Contents
- History of breeding
- Description of the climbing rose Red Lighthouse and characteristics
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Methods of reproduction
- Planting and caring for a climbing rose Red Lighthouse
- Pests and diseases
- Application in landscape design
- Conclusion
- Reviews of the climbing rose variety Red Lighthouse
Rosa Krasny Mayak is one of the best varieties bred during the Soviet era in the Nikitsky Botanical Garden. At that time it was one of the major breeding centers, which dealt not only with flowers. But the latter paid considerable attention, as the cities required a large number of flower beds. The variety is still popular with Crimean owners of private houses. But in city parks, it was replaced by odorless Dutch roses.
History of breeding
Climbing rose Red Lighthouse is a hybrid obtained by Vera Nikolaevna Klimenko in 1956. The breeder at that time worked in the Crimea, in the Nikitsky Botanical Garden. For his collection, a new variety of climbing rose was bred.
The American variety Excels and the German Kordes Sondermeldung were chosen for crossing. The frost resistance of both varieties is above average, and this was one of the arguments when choosing parental forms for breeding a new hybrid. The result of the work of V. N. Klimenko was a variety with the name Red Lighthouse, characteristic of that time.
There are several classifications for roses:
- cultivars: group of Vihuriana hybrids;
- garden plants: large-flowered climbing rose.
The variety was obtained back in 1956, but there is no information about whether it was included in the State Register of the USSR. The Red Lighthouse was added to the State Register only in 2014 under the number 6904165.
Description of the climbing rose Red Lighthouse and characteristics
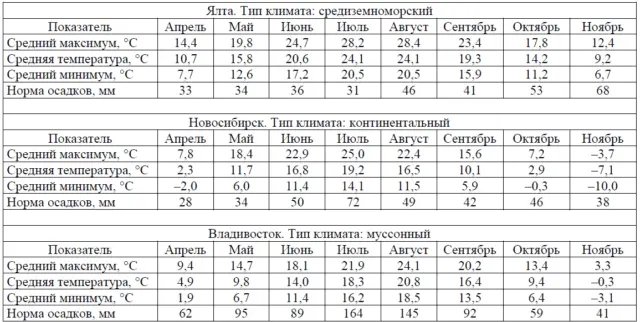
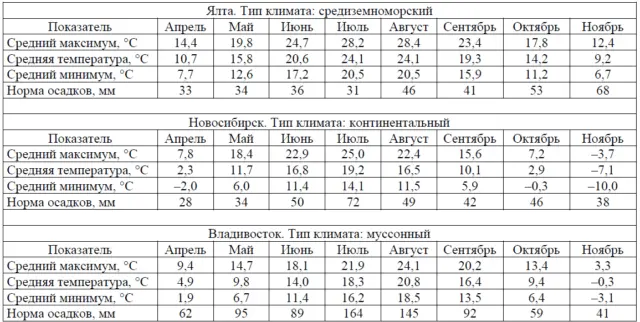
A tall hybrid, reaching 3,5 m in favorable conditions. But the size of the bush varies depending on the climatic zone. If in Yalta it reaches its maximum height, then in Novosibirsk it does not grow above 1 m.
Shoots are strong, creeping and tenacious. Grow vertically. The color of the stems is dark green. Additional decorativeness of the climbing rose Red lighthouse is given by young shoots that have a purple-red color. Spines on the stems are frequent, needle-shaped, reddish in color.
Leaf blades are rounded, large, with a glossy surface. The coloration is dark green.
A climbing rose bush looks good in a flower bed as a central figure.
The buds are semi-double, large. Diameter 7-8 cm. Peduncles are strong. Collected in large inflorescences of 10-13 roses each.
The number of petals in one bud is more than 20. The color changes as the rose matures. Immediately after the bud opens, the petals are scarlet-red, with a barely noticeable velvet. As it matures, the velvet becomes more noticeable, and the color of the petals changes to a fiery red with an orange tint. The center is yellow.
The shape of roses also changes during flowering: from a rounded bud with a pointed top to a fully opened saucer-shaped flower.
Flowering is very plentiful and long, about a month. The time for the appearance of roses is June-July.
Buds are formed on two-year-old shoots. This feature makes it impossible to grow climbing roses in some regions of Our Country.
Frost resistance study
In the Nikitsky Botanical Garden, frost resistance studies were carried out. When the stems freeze, the rose not only does not bloom, but also cannot fully grow.
As a result of the tests, it was found out:
- the south coast of Crimea – an ideal region for the Red Lighthouse variety. The bush grows to a maximum height of 3,5 m. The diameter of the flowers is 6-7 cm. Good disease resistance. Winter hardiness is not important as the region is warm.
- Vladivostok – bush height up to 3 m. Diameter of roses 6-12 cm. Disease resistance is lower. Withstands frost.
- Novosibirsk – grows no more than 1 m. Does not bloom. Disease resistant. The above-ground part of wintering does not withstand.
It was concluded that the climbing rose Krasny Mayak is not suitable for cultivation in continental Our Country. This is due to the fact that the bush cannot endure frost, and flower buds form only on the shoots of the second year. Unlike wild rose rootstocks, Red Lighthouse is also unable to go into a “temporarily non-flowering state”. The term means that after extreme cold weather, the plant does not bloom for two years. During this time, it forms new skeletal axes that bloom after a mild winter.
The test results showed that the climbing rose variety Krasny Mayak can be recommended for the North Caucasus region, the Crimean Peninsula and the southern part of the Far East.
With a slight temperature difference, the climbing rose Red Lighthouse does not withstand the continental climate
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Among the advantages of the climbing rose Red Lighthouse it should be noted:
- high resistance to heat;
- resistance to fungal diseases;
- drought resistance of the average level;
- long and abundant flowering;
- nice soft rose scent.
The latter can also be a disadvantage if the garden owner is allergic to strong odors.
Disadvantages relate more to personal predilections than to objective hindrances. Many note that it is difficult to remove faded roses and cut off excess shoots from tall bushes. But nothing prevents the formation of standard plants. If a climbing rose was bought to decorate an arch or gazebo, you will have to put up with the inconvenience.
Not all gardeners like a single bloom in early summer. It is still impossible to cut the stems in the summer, and dry roses on the bush look ugly. Therefore, the lack of remontance in the variety can be attributed to the disadvantages.
Another disadvantage is the presence of a large number of thorns on the shoots of the plant. But this disadvantage turns into a virtue if a hedge is formed from the bushes of a climbing rose.
Methods of reproduction
Climbing roses can be propagated in three ways: layering, cuttings and grafting. The first option is very convenient for inexperienced gardeners and those who have little time. The last one is the most difficult. It is suitable for flower growers with experience.
Reproduction by layers
The most optimal way to propagate climbing rose bushes. In the spring, they choose a suitable last year’s shoot and bend it to the ground. Part of the stem, along with the emerging buds, is sprinkled with earth and left for several weeks.
Until the shoot grows additional roots, it will feed on the mother bush. Closer to autumn, the stem is cut off from the main plant, carefully dug it out along with the roots and planted in a permanent place.
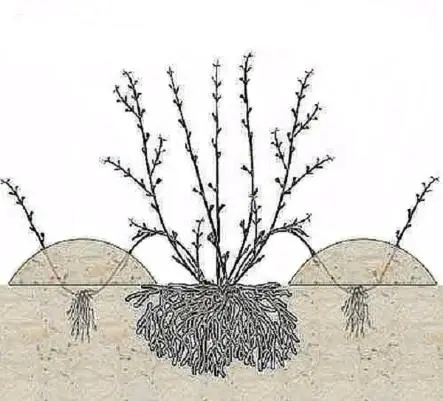
Layering can propagate not only climbing, but also ordinary roses with vertical stems
Cutting
Some gardeners believe that pencil-thick stems should be selected for cuttings. From this point of view, the method is not well suited for climbing varieties. Their shoots capable of cutting are much thinner. But you can try.
The cutting method is usual:
- In spring or autumn, after trimming, choose a suitable whip. You can also choose a two-year-old shoot that has begun to form a bud.
- Cut the stem into pieces so that each cutting has at least three productive buds. Usually the length of such a cutting is 10-15 cm.
- pour soil into a suitable container.
- Stick the cutting into the soil so that one of the buds is underground.
- Cover the container with a glass jar or PET bottle and place in partial shade.
After a month and a half, the cuttings will have roots.
Reproduction by grafting
Method least suitable for climbing roses due to too thin stems. Grafting is usually done on local wild rose hips to avoid freezing of the roots. This method is best left to professionals with a wealth of practice. In warm regions where the Red Lighthouse can fully bloom, the first two breeding methods are much more convenient and easier.
Planting and caring for a climbing rose Red Lighthouse
For a seedling, you need to choose a dry, well-lit place. The red beacon, like all climbing roses, does not like wet and shady places. When choosing a site, you need to check with the wind rose. The plant must be protected from the north wind. You can not plant roses too close to each other. Later, the bushes will grow and begin to interfere with each other.
Climbing roses prefer loose fertile soil. If the site is located on clay, you will have to prepare a fertile mixture. You can buy soil in the store. Otherwise, the rules for planting climbing roses and other garden flowers do not differ.
Pests and diseases
Rose bushes are parasitized by 270 species of pathogenic fungi. The most common are black spot, rust and powdery mildew.
The originator of the variety indicated that the variety is resistant to these diseases. But given the recommended breeding zone, resistance is related to climate: fungi stop developing at air temperatures above 30 ° C.
In order to prevent climbing varieties, they try to plant them in open, well-ventilated areas. The wind quickly dries out moisture, which is necessary for the development of pathogenic microflora.
There is no special protection against pests. The most dangerous are: rose aphid (Macrosiphum rosae), rose rose descending sawfly (Ardis brunniventris) and spider mite (Tetranychus urticae). The latter loves dry air and can attack a rose bush in the summer.

Golden bronze is not able to seriously damage the plant, it spoils the decorative appearance of the flower
Application in landscape design
Climbing rose bushes “Red Lighthouse” are almost universal. They are suitable for:
- vertical gardening;
- design of arches;
- creation of green fences;
- gazebo decorations;
- group plantings with other colors.
Instead of a tall bush with creeping shoots, you can form a bole. This shape is well suited for a club composition.
Conclusion
Rose Red Beacon is great for decorative garden decoration, without requiring complicated care. In the southern regions, it does not even need to be covered for the winter. Only shaping and sanitary trimmings are needed. But the bushes will delight with flowers for a whole month.









