Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Clarithromycin is an antibiotic that is designed to cure many dangerous infections caused, among others, by by streptococci, chlamydia and staphylococci. The amount of the antibiotic dose depends on the type of bacterial infection in the patient. What precautions should you take with Clarithromycin?
Clarithromycin is a new generation macrolide antibiotic, but it cannot be given in all situations. Contraindication to the use of Clarithromycin is, inter alia, pregnancy, kidney and liver failure. During treatment, it is also necessary to use probiotics that will take care of the intestinal bacterial flora.
Clarithromycin – action
Clarithromycin prevents the biosynthesis of proteins in the bacterial ribosomes. It is well absorbed in the digestive tract and enters every tissue of our body, except the central nervous system.
The indication for the use of Clarithromycin is i.a. infection:
- some streptococci;
- golden staphylococcus;
- Listeria monocytogenes;
- Legionella pneumophila;
- chlamydia.
Clarithromycin – indications
Clarithromycin is given during the following bacterial infections:
- upper respiratory tract infections, e.g. tonsillitis;
- lower respiratory tract infections, e.g. bronchitis;
- skin infections, e.g. furunculosis;
- bacterial infection of wounds;
- periodontal and oral infections such as periodontitis;
- infections caused by Mycobacterium avium or Mycobacterium intracellulare;
- Helicobacter pylori infections;
- localized infections with Mycobacterium chelonae, Mycobacterium fortuitum, or Mycobacterium kansasii.
Clarithromycin – dosage
Clarithromycin treatments are usually given with two doses. Their height depends on the age of the patient. Dosage:
- adults and children over 12 years of age – 0,5 to 1 g per day;
- children – 15 mg of Clarithromycin per kilogram of body weight;
- children weighing less than 8 kg – 7,5 mg per kilogram body weight.
Clarithromycin – contraindications
The antibiotic should not be used in pregnant women and in people with renal or hepatic insufficiency. Clarithromycin should also not be combined with cisapride, pimozide and terfenadine.
During pregnancy, Clarithromycin should only be used if absolutely necessary.
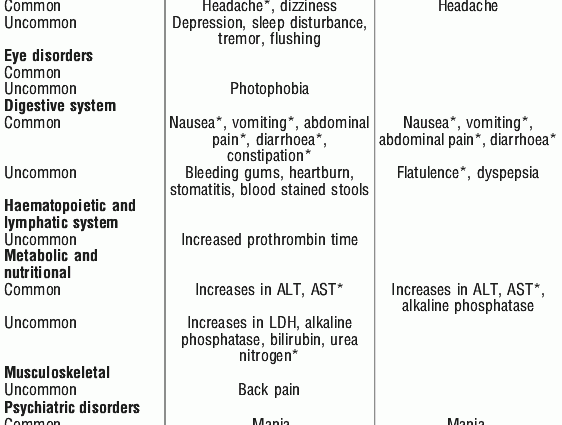
Clarithromycin – side effects
Clarithromycin side effects are related to:
- digestive system – nausea, heartburn, abdominal pain, inflammation of the intestines, diarrhea, vomiting, taste disturbances;
- headache;
- hepatic dysfunction, e.g., cholestatic hepatitis with jaundice;
- hypersensitivity such as rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, hives, and even a severe anaphylactic reaction;
- neurological symptoms, e.g. nightmares, hallucinations, psychosis;
- inflammation of the tongue;
- tinea;
- discoloration of the tongue.
You should not drink alcohol during treatment with Clarithromycin. Alcohol can be drunk only 3 days after the end of the antibiotic treatment.
It should also be remembered that Clarithromycin interferes with the effect of oral contraceptives. Therefore, it is worth using additional barrier contraception during treatment.
Before use, read the leaflet, which contains indications, contraindications, data on side effects and dosage as well as information on the use of the medicinal product, or consult your doctor or pharmacist, as each drug used improperly is a threat to your life or health.