Contents
Conditional formatting in Excel automatically changes the appearance of a cell based on its contents. For example, you can highlight cells in red that contain invalid values. This lesson will focus on conditional formatting, one of the most interesting and useful tools in Excel.
Imagine that you have an Excel sheet containing a thousand rows of data. I think it will be quite difficult among all this amount of information to discern patterns or necessary data. Like charts and sparklines, conditional formatting helps you visualize information and make it easier to read.
Understanding Conditional Formatting
Conditional formatting in Excel lets you automatically format cells based on the values they contain. To do this, you need to create conditional formatting rules. The rule might sound like this: “If the value is less than $2000, the color of the cell is red.” Using this rule, you can quickly identify cells containing values less than $2000.
Create a conditional formatting rule
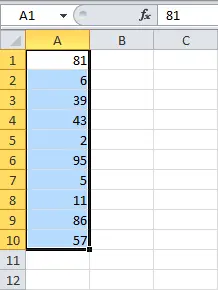
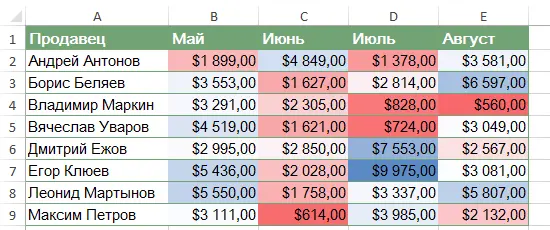
In the following example, an Excel worksheet contains sales data for the last 4 months. Let’s say we want to know which salespeople are meeting their monthly sales target and which are not. To complete the plan, you need to sell more than $4000 per month. Let’s create a conditional formatting rule that will select all cells in the table with a value greater than $4000.
- Select the cells for which you want to check. In our case, this is the range B2:E9.

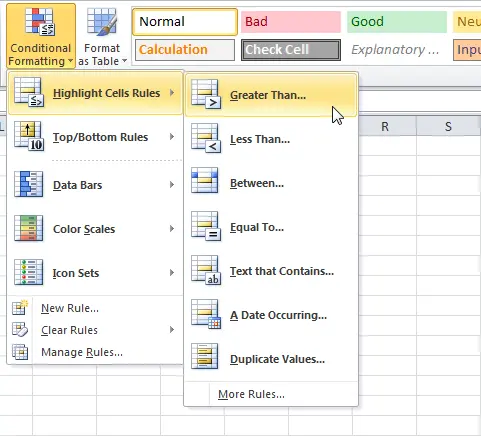
- On the Advanced tab Home press command Conditional Formatting. A dropdown menu will appear.
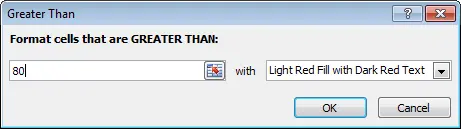
- Select the desired conditional formatting rule. We want to highlight cells whose value Больше $ 4000.

- A dialog box will appear. Enter the required value. In our case, this 4000.
- Specify a formatting style from the drop-down list. We will choose Green fill and dark green text… Then press OK.

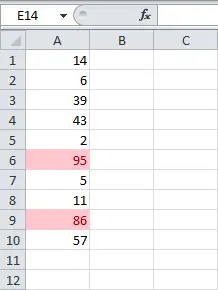
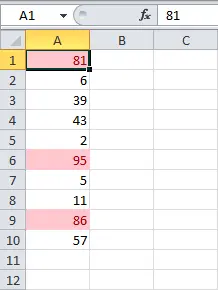
- The conditional formatting will be applied to the selected cells. Now you can easily see which sellers have completed the monthly plan of $4000.

You can apply several conditional formatting rules to the same range of cells at once, which allows you to more flexible and visualize the information you need.
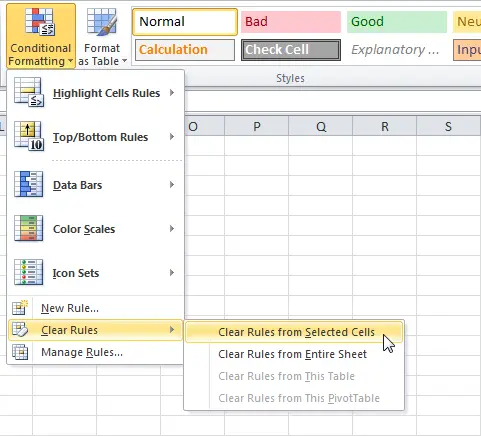
Remove conditional formatting
- Push command Conditional Formatting. A dropdown menu will appear.
- Move the mouse pointer over the item Delete Rules and select which rules you want to remove. In our example, we will choose Remove rules from entire sheetto remove all conditional formatting on the worksheet.

- The conditional formatting will be removed.

You can select item Rule managementto see all conditional formatting rules created on this worksheet or in the selection. The Conditional Formatting Rules Manager allows you to edit or delete custom rules. This is especially useful if you have created several rules on the same sheet.
Preset Conditional Formatting Styles
Excel comes with a set of predefined styles that you can use to quickly apply conditional formatting to your data. They are grouped into three categories:
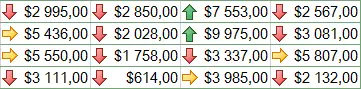
- Гhistograms are the horizontal bars added to each cell in the form of a stacked chart.

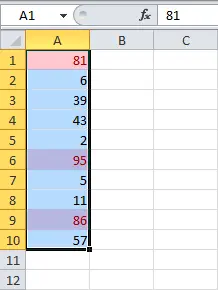
- Color scales change the color of each cell based on their values. Each color scale uses a two or three color gradient. For example, in the Red-Yellow-Green color scale, the maximum values are highlighted in red, the average values in yellow, and the minimum values in green.

- Icon setss add special icons to each cell based on their values.

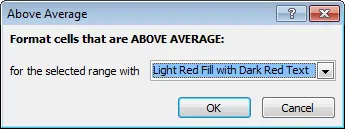
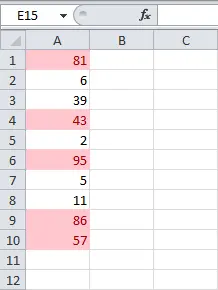
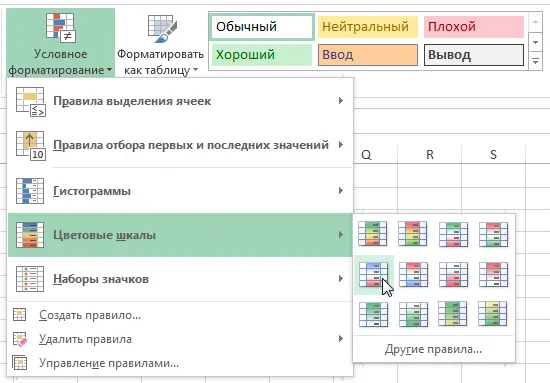
Using preset styles
- Select cells to create a conditional formatting rule.

- Push command Conditional Formatting. A dropdown menu will appear.
- Hover your mouse over the desired category, and then select a preset style.

- The conditional formatting will be applied to the selected cells.