Contents
Large-flowered clematis are a real decoration of the garden. Such flowers are able to deliver real aesthetic pleasure to visitors, and for the grower to become a real pride. One of these species is Clematis Wildfire, whose impressive size is in harmony with its beauty and grace.
Description Clematis Wildfire
Clematis large-flowered Wildfire, the description and photo of which are given below, was bred by Polish breeders. It is widely used for decorative purposes, for vertical gardening, decorating arbors, they are often planted along fences, walls of buildings, nets. In the photo below – flowering clematis of the Wildfire variety.

The main characteristics of the plant are shown in the table below:
Parameter | Value |
A type | Perennial herbaceous plant of the Ranunculaceae family |
Stem | Curly, 2-3 m |
Leaves | Green, triple. Petioles keep the plant on a support |
Flowers | Large, up to 20 cm, with 6-8 violet-blue petals, in the middle of which there is a longitudinal burgundy or purple blurry stripe |
Flowering period | May-September |
Reproduction | Seeds, cuttings, shoots, dividing the bush |
Planting and caring for Clematis Wildfire
Clematis Wildfire can be planted in open ground both in spring and autumn. In both cases, this must be done before the onset of adverse conditions – summer heat or frosts that can destroy immature plants. The best time is the period from late April to mid-May, as well as September. Planting holes are best prepared in advance and made large enough. Their depth should be 50-60 cm, since it is desirable to pour a drainage layer 10-15 cm thick from broken brick, expanded clay or crushed stone onto the bottom. Wildfire clematis is planted with a deepening of the root collar by 5-10 cm. If there are no buildings or fences near the planting site, the plant is tied to a support. The root zone is abundantly shed with water and mulched with peat to retain moisture in the soil.
The subsequent care of Wildfire clematis is simple. Up to 3 years, watering is carried out quite often, then its intensity is reduced. From the same time, intensive growth of new shoots begins, which can be regulated by pruning or pinching out growth points.

You can use special compounds for this, such as Kemira-universal or complex mineral fertilizers, which must be applied in dissolved form. The plant also responds well to fertilizing with a solution of slurry.
Reproduction
To preserve all the varietal characteristics of the plant, Clematis Wildfire should be propagated not by seeds, but by any vegetative method:
- cuttings;
- layering;
- division of the bush.
Cuttings are the easiest way to propagate Clematis Wildfire. You can do this from May to September. Cuttings are cut from the vines of plants no younger than 2 and no older than 5 years. It is best to use a sharp clerical knife and a regular cutting board for this. The cut is made in such a way that 1-2 cm remains above the internode, and 5-6 below. Cuttings can be rooted immediately using containers filled with nutrient soil. It can be prepared independently by mixing sand and peat in equal proportions. To reduce the evaporation of moisture, the sheet plate is cut off.
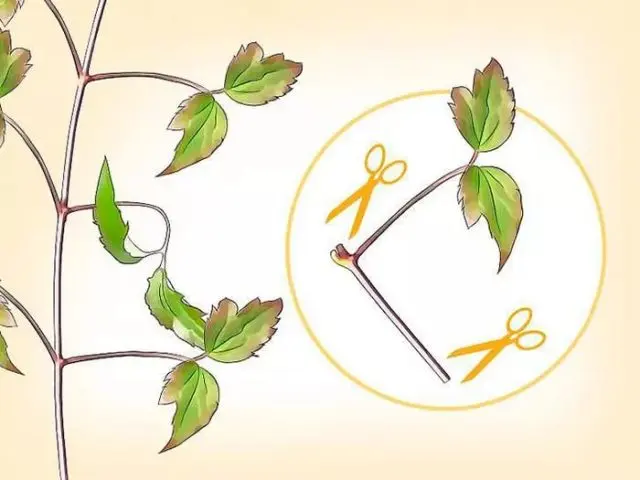
Clematis Wildfire can also be rooted in water. In this case, a bunch of cuttings is placed in a glass of water. In about 1,5-2 months they will give their own roots. After their length reaches 3-4 cm, the cuttings can be planted in the ground. Further exposure to water will lead to their death.
Propagating Clematis Wildfire by layering from the mother bush is also quite simple. To do this, a young flexible shoot is added in the spring. After some time, the internodes will begin to take root, and a young shoot will develop from each. For the winter, the layers are left with the mother plant, and in the spring they are cut off and seated in a permanent place.
The breeding method of clematis Wildfire by dividing the bush is also a way to rejuvenate it. Over time, the volume of the roots of the plant increases many times, this leads to the fact that the shrub begins to experience a lack of nutrients. In this case, it is more expedient to divide the bush into several parts, each of which will subsequently become an independent plant. You can divide plants that have not reached the age of 7 years.
This procedure can be carried out in autumn or spring. The shoots are cut almost to the base, leaving only a few renewal buds on the stumps. After that, the bush is dug out of the ground and divided with a sharp knife into several parts, divisions, each of which should contain both the root system and renewal buds. The resulting delenki are planted in prepared pits, fall asleep and spilled with plenty of water.
Video about planting Clematis Wildfire:
Diseases and pests
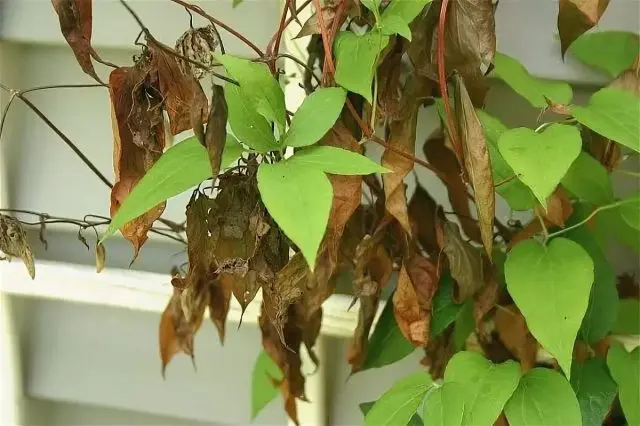
Clematis Wildfire can be affected by both viral and fungal diseases. The most common diseases of this plant are the following:
- Withering. Caused by a soil fungus that infects the roots. The disease can occur due to excessive soil moisture or lack of sunlight. Affected plants must be destroyed. Prevention is the treatment of plantings in the spring with an aqueous solution of copper sulphate 1%.
- Gray mold. A fungal disease that manifests itself in cold damp weather in the form of a gray coating on the leaves. The affected plants are destroyed, and the plantings are treated with a solution of foundationol.
- Spotting (ascochyta) leaves. It manifests itself in the form of brown spots on the leaves, which then dry out and color, forming holes. The affected leaves must be cut off, and the plants should be treated with a solution of copper sulfate.
- Mučnistaâ rosa. It often manifests itself in hot weather in the form of a white coating on leaves and flowers. The affected parts of the plant must be cut off and destroyed, and then the bushes should be treated with a solution of copper sulfate or soda ash.
- Rust. This fungal disease can be detected by the rash of spore pads that appear on the leaves. When rust appears, the infected parts of the plant are cut off, and then the Bordeaux mixture is planted.

Of the insect pests, the following can cause the most problems for Clematis Wildfire:
- Nematodes. Insects that live in the ground and feed on plant roots. It is very difficult to get rid of nematodes, therefore it is more expedient to refuse to grow Wildfire clematis in this place. As a biological protection, you can plant calendula, marigolds or garlic nearby.
- spider mite. It is found by a thin cobweb that entangles the leaves. It feeds on the sap of the plant, inhibiting it. When a spider mite appears, the plants are treated with an infusion of garlic or Actellik.
- aphid. Sucks the juices from the plant. If aphid colonies are found, plants should be treated with insecticides.
To prevent the appearance of pests and diseases, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatments of plants in a timely manner, as well as loosen and weed the soil, and prevent strong plantings.
Conclusion
Clematis Wildfire knowingly received such a name, which means “wild fire” in English. The flowers of this plant really resemble flames of an unnatural purple-red color. They look great both simply on a green background, and in combination with flowers of a different color. Wildfire clematis is unpretentious in care, so even novice flower growers can grow them.









