Contents
What is colpitis in women?
Colpitis in women is an inflammation of the vaginal mucosa with a possible capture of the vulva, which has an infectious or non-infectious nature. In medicine, you can find the term “vaginitis”, which means the same disease and is a synonym.
Pathology is widespread in gynecological practice. Such a diagnosis is made at least once by 60% of women of childbearing age (from 18 to 45 years). But the disease does not bypass girls, although they are more likely to suffer from vulvovaginitis.
The peak incidence among children occurs at the age of up to 6 years, and illiterate intimate hygiene becomes the cause. Colpitis also affects women who have entered the postmenopausal period, which is most often associated with the natural aging processes of the body.
The disease can be of both specific and non-specific origin, which is determined by etiological reasons. Specific colpitis provoke gonococci, mycoplasmas, Trichomonas, chlamydia, candida and viruses. A nonspecific inflammatory process is caused by Escherichia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococcus and staphylococcus aureus.
Can colpitis go away on its own?
Considering colpitis as a non-serious disease, many women believe that the disease is able to go away on its own. Cases of cure, of course, occur, but this happens extremely rarely and only on condition that the disease is non-specific, and the body’s immune defenses are not weakened.
Most often, the following situation is observed: a woman who has not used any treatment, after a few days, finds that the symptoms that bother her have disappeared. But this does not mean that the inflammatory process is neutralized, it just turned into a sluggish form. Under the influence of certain provoking factors, colpitis after some time is activated again. Therefore, do not expect that the disease will go away on its own. If signs of the disease are found, it is necessary to go to the doctor, find out the cause of colpitis and begin treatment.
Can there be a temperature with colpitis?
The widespread opinion that any infectious disease should be accompanied by an increase in temperature in relation to colpitis is unjustified. But this does not mean that the disease is safe and unable to harm the female body.
High temperature during the inflammatory process in the vagina is most often absent, even if the disease is in an acute stage. Rarely, the values on the thermometer can rise, but only to subfebrile indicators, that is, in the range from 37 to 38 ° C.
Symptoms of colpitis in women
Among the symptoms of inflammation of the vaginal mucosa, the following are most common:
Allocations, the nature of which will depend on the etiology of the disease and the severity of the pathological process. In any case, their volume will increase compared to the period when the woman was absolutely healthy. Leucorrhea can be frothy, watery, cheesy, sometimes purulent. With atrophic colpitis, blood clots are observed in them;
Unpleasant smell – mostly unsharp, but sour;
Puffiness in the area of the external genital organs, their redness and irritation;
Feeling of itching and burning, which begins to increase during a long walk, as well as during night rest and in the afternoon;
Insomnia, increased irritability, neuroses caused by a complex of symptoms of the disease that constantly disturb a woman;
Periodically occurring pain, localized in the pelvis. They can intensify during the act of defecation or in the process of intimacy;
Frequent urge to urinate, in rare cases, urinary incontinence is observed;
An increase in body temperature to subfebrile values.
The acute phase of the disease is accompanied by an increase in symptoms, which, depending on the cause of colpitis, will differ somewhat. When the inflammatory process becomes chronic, the symptoms become mild. But the most stable symptom that worries a woman is itching, which does not stop even against the background of mild discharge.
Causes of colpitis in women
Various reasons can cause the development of the inflammatory process at different ages:
In childhood, the disease develops mainly against the background of opportunistic microflora entering the vagina from the gastrointestinal tract. Streptococci, staphylococci and even pinworms become provocateurs;
In women of reproductive age, specific colpitis of an infectious nature is more often detected. Trichomonas type of disease prevails, which is sexually transmitted. Candidiasis colpitis is somewhat less common, the cause of which is mainly hormonal failure when carrying a child;
In women after menopause, nonspecific colpitis is most often observed, which is caused by staphylococci and streptococci. However, candida, atrophic, and other types of colpitis can be diagnosed. But they usually develop in the presence of additional risk factors.
So, at any age, the causes of the development of the disease are either their own conditionally pathogenic microflora, or infectious microorganisms belonging to the group of fungi, viruses or bacteria.
Types of colpitis
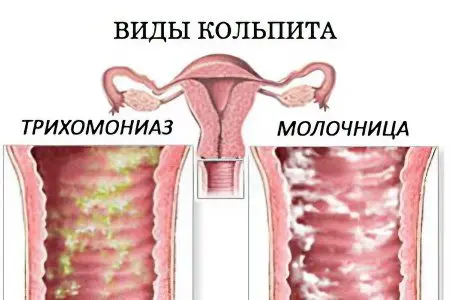
Types of colpitis are distinguished depending on what caused the inflammation of the mucosa. Each type of disease has certain clinical manifestations and differences, which requires specific treatment.
The following types are considered the most common:
Trichomonas colpitis. Inflammation is caused by trichomonads, the simplest flagellar parasitic microorganisms. The most common route of transmission is sexual intercourse, however, infection is also possible through personal items. The disease is easily diagnosed and does not present difficulties in treatment. The discharge is usually frothy and profuse, with an unpleasant odor and purulent inclusions. The main drug most often used for treatment is metronidazole in combination with topical therapy;
Candidal colpitis. Inflammation is caused by the reproduction of fungi, which, as a result of provoking factors, exhibit pathological activity. Among the most striking clinical symptoms are cheesy discharge and itching. Infection can occur both sexually and as a result of a weakened immune system. It is treated with antimycotic drugs in combination with local therapy;
Atrophic colpitis. This inflammation is caused by a decrease in estrogen production in the body. A woman experiences burning and dryness in the genital area, pain during intimacy. Treatment is based on hormone replacement therapy.
Risk factors for the development of colpitis
If certain microorganisms become the causes of the development of the disease, then there are risk factors that can help them either penetrate the vaginal mucosa, or begin to actively multiply.
Some of these triggers include:
Insufficient or incorrect intimate hygiene;
Lack of a regular partner, refusal to use barrier contraception, that is, from condoms;
Pathologies of the endocrine system: hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus;
Injuries of the genital organs of mechanical, chemical and thermal origin. These can be ruptures during delivery, prolonged use of an intrauterine device, rough sexual intercourse, etc .;
Wearing low-quality underwear made from low-grade synthetic materials;
Children’s diseases, the causative agents of which reach the girl’s genitals by hemolytic means. Among these are scarlet fever and measles;
Hormonal changes in a woman’s body. Among them are pregnancy, menstruation, breastfeeding, menopause;
Taking certain medications, most often antibiotics. However, both hormone-containing drugs and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can cause inflammation;
Passage of radiation or chemotherapy for cancer;
Hypoestrogenism, that is, insufficient production of estrogen in a woman’s body;
Decreased immunity or severe immunodeficiency in HIV infection;
Lack of vitamins, strict diets;
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as diseases of an allergic nature;
abortion.
Complications and consequences of colpitis

The lack of timely medical treatment of any type of colpitis threatens with serious complications for women’s health.
Among the possible adverse effects, the following are especially dangerous:
The acute form of the disease can transform into a chronic sluggish disease. Chronic inflammatory process in the vagina is not only difficult to treat with medication, but also reduces the quality of life of a woman with frequent relapses;
Spread of pathogenesis to the upper parts of the genitourinary system. Among the diseases of this area, colpitis can cause urethritis and cystitis;
The formation of cervical erosion, endometritis (inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus), cervicitis (inflammation of the cervical canal), salpingo-oophoritis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries);
All specific colpitis, not diagnosed and untreated in time, can eventually lead to infertility or serious difficulties in conceiving and bearing a child. Often chronic colpitis are the causes of ectopic pregnancy;
The formation of synechia in girls, which is expressed in the fusion of both small and large labia with each other;
The appearance of bleeding erosive areas on the vaginal walls, which become the gateway for various infections;
The risk of developing complications of an infectious nature after gynecological examinations and surgery.
The sooner the diagnosis and treatment is carried out, the lower the risk of complications.
How to cure colpitis?
Treatment of the disease should be carried out by a professional. Self-treatment of colpitis with improvised means is unacceptable. Before choosing one or another remedy, the doctor will conduct certain diagnostic measures and studies that will determine the cause of the inflammation. In accordance with the results obtained, a treatment regimen will be developed. In addition, the choice of therapy will be influenced by the form and type of the disease, the age of the patient and her state of health.
The disease requires an integrated approach, and first of all it is etiotropic treatment. That is, the impact should be made on the direct causative agent of inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. The doctor’s arsenal includes antibacterial, hormonal, antimycotic and antiviral agents. Sometimes combination therapy is required, which involves a combination of several types of drugs.
The first stage comes down to taking antibacterial drugs, at the same time, suppositories, capsules or vaginal tablets are applied topically. In addition, local treatment consists in the use of various disinfectant solutions and antiseptics. A woman is prescribed douching and washing with solutions of boric acid, potassium permanganate, soda. Such treatment must be carried out for at least 14 days.
The second stage – restoration of the normal microflora of the vagina by reproduction of the natural biocenosis in the mucous membrane. For this, vaginal suppositories containing lactobacilli are used.
In addition to local and etiological treatment, therapy of concomitant diseases is necessary. If the provoking factor is not eliminated, the disease will recur again and again. So, it may be necessary to correct the hormonal background in senile colpitis, treat diabetes, reduce body weight, and eliminate the pathology of the endocrine glands.
In the case when doctors manage to eliminate the provoking factor, then the prognosis for a complete recovery from colpitis is favorable.
In addition, until the moment of cure, you need to adhere to certain recommendations, including:
Refusal of sexual activity at the time of treatment. Confirmation of the elimination of inflammation should be laboratory, since the disappearance of symptoms is not an indication of recovery;
If necessary, a therapeutic course must be completed not only by a woman, but also by a man. Since a specific form of the disease can be asymptomatic in the sexual partner, there is a high risk of re-infection after the resumption of sexual activity;
Implementation of hygiene procedures at least twice a day using antiseptics;
If a girl has undergone an inflammatory process, then parents need to carefully monitor her hygiene. It is necessary to wash the child after each act of defecation and urination. Linen should be washed using quality detergents and be sure to iron. It is important to ensure that the child does not suffer from itching and does not comb intimate places. These measures will help to avoid re-infection;
During therapy, you should follow a diet. It comes down to eliminating salty and spicy foods. It is important to include sour-milk drinks in the diet;
Nuances of treatment during pregnancy
Special attention deserves the treatment of colpitis in pregnant women. After all, it is they who turn out to be the most vulnerable category of patients, since not only their natural immunity is disturbed, but also a serious hormonal restructuring occurs. Therefore, even nonspecific colpitis during this period threatens to be complicated by a bacterial infection. The tactics of treatment in this case can also be determined only by a doctor, but the selection of therapeutic agents is complicated by the position of the woman.
Nevertheless, it is impossible not to treat the disease, since the inflammatory process has a negative impact not only on the patient herself, but also poses a threat to the child in the womb. He is at risk of infection during delivery.
Most often, a pregnant woman is recommended to undergo a course of antibiotic therapy, maintain immunity with the help of immunomodulators and attend physiotherapy procedures. Of the antibiotics, gynecologists prefer Vagotil, Pimafutsin, Terzhinan. However, they should be prescribed with extreme caution and under special supervision. In addition, the priority remains local treatment, which is the safest for the unborn child.
Prevention of colpitis in women
No less important is the prevention of colpitis, as it helps to eliminate risk factors for the development of the inflammatory process and is often interspersed with therapeutic effects.
Therefore, it is important to take the following preventive measures:
Regularly, at least once a year, visit the local gynecologist. Modern doctors recommend coming for preventive examinations every six months. This will allow timely detection of pathological processes in the genital organs and immediately begin treatment. If the signs of the disease began to appear during pregnancy, then you should not wait for the next date of the visit to the doctor, it is better to immediately go to the antenatal clinic and report your problem;
It is necessary to carefully monitor intimate hygiene, which boils down to washing with high-quality hypoallergenic disinfectants. Particular attention should be paid to the possibility of introducing intestinal microflora into the vagina. Often this is due to improper use of toilet paper. It is important that the wiping movements are directed from front to back. In addition, you need to monitor the regular change of underwear. It itself must be made from natural fabrics, since synthetics create a moist and warm environment favorable for the reproduction of bacteria;
Any medications should only be prescribed by a doctor. This is especially true for the use of antibacterial agents, which are often taken uncontrollably;
It is necessary to go to the doctor when the first signs of colpitis appear. This is due to the fact that in the early stages of the development of the inflammatory process, it is eliminated much easier and faster. Such a measure will not allow the disease to become chronic and cause the development of serious complications for women’s health;
We should not forget about strengthening the body’s defenses. Maintaining normal immunity will make it possible not only to prevent the development of the disease, but also to get rid of it faster. To do this, you need to give up bad habits, adhere to proper nutrition, do not forget about regular walks and physical education.
The last measure in relation to getting rid of the disease is to undergo physiotherapy treatment. It can significantly improve the condition in the chronic form of colpitis. Among all methods, electrophoresis with zinc, ultraviolet irradiation using a short wave and a half-bath with an oxidizing agent – potassium permanganate are especially popular.









