Contents
What is colloid goiter of the thyroid gland?
Colloidal goiter of the thyroid gland is an enlargement of the organ caused by the accumulation of colloid in the follicles. In this case, the follicle is a unit of the gland, which is similar in shape to a miniature sac. Its diameter does not exceed 1 mm. Inside it is formed by cells – thyrocytes, and outside it is tightly covered by the smallest blood vessels and nerve endings. It is inside the follicle that the hormones T4 and T3 are formed and produced. The accumulation of follicles in an amount of 20 to 50 pieces is called thyreon.
The colloid is a jelly-like substance containing thyroglobulin, amino acids and iodine. Colloidal goiter occurs when the outflow of colloid from the follicles is disturbed.
Symptoms of colloid goiter of the thyroid gland
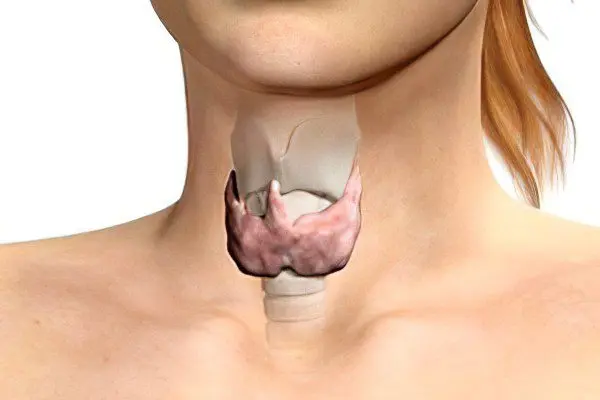
When the disease is at the initial stage of development, the symptoms may not bother the person. Most often, the patient turns to the doctor when the thyroid gland begins to increase in size.
In this case, the first signs of colloid goiter appear, among which the following can be distinguished:
The person experiences a feeling of pressure in the neck;
As the goiter grows, swallowing becomes difficult;
In the area of the thyroid gland, there is a feeling of perspiration, causing the patient to cough;
The voice becomes hoarse;
Dizziness and noises in the head may appear, which is caused by compression of nerves and blood vessels;
A person experiences pain in the area of the formed node. This feeling occurs if the node increases rapidly, inflammatory processes begin to develop or hemorrhages form;
There is a lump in the throat;
Depending on the number of enlarged nodes, the goiter protrudes either on one side or on both, resembling the shape of a butterfly;
When the colloid node exceeds 1 cm, the patient is able to feel it on his own.
Depending on which function of the thyroid gland will be impaired, when a colloid goiter occurs, the patient may experience completely different symptoms:
Signs of hypothyroidism are observed when the overgrown colloid replaces thyrocytes. The patient complains of weakness, deterioration of thought processes, loss of appetite. Patients are often edematous, their metabolism slows down, they begin to gain weight, dry skin appears, sweating decreases;
When the follicles produce excessive amounts of hormones, the patient suffers from signs of hyperthyroidism. In this case, the patient is irritable, tearful, aggressive, quickly tired. Appetite increases, but at the same time, a person loses weight, suffers from diarrhea, and urination becomes more frequent. The number of heartbeats increases, body temperature may rise;
If the production of hormones remains normal, but there is an accumulation of colloid in the follicles, the patient complains of a noticeable increase in the thyroid gland. This condition is called euthyroidism. Formed colloid cysts compress adjacent vessels and nerves, which leads to frequent dizziness, shortness of breath in a horizontal position, and difficulty in swallowing.
Causes of colloid goiter of the thyroid gland
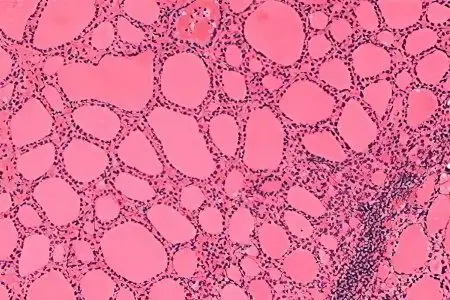
There are several factors that lead to the development of colloid goiter, among them are the following:
Insufficient intake of iodine with food and water, the thyroid gland tries to compensate for its deficiency by capturing this element. The intake of iodine is carried out from the blood. This increases the production of colloid against the background of parallel growth of the gland;
Age. When a person has crossed the line of 40 years, the activity of individual follicles is activated, which is associated with age-related changes in the thyroid gland. Cells wear out faster, and an impressive part of them dies off. The result of this process is the formation of large cavities in the follicles, in which the colloid begins to accumulate;
Belonging to the female sex. Women are more likely to experience hormonal surges in their bodies than men. They are associated with childbirth, pregnancy, breastfeeding, abortion, menopausal changes. This leads to the failure of the outflow of the colloid and its accumulation in the thyroid gland;
Exposure to radiation and unfavorable environmental conditions often cause mutations that occur in the cells of the thyroid gland. They can also be caused by exposure to nitrates or a course of radiation therapy;
Hereditary factor. When your close relatives have a colloid goiter, then there is a risk of developing it in you. This is due to gene mutations that are inherited;
Poisoning with toxic substances, tobacco smoke, work in hazardous industries – all this affects the functioning of the body as a whole, and the activity of the gland in particular. It is this organ that is most sensitive to metabolic disorders and imbalance of hormones produced by other organs: the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, ovaries;
Serious psychological trauma, regular stress, life against the background of nervous exhaustion – all this becomes a trigger for disruption of the thyroid gland;
Frequent infections and inflammatory processes weaken the body’s immune system, which makes the thyroid gland more vulnerable to toxins released by microorganisms, viruses and bacteria that have entered the human body;
Subcooling, which provokes a spasm of blood vessels throughout the body. As a result, the outflow of the colloid is disturbed and it stagnates in the follicles, which stimulates the development of goiter.
Types of colloid goiter of the thyroid gland
There are three types of colloid goiter of the thyroid gland:
diffuse education. It is characterized by the fact that the entire thyroid gland is affected evenly, and nodes are not formed. Most often, people under the age of 40 suffer from pathology. In this case, the body increases significantly, which becomes the reason for contacting the doctor;
Nodular colloid goiter. In this case, both multiple nodes and a single node can appear. This pathology most often affects the female population and is often accompanied by the development of uterine fibroids. The formation of a multinodular goiter is said to occur when the number of nodes exceeds two;
Cystic colloid goiter. In this case, colloidal masses accumulate in the cavity of the cyst. She herself is surrounded by a shell – dense and elastic.
By itself, colloid goiter is one of the safest forms of thyroid pathology. However, it is important to make a diagnosis in time and distinguish a colloid formation from a tumor process.
[Video] Dr. Petrik M.V. – Thyroid Nodules. How to assess the danger and what to do:
As a rule, the operation goes without complications, and after a short time (less than a week), the patient can return home. For the first three weeks, he will need to prioritize a quiet lifestyle, limit physical activity and stick to a specific menu of liquids and purees. If necessary, doctors prescribe hormones to compensate for their deficiency.
Prevention of colloid goiter of the thyroid gland
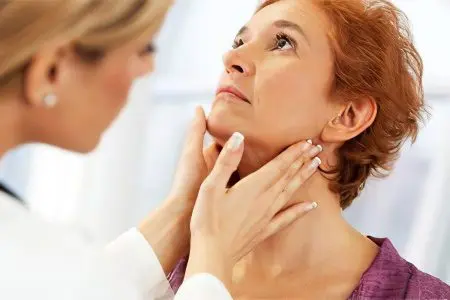
Preventive measures will, if not avoid, then minimize the risk of colloid goiter.
Therefore, you should follow some simple recommendations:
Avoid visiting places with high radiation or unfavorable environmental conditions;
Do not self-medicate, in particular, avoid taking iodine and calcium supplements without first consulting a doctor;
Include cabbage, potatoes, corn in your diet;
Avoid hypothermia;
Use as seasoning not ordinary salt, but enriched with iodine;
Support the immune system, use vitamin complexes in the autumn-spring periods;
Go in for sports, take walks in the fresh air more often;
Perform breathing exercises;
Adhere to the correct daily routine, allocate enough time for sleep;
Do not forget about regular preventive examinations at the endocrinologist. Especially in the case when there is a dangerous heredity.
As for the prognosis for recovery, in most cases it is favorable. If the disease was detected on time, correctly diagnosed, and the patient is regularly examined by an endocrinologist, then the risk of goiter degeneration into a malignant formation is low. Also, do not forget about preventive measures.









