Crunch and clicks in the knee joints most often disturb people of mature age. However, sometimes young patients also present such complaints. In the latter case, they are most often associated with heavy physical exertion or long workouts.
The crunch in the joint doctors call crepitus. This sound can appear in the knee due to the fact that air bubbles burst in it, which are formed in the synovial fluid during walking. Most often, such crepitations occur due to a person’s sedentary lifestyle. However, this condition cannot be called pathological.
The crunch, which is a symptom of the disease, occurs due to the fact that the bone structures of the joint rub against each other. It can occur as a monosymptom, or it can be combined with other manifestations of the pathological process, for example, with swelling and pain.
A crunch in the knee can be caused by injuries, as well as the presence of excess weight in a person. Under its pressure, the structural components of the joints are destroyed, which leads to the appearance of the corresponding sounds. Sometimes the knees crackle due to improperly fitting shoes.
What can crunch in the knee?
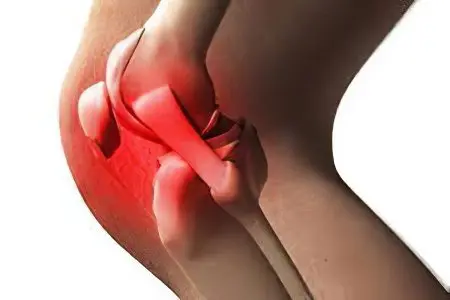
Crunch in the knee joint can create its solid structures, including:
Terminal part of the femur.
Proximal tibia.
Menisci and hamstrings.
Articular cartilage and capsules.
Moreover, both one and several knee elements can crunch at once.
Sometimes lesions of the soft structures of the knee lead to extraneous sounds, in this case they are explained by a violation of the equivalence between the hard articular surfaces.
Causes of crunch in the knee joints

There are the following reasons that can lead to the occurrence of a crunch in the knee joints:
Gonarthrosis. This disease is accompanied by dystrophic changes in the tissues of the joint, as they cease to receive normal nutrition. As a result of such a violation, the cartilage is destroyed, and the joint itself is deformed. The disease often leads to the fact that people become disabled. More often, the pathology develops in women. Primary gonarthrosis develops due to hormonal, metabolic or genetic disorders in the body. The secondary form of the disease can manifest itself after an injury or surgery on the lower extremities. In addition to a crunch in the knee joint, a person will experience pain. As the pathology progresses, it intensifies, and the mobility of the joint is increasingly limited.
Meniscus injury. Most often, the menisci are damaged due to the influence of an external force on them, for example, when the knee is sharply extended, when making sharp turns or jumping from a height. In addition to a crunch in the knees, a person has pain, he cannot sit down normally or even walk. During movement, the joint begins to click. Synovial fluid can accumulate in the cavity of the knee joint, which is secreted in response to inflammation of the synovial membranes of the joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis. This pathology has an autoimmune nature, most often affects women. Sometimes only one joint is affected, and sometimes several at once. The reasons for the development of the disease have not yet been established. Injuries, hypothermia, past viral infections, etc. are considered provoking factors. In addition to a crunch in the knee, a person will experience pain, which intensifies during movement and touching the affected area. In the mornings, the joints seem to be stiff, and the knees are swollen. The periarticular tissues themselves swell, and fluid can accumulate in its cavity. The crunch occurs during movement.
Gouty arthritis of the knee. This disease develops due to the fact that the metabolism of uric acid is disturbed in the body. Its salts begin to be deposited in the tissues and joints, which causes the corresponding sounds in them. The knee is rarely attacked by gouty arthritis, but it does happen. Men of mature age suffer more often. In addition to crepitus, the patient complains of pain and limited mobility. The knee is swollen, and the skin over it may be red and hot to the touch.
hypermobility syndrome. With this pathology, the knee joint is characterized by increased flexibility and mobility. The disease develops due to genetic abnormalities, but sometimes it can be acquired as a result of an injury, hormonal disruptions, or neurological disorders. The main manifestation of the syndrome is precisely the crunch, which may be accompanied by pain.
Violation of the body’s metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. These trace elements form bone tissue, if they are not enough, then this will definitely affect its condition. In addition to a crunch, a person will complain of limited mobility in the joint, pain that can begin to haunt even at rest. If you do not get rid of the problem, then the joint is deformed.
Overweight. Obesity puts a lot of stress on the knee joint. This leads to the fact that it is gradually destroyed. If you get rid of extra pounds in time, then the pathological process can be stopped. The higher the degree of obesity, the more serious damage to the structures of the knee.
Joint chondromatosis. With chondromatosis, metaplasia of the cartilage of the joint is observed. As a result of this process, chondromic bodies are formed, which block the normal mobility of the knee. Most often both legs are affected. In addition to a crunch in the knee, a person will experience pain. The joint swells, which negatively affects the range of motion of the patient.
Bursitis. Bursitis is an inflammation of the synovial bursae. The main cause of the disease is the injuries of the joint and excessive physical exertion on it. Sometimes pathogenic flora leads to inflammation of the synovial bags. Symptoms of bursitis include: crunching in the knee, swelling of the soft tissues, limited joint mobility and pain.
Dissecting osteochondritis or Koenig’s disease. With this pathology, exfoliation of the cartilaginous plate is observed, which overlaps the bone. With osteochondritis, it is the knee joint that most often suffers. The disease debuts in people aged 20-40 years. Injuries, impaired blood supply, excessive stress on the joint can provoke its development. Pathology is always accompanied by painful sensations and a crunch. In severe cases, a complete blockade of the joint is observed.
Joint osteophytes – These are growths of bone tissue, which normally should not be. They are growths on the bone. The reason for their formation is repetitive stress on the joint, metabolic disorders in the body, as well as osteoarthritis. With large osteophytes, the joint will crackle during movement, cease to function normally, and begin to hurt.
Dislocation or fracture. Any injury to bone structures is accompanied by a characteristic crunch. Sometimes the joint may crackle even after the damaged tissue heals. This is observed in the case of the attachment of a pathological process, for example, with the growth of osteophytes or with bursitis.
Damage to the tendons and ligaments of the knee joint. Damage to the tendons and ligaments leads to the fact that the structures of the knee joint lose their stability, their anatomy is disturbed, which leads to the appearance of a crunch.
Chondromalacia patella With this disease, the cartilage tissue of the joint is destroyed. It becomes thin, cracks appear on it. As the pathology progresses, the patella and condyles of the femur will suffer. Chondromalacia can be provoked by previous knee injuries and excessive loads on it. Cracking and pain will occur during movement of the joint.
Video: broadcast Live Healthy! “Why are my knees cracking? Studying your body









