, abdominal wall and internal organs.
Over time, fat reserves increase, body weight grows, which negatively affects health. It has been proven that only 5% of cases of obesity are caused by metabolic disorders.
A provoking factor that has a direct impact on human eating behavior is a violation of the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system. The more actively it works, the higher the rate of production of ACTH and cortisol. At the same time, somatotropic hormone, which is responsible for the breakdown of fats, begins to be produced in a smaller amount. In parallel, the level of insulin in the blood rises, the absorption of thyroid hormones is disrupted. All this leads to an increase in appetite and a slowdown in the process of assimilation of fats.
So, the main cause of obesity is overeating.
However, there are some factors that contribute to the set of extra pounds, among them:
Low physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
Genetic predisposition to enzymatic failures. This is expressed in the excessive activity of the lipogenesis system and in the low activity of the enzymes responsible for the breakdown of fats;
Irrational power scheme. Fat begins to actively accumulate when carbohydrates, salt, fats, and sugars are present in large quantities in the diet. Dangerous alcohol abuse and eating in the evening, especially before bedtime;
Diseases of the endocrine system, including Itsenko-Cushing’s disease, hypogonadism, hypothyroidism and insulinoma;
Overeating due to stress;
Sometimes obesity is due to the physiological state of a person. For example, women eat more than normal during pregnancy, while breastfeeding, and then it becomes a habit;
Often the reason that a person overeats is taking hormonal drugs, treatment with psychotropic drugs.
Depending on the cause that led to obesity, primary and secondary obesity are distinguished. The primary develops due to the influence of some external factor: overeating, low physical activity, the predominance of fats and carbohydrates in food, etc. Often people have a family predisposition to be overweight.
Secondary obesity is a set of body weight due to hereditary diseases (Gelino syndrome, adiposogenital dystrophy, etc.) or due to cerebral pathologies (mental disorders, brain tumors, etc.).
Obesity and type 2 diabetes
Obesity and type 2 diabetes are closely related, as the presence of extra pounds greatly exacerbates the risk of developing this dangerous disease. It has been established that the third degree of obesity increases the likelihood of developing diabetes by 10 times. Type XNUMX diabetes itself is an acquired and non-insulin dependent disease.
It is the lifestyle that leads to weight gain that becomes the starting factor for increasing blood sugar levels. However, with adequate physical activity, the glucose that enters the bloodstream is transformed into energy, since it is necessary for the muscles to work. If a person leads a sedentary lifestyle and at the same time consumes a large amount of carbohydrates, then more insulin will be required to process glucose. Excess sugar contributes to the formation of fat not only in the subcutaneous layer, but also around the internal organs. Naturally, for the production of insulin, the pancreas has to work in an enhanced mode, which leads to the depletion of the organ. Thus, against the background of overeating, a person gains extra pounds of fat and, in parallel, he develops diabetes.
In order to prevent such a situation, it is necessary to properly organize your diet, refuse to consume large amounts of carbohydrates, and also increase physical activity on the body. If the necessary measures are taken in time, then type 2 diabetes will be eliminated and this will not require insulin therapy.
Degrees of obesity
There are four degrees of obesity, each of which is characterized by a certain set of characteristics. The degree of obesity is determined by calculating the body mass index. The higher the degree of obesity, the greater the risk of developing various pathologies.
Obesity 1 degree
Obesity of the 1st degree is said to be in the case when a person’s BMI is high and ranges from 30,0 to 34,9. If a person has the first degree of obesity, then he already needs a medical examination, followed by the preparation of an individual treatment program. It has been established that a BMI exceeding 30 poses a direct threat to health. Although many patients at this stage of obesity may have absolutely no complaints related to the state of their body.
However, obesity of the 1st degree is an occasion for a thorough examination and weight loss.
In addition to the fact that a person will increase body weight, the following symptoms may develop:
The occurrence of inexplicable weakness;
Rapid fatigue, excessive drowsiness;
Increased sweating;
Increased irritability;
Dissatisfaction with appearance;
Nervousness;
Dyspnea;
On the part of the digestive system, such disorders as constipation and periodic nausea are not excluded;
Edema may occur, which are localized mainly in the lower extremities;
The first problems with the joints and spine begin to appear, which are expressed in pains of low intensity.
With a change in lifestyle at the first stage of the development of obesity, all pathological processes are reversible.
Obesity 2 degree
Type 2 obesity is diagnosed in a patient if his BMI is very high and is in the range between 35,0 and 39,9. At the same time, the body weight of a person, compared with normal, increases by 30-40%.
More massive obesity leads to the fact that all the symptoms of ill health that bothered the patient with the first degree of obesity begin to intensify. Weakness grows, the person is increasingly in a depressed mood. Bitterness in the mouth joins nausea, which indicates disorders in the liver and gallbladder.
Joint pains increase, the load on the spinal column increases. Already at this stage of the development of obesity, an increase in blood pressure, disruption of the heart muscle is possible. Edema of the lower extremities intensifies and can persist throughout the day.
Obesity 3 degree
Obesity of the 3rd degree is said if the body mass index is excessively high and slightly exceeds the mark of 40. At the same time, there is an increase in actual body weight compared to ideal by 50-99%. To determine the ideal body weight, middle-aged men need to subtract 100 from their own height in centimeters, and 110 for women.
As for the symptoms of the 3rd degree of obesity, they are as follows:
Disturbances in the work of the heart and blood vessels progress (arterial hypertension, tachycardia increase, muffled heart tones are heard);
The respiratory system suffers with the development of chronic cor pulmonale and the formation of respiratory failure;
There are disorders in the digestive system;
The liver parenchyma is permeated with fatty infiltrates, which makes it difficult for the organ to function normally;
Sometimes pancreatitis and chronic cholecystitis develop;
Pain in the spine increases, the ankle and knee joints suffer.
In women, obesity of the third degree most often leads to menstrual irregularities, sometimes menstruation completely stops. In men, potency always worsens.
Obesity 4 degree
Obesity of the 4th degree is characterized by a significant excess of BMI (from 40 or more). At the same time, the actual weight of a person is twice the ideal body weight. Often such patients weigh more than 150-200 kg. There are cases when the body weight of people reached 300 or more kilograms.
With such a pronounced obesity, absolutely all human organs and systems suffer. Often such people are not even able to take care of themselves. Patients develop multiple severe pathologies, including diabetes mellitus, endocrine disorders, heart failure, etc. The skin is severely affected, which a person is not able to hygienically process on his own. Due to bed rest, bedsores are formed. With 4 degrees of obesity, 100% of patients receive a certain disability group.
People with such overweight need urgent treatment, because in its absence, a quick death is inevitable.
Photo obesity 4 degrees
It’s not worth it to run this disease. What can expect people who do not think about their health? For clarity, here is a photo of obesity of 4 degrees:
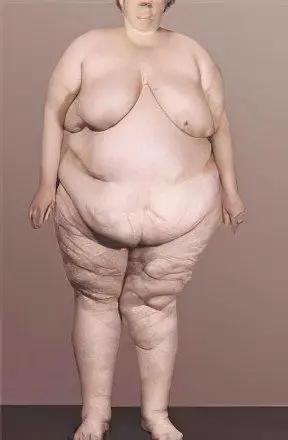 | 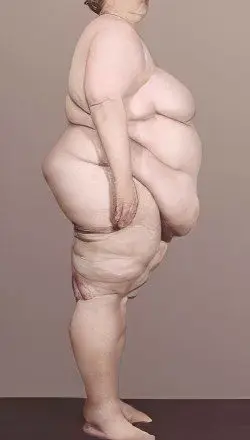 |
| increase | increase |
How is obesity treated?

The treatment of obesity involves a complex effect on the body. It is important not only to immediately reduce body weight, but also to keep it normal. Reducing body weight will positively affect the health of a person as a whole. However, the weight should come off gradually. So, in the first six months of treatment, you should not lose more than 10% of your total body weight. If this goal has been achieved, then the fight against obesity can continue.
Non-drug treatments for obesity are as follows:
Following a low-calorie diet
If the calorie content of the daily diet is reduced to 1500 kcal, then on average, in six months it will be possible to get rid of 8% of body weight. If a person has moderate obesity, then it will be enough for him to take about 500 kcal from the total diet to start losing weight. In more advanced cases, a reduction in the caloric content of the diet by an average of 1000 kcal will be required. In this case, it will be possible to lose from 0,5 to 1 kg in 7 days.
It is possible that the patient will be recommended a very low-calorie diet with a daily intake of 800 kcal. But such schemes can be implemented only for a short period of time, and the patient himself must be under medical supervision. More than 3 months, such a diet should not be maintained.
It is possible to conduct therapeutic starvation with a maximum restriction of the daily diet. However, this technique is applicable only in a hospital with 3-4 degrees of obesity.
As a rule, people manage to lose weight fairly quickly, but the main danger lies in the fact that subsequently they also begin to quickly gain lost kilograms, eventually reaching a higher degree of obesity. To prevent this from happening, a change in eating behavior as a whole is required with a mandatory correction of lifestyle.
Physical exercise
Physical activity makes it possible to enhance the effect of dieting. In addition, an active lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing a huge number of diseases, and, first of all, diseases of the heart and blood vessels. The selection of exercise therapy is carried out on an individual basis and depends on the level of training of a person, on the state of his health. Almost without exception, obese patients are recommended to walk for 30-45 minutes a day or more.
As for the medical correction of obesity, it comes down to taking medications.
They are divided into two groups:
Anorectic drugs that either increase satiety or suppress appetite.
Drugs that reduce the absorption of nutrients in the intestines.
They are taken only when dieting and exercising. Self-treatment is strictly prohibited, as these drugs have a lot of side effects. In addition, some of them can be addictive.
The currently preferred drugs are Meridia (Sibutramine) and Xenical (Orlistat). The action of Meridia is based on the fact that the patient feels full more quickly. This causes him to eat less food. Xenical, in turn, contributes to the deterioration of the absorption of fats in the intestine.
We should not forget about psychological assistance to patients with obesity, in addition to the fact that such people are prone to depression and neurosis, they need to correct their eating behavior and lifestyle. In this regard, psychotherapeutic conversations and hypnosis are effective.
Surgical treatment of obesity is not excluded. For this purpose, part of the small intestine is removed, which reduces the absorption of nutrients by the body. In some cases, gastroplasty is performed, during which a small stomach is formed.
Interventions such as gastric bypass and gastric banding are also popular in world practice. Thanks to these interventions, people quickly lose up to 20-30 kg, but the long-term consequences of such operations remain poorly understood. Therefore, this type of treatment is applicable only in patients with 3-4 degrees of obesity and only in the case when other methods of dealing with excess weight do not bring a positive effect.
Answers to popular questions:

How do you know if a person is obese? In order to find out if a person is obese, it is necessary to calculate the body mass index. It is calculated using the formula BMI = weight in kg / height in meters squared. The preobesity phase is indicated by an indicator from 25,0 to 29,0. If the resulting number is higher, then the person already has obesity.
Is it possible to get pregnant with obesity? It is possible to get pregnant with obesity, but with grades 3 and 4, the chances of conception are extremely small. In the event that pregnancy does occur, the risk of developing various pathologies of pregnancy remains high.
Does obesity affect potency? Yes, obesity has a negative effect on potency. Especially in this regard, hypothalamic obesity is dangerous with the deposition of fat in the lower body. Problems with potency are observed in almost all men at stages 3 and 4 of obesity.
Is it possible to eat watermelons with obesity? Watermelon contains a large amount of sucrose – fast carbohydrates that contribute to weight gain, so with obesity it can be consumed in a very limited amount.
Are obese people recruited into the military? The army does not take with obesity 3 degrees, when the BMI is in the range from 35,0 to 39,9. In this case, the man is considered temporarily unfit (for up to 6 months). During this time, he must undergo a stationary examination. Such a decision can be made again, for another 6 months. If the treatment of obesity does not give a positive result after a year, then the person is recognized as partially fit and exempt from conscription.









