Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Clarithromycin is a type of antibiotic, an erythromycin derivative, an extended-spectrum drug used for pneumonia, bronchitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, furunculosis, folliculitis and other dermatitis. It turns out, however, that clarithromycin is not as safe as penicillin.
Clarithromycin – action
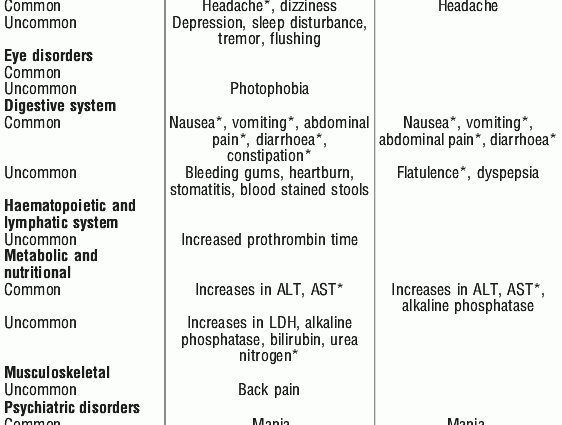
Clarithromycin belongs to the group of macrolide antibiotics which act by inhibiting the protein biosynthesis in bacterial cells. Clarithromycin inhibits the growth of the bacterial cell but does not kill it, which is why clarithromycin and macrolides are called bacteriostatic antibiotics. They can be used against many bacteria. Their use in respiratory diseases is considered an alternative to β-lactam antibiotics, i.e. penicillin, among others. The effectiveness of clarithromycin depends on obtaining the appropriate concentration in the body, which will inhibit the growth of the pathogenic microorganism and at the same time will not harm the body, hence it is so important to follow the dose prescribed by the doctor. The organism that is sensitive to the antibiotic heals itself, and sometimes resistance to the antibiotic develops, which may be congenital or acquired. There are also side effects caused by taking clarithromycin, including problems with the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, which usually disappears after the end of the treatment.
Clarithromycin – application
Clarithromycin is used to treat:
- upper and lower respiratory tract infections,
- ear inflammation,
- skin and soft tissue infections,
- dental infections,
- infections caused by mycobacteria.
Clarithromycin is well absorbed from the digestive system, the highest concentration is reached 2-3 hours after ingestion. It is excreted in urine and feces, its metabolism takes about 8 hours. During the treatment, you should avoid drinking alcohol, as it has an adverse reaction with the drug. The result may be a metabolic change of the antibiotic, intensification of undesirable side effects, including excessive strain on the liver. Alcohol can only be consumed 3 days after stopping clarithromycin.
Clarithromycin and hormonal contraception
The use of clarithromycin should not be used in conjunction with the contraceptive pill, as the antibiotic prevents the hormonal pills from being fully absorbed from the digestive system. Having less hormones taken in can prevent ovulation from being blocked and fertilization can occur. Clarithromycin works like this, especially if it is taken at the beginning of the cycle. A barrier method is recommended for women taking contraceptive pills during this antibiotic treatment. Clarithromycin is not recommended for pregnant women, it can only be used in certain cases.
Clarithromycin and penicillin
Very often, when comparing other drugs with penicillin, the latter fares much better. Penicillin is recognized as a safe antibiotic, but unfortunately not all people can tolerate it. Then clarithromycin is the frequently chosen counterpart. Macrolide antibiotics have a negative effect on the work of the heart, but this is not considered a final reason not to give this drug. It is assumed that if the treatment does not exceed 10 days, the antibiotic should not damage the heart. In the treatment of Lyme disease, this antibiotic is given for a long time and the risk of this side effect increases. That is why it is so important to read the leaflet, where all side effects of a given medicine should be marked and where information on using this medicine with others should be included.
Before use, read the leaflet, which contains indications, contraindications, data on side effects and dosage as well as information on the use of the medicinal product, or consult your doctor or pharmacist, as each drug used improperly is a threat to your life or health.