Contents
Control your weight during pregnancy
During the 9 months of pregnancy, what matters most to the pregnant woman is not to watch the needle of the scale over the weeks, but to ensure that she has a balanced diet, sufficient in quantity and quality. to stay in shape and provide the baby with everything he needs to develop well.
If the pregnancy is so called, it is good that this event is characterized by a more or less important weight gain of the mother and that this is completely normal!
Most of this increase in weight is due to the physiological transformations that take place in the body of the pregnant woman to prepare for the coming into the world of her baby:
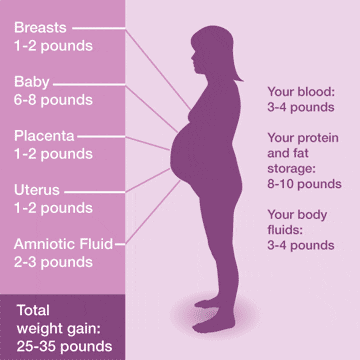
- increase in plasma volume (around 40 to 50%): this real precious blood reserve in the event of the mother’s hemorrhage is also essential for the vascularization of the placenta
- the creation and significant development of the placenta, a true organ in its own right that allows the exchange of nutrients, oxygen and waste between the mother’s body and that of the baby in order to ensure the growth of the latter. Her weight increases as the baby grows
- the transformation of the uterus which softens and enlarges throughout the pregnancy to accommodate the child
- an increase in the size of the breasts that are preparing for possible breastfeeding
- the constitution of amniotic fluid which is similar to a pocket of water, the volume of which varies from 500 ml to 1200 ml
- water retention which can be more or less important
The baby’s weight also counts for a lot in the weight gain of the future mother since it accounts for about 25%.
The big variable, from one mother to another is the weight accumulated in the form of fat which constitutes an energy reserve for the mother and the child.
How many kilos do you gain according to your early pregnancy BMI?
Because of all these physiological changes, it is quite normal to gain weight during the 9 months of pregnancy. But the big question that arises for mothers-to-be is often the following: is there a “normal” weight gain?
If everyone has their opinion on the subject, the medical community has obviously decided on the question because there is a certain link between weight gain during pregnancy and the occurrence of complications for the mother, for the child and during the childbirth.
It is now clearly established by the medical profession that the ideal weight gain during pregnancy is correlated with the Body Mass Index (BMI) of the mother before pregnancy.
Note: BMI is calculated as follows: BMI = Weight / (Height x Height) with the measurements of weight in kilograms and height in meters.
According to the medical profession, there is therefore an ideal weight gain which corresponds to that which generates the least risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth for the child and for the mother.
The current French recommendations follow the new recommendations of the American Institute of Medicine of 2009 which are as follows:
- If the mother is thin before pregnancy (BMI
- If the mother is normal weight before pregnancy (BMI between 18.5 and 24.9), the recommended weight gain interval is between 11.3 kg and 15.9 kg
- If the mother is overweight before pregnancy (BMI between 25 and 29.9), the recommended weight gain interval is between 6.8 kg and 11.3 kg
- If the mother is obese before pregnancy (BMI> 30), the recommended weight gain interval is between 5 kg and 9 kg
Thus, according to the recommendations of the American Institute of Medicine of 2010 which are validated by numerous studies, the threshold which must be retained as that beyond which the risk of maternal-fetal complications is increased for women of normal weight is of 16 kg. It is lowered to 9 kg for obese patients.
How to avoid cravings?
To avoid excessive weight gain during pregnancy, the golden rule is to eat normally, in a balanced way, listening to your body, its feelings of hunger and satiety.
Here are also some tips that will come in handy if you tend to gain weight easily:
- Always eat breakfast, even if you eat it late in the morning: one to three slices of buttered bread depending on your appetite, a piece of fruit, a dairy product and a few almonds.
- For lunch and dinner, be sure to eat a source of protein (meat, fish, eggs, ham or chicken breast) and vegetables (raw or cooked). Vegetables can be fresh of course, but also canned or frozen.
- At each of the three main meals, finish your meal with a piece of fruit, preferably fresh for its high fiber content which makes it both satiating and satietogenic.
- Take the time to chew well. This advice may seem simple, but it is extremely valuable!
- Allow yourself a small, reasonable treat every day: 2 squares of 70% cocoa chocolate, jam in the morning, a piece of cheese, a hot chocolate, a pancake with sugar, etc.
- If you tend to nibble, systematically impose one or two snacks a day with a seasonal fruit (preferably whole and not in juice or in compote) with ten almonds for example.
- Take stock of your sugar intake. If you take in more than the equivalent of 4 sugars per day, turn to a synthetic sweetener. Some are of very good quality, especially those made from stevia which is all natural.
- If you have an active social life, allow yourself a maximum of great pleasure per week: a meal at a restaurant, an invitation, a pastry or a pastry and avoid combining two hearty or unbalanced meals consecutively.
Which foods to favor during pregnancy?
Some metabolic needs increase, in particular those for iron and vitamin B9 which can no longer be met through food. Doctors systematically prescribe a supplement to pregnant women to avoid any risk of anemia and malformation of the baby.
During the last trimester of pregnancy, when the fetus is building its bones, the need for calcium increases dramatically. It is essential to consume a maximum of dairy products (milk, Petits-Suisse, faisselle, fromage blanc or yogurt): at least one at each meal, more one in the morning and another in the afternoon.
Fish
Real health food, fish contain all these substances whose needs are increased during pregnancy and which are absolutely essential for the proper development of the baby: iodine, iron, selenium, vitamin D, vitamin B12 and especially Omega 3.
The fattest fish are the richest in Omega-3s and greatly participate in the development of the cells of the eyes and the brain of the fetus.
So opt for fatty fish, and to avoid the accumulation of mercury, prefer small fish – those at the start of the food chain – such as herring, mackerel, fresh sardines, trout, eel. or anchovies for example.
Other fish are also excellent sources of Omega 3 and quality protein. The list is long: pollock, sole, cod, perch, mullet, sea bream or red mullet, hake, whiting, dab, etc.
Ideally: eat fish twice a week: once oily fish, once less oily fish.
Legumes
Legumes also have undeniable and essential nutritional benefits during pregnancy. Rich in proteins and essential amino acids, fibers and minerals, they are also a precious supplier of Vitamin B9 (also called folic acid or folate), this famous essential vitamin which intervenes in the closure of the neural tube (future spinal cord) of the embryo.
Legumes are also high in phytic acid which makes them quite difficult to digest. To take advantage of their health benefits and make them more digestible, two tips:
- Soak them overnight in cold water with a squeeze of lemon
- Add a teaspoon of baking soda to the cooking water.
Legumes, also called pulses, include: lentils (oranges, green, black), lentils, dried beans (pink, red, white, black, coconut, azuki, tarbais, mungo, flageolet beans, cornilla), broad beans, peas (split, chick, whole).
The oils
They often have a bad reputation and yet, they are absolutely essential for the proper functioning of the body and are essential during pregnancy to ensure the good neurological development of the future baby and its visual maturation.
To bring the balance of essential fatty acids, Omega-3 / Omega-6, the ideal is to consume 1 tablespoon of an olive oil – oil rich in Omega-3 mixture at noon and in the evening.
The oils richest in Omega 3 are the following:
- Perilla oil: the richest vegetable oil in omega-3 in the world with its 65%
- Camelina Oil – 45% Omega-3
- Nigella Oil – 23% Omega-3
- Hemp oil – 20% Omega-3
- Walnut oil – 13% Omega-3
- Rapeseed oil or canola oil: 9% Omega-3
- Soybean oil – 8% Omega-3
Linseed oil for its part contains more than 50% Omega 3 but should be consumed in moderation in pregnant or breastfeeding women (but also in children and adolescents) because of its phytoestrogen content.
Fruits and vegetables
Healthy foods par excellence, fruits and vegetables provide plenty of vitamins, minerals, fiber and antioxidants.
To take advantage of all their nutritional benefits, the important thing is to choose them fresh and in season. Vitamins and fiber will be better preserved when fruits and vegetables are served raw. As a starter, opt for a plate of raw vegetables (carrots, tomatoes, salad, mushrooms, zucchini tagliatelle, etc.), for dessert and as a snack, always prefer a whole raw fruit to a compote or a baked fruit. for example.
For the cooked versions, whether they are vegetables or fruit, the mildest cooking methods should be favored in order to preserve the vitamins, fibers and antioxidants: in the oven at medium temperature, in a pan or in the oven. wok. However, avoid boiling food in too much water.
What foods should be avoided during pregnancy?
While certain foods are to be preferred because of their nutritional benefits, others are to be avoided or even prohibited throughout the duration of pregnancy because of the risk of food poisoning which can be dangerous for the baby.
This concerns:
- Raw meats, raw fish and seafood which can loss responsible for listeriosis or toxoplasmosis, very serious for the child. The same goes for rare, smoked, raw and marinated cold cuts, including rillettes, pâtés, terrines and foie gras.
- Raw eggs: they are also to be banned during pregnancy because of a well-known risk of poisoning: salmonellosis. Take the reflex to always check the composition of all the desserts made. Chocolate mousses, cream pastries, but also ice cream contain raw eggs, for example.
- Raw milk cheeses, cheeses with a bloomy rind as well as blue-veined cheeses such as Roquefort or Bleu d’Auvergne, but also products bought by the cut because of the risk of listeria.
- The alcohol is for its part to be avoided during the whole pregnancy because of its direct deleterious effects on the fetus and the baby, in the short and long term.
Finally, soy-based foods (bean sprouts, tofu, tempeh, seitan, yogurts and soy milk), should be avoided or at least consumed with the greatest moderation because of photoestrogens, supposedly be endocrine disruptors.