Contents
The disease can develop as a result of wearing jewelry, especially if it contains nickel or chromium, as well as the use of perfumes, contact with chemicals used in the production of clothing or shoes, and even the use of topical medications. It most often affects women, especially those who willingly and often use cosmetics.
There are different causes that lead to contact eczema. In some people it is a reaction to contact allergens (haptens), in others skin changes appear only after additional exposure to sunlight. Some people are diagnosed with the so-called Occupational eczema associated with allergy to harmful substances found at work or irritants that directly damage the skin, such as paints, varnishes or lubricants. Doctors refer to irritant contact eczema as irritant contact eczema or toxic contact eczema.
Who is at risk of contact eczema?
Allergic contact eczema is the most common type of eczema. It is formed as a result of skin contact with a contact allergen. The most common change-inducing substances are nickel (an admixture with precious metals or the main material of jewelry as well as buttons, belt buckles), chrome (an ingredient in cement and tanning products), fragrances and rubber (see box).
Characteristic of allergic contact eczema is the formation of skin eruptions after several to several dozen hours after exposure to hapten. People who have long-term contact with these substances are the most vulnerable, which may result in the development of contact allergy.
Irritant contact eczema is an inflammatory skin disease caused by non-specific irritants.. What does it mean? Most people exposed to a sufficiently high dose of irritants will sooner or later develop an inflammatory reaction. This applies in particular to nurses, cooks, turners, housewives and cleaning professionals.
Some people can also develop airborne eczema, which is caused by airborne substances (organic, inorganic dust, aerosols or airborne volatile essential oils) that deposit on the skin of exposed areas of the body, provoking the typical pattern of contact eczema.
Diagnosis is not always easy, because eczema can resemble rosacea or photoallergic contact dermatitis (eczema that results from the simultaneous action of an allergen and the sun).
Do you suspect you are allergic? Perform tests – you can choose mail-order allergy tests for 20 and 30 allergens.
Contact eczema – a threat to cooks
It is cooks and people whose work is related to the preparation of food, are exposed to protein contact eczema. This type of eczema is mainly observed in people with atopic diathesis who have constant contact with protein products.
Protein contact eczema is closely related to contact urticaria – hives may precede, co-occur or follow the eczema phase – both throughout the patient’s life and during one bout of the disease.
How does contact eczema manifest itself?
Increased erythema, numerous papules, vesicles with signs of exudation, erosions accompanied by redness and severe itching of the skin. Flaky papules and vesicles are most often located on the skin of the hands and fingers and usually limited to the place of contact with allergenic objects.
- Pimples on the neck – what causes them?
In allergic eczema, the inflammation is more severe on the dorsal side. In non-allergic eczema – in the folds between the fingers and on the palm side. In people with airborne eczema, changes include the area around the eye sockets. Sometimes, however, changes occur over the entire body surface. The skin then becomes dry, flaky and thickened. Rips and cracks are clearly visible in it.
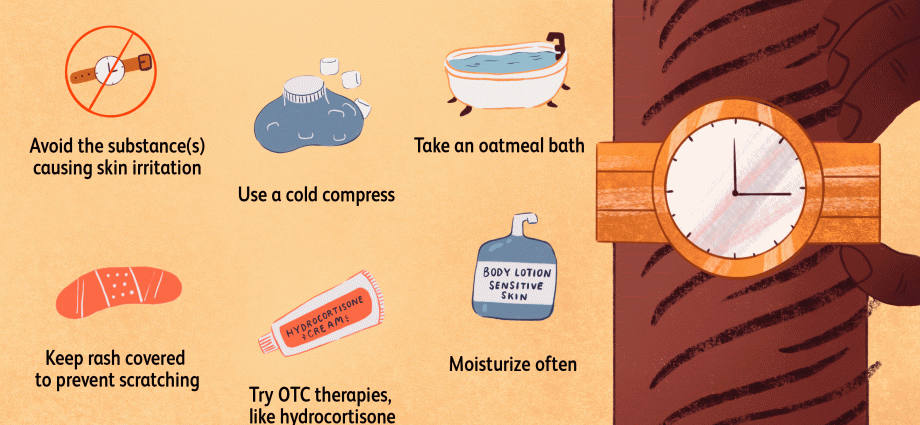
What to do in the event of symptoms?
Discontinue contact with the inducing substance immediately and wash your hands. In the event of severe itching, it will bring relief taking an antihistamine (some are available over the counter). If the symptoms persist, contact a dermatologist, allergist, internist or family doctor as soon as possible.
Contact eczema is diagnosed on the basis of a characteristic image of skin lesions and establishing a relationship between their appearance and, for example, professional work. In order to diagnose allergic contact eczema, the doctor may also decide to perform patch tests, which consist of applying small rolls of tissue paper soaked in various substances that cause contact eczema to the skin. The test readings are taken after 2, 3 and 4 days. The appearance of redness, lumps or bubbles at the site of contact with haptens may indicate an allergy to the substance. You may be allergic to many substances at the same time.
Avoiding the factors that cause contact eczema is most important in treatmentas well as intensive lubrication of the skin, which allows to strengthen and rebuild the skin barrier. In acute conditions, the doctor may prescribe general and topical glucocorticosteroids and antipruritic drugs.
Contact eczema – when treatment doesn’t help
Despite avoiding substances that cause contact eczema, skin changes only disappear in 30-50 percent. people. Then you need to take special care of appropriate prophylaxis. If eczema is caused by allergens in the workplace or during housework, it is worth wearing gloves or protective clothing.
- Micropigmentation. How does cosmetics support medicine?
And although for people struggling with eczema on a daily basis, it is a poor consolation, it is worth recalling that contact allergens, in addition to side effects leading to chronic eczema changes and in some cases to allergic contact dermatitis, also have good sides. It turned out that they can also be used in local immunotherapy of skin diseases, e.g. in alopecia areata.
It has been shown that in skin conditions that cause head hair loss, certain contact allergens (such as heat acid) can be used to stimulate hair growth. Contact allergens can also be used in the chemoimmunotherapy of cutaneous melanoma.
Tekst: Leonard Liga