Contents
The proportion of diagnosed cases of adnexitis among other gynecological pathologies is very high. If the inflammatory process that has arisen in the reproductive system is not eliminated in a timely manner, it provokes severe complications and serious negative consequences for the female body. It is very dangerous when the course of adnexitis becomes chronic, because in this case many women face infertility.
Adnexitis – what is it in women?
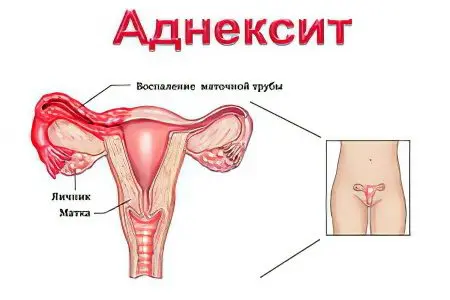
Adnexitis, or salpingoophoritis, is an inflammation of the uterine appendages (ovaries, fallopian tubes and ligaments). The disease can be acute or chronic, occurring on one or both sides of the uterus.
Pathogenic bacteria with adnexitis are introduced into the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube, involving the muscular and serous layers of the organ in the inflammatory process. Further, the inflammation will spread to the peritoneum of the small pelvis, passes to the ovaries. The infection penetrates directly into the ovary after ovulation, getting there through the corpus luteum or bursting follicle.
Extensive inflammation in adnexitis contributes to the formation of a conglomerate from the ovary and fallopian tube, and then the formation of a tubo-ovarian abscess occurs. The patency of the fallopian tubes as a result of adnexitis is sharply reduced due to the formation of numerous adhesions and strands. The outcome of the acute form of the disease may be a rupture of the tubo-ovarian abscess.
Dangerous complications in the chronic form of inflammation of the appendages:
Attachment of anaerobic infection;
The development of sepsis
Perforation of the peritoneum.
Chronicization of adnexitis occurs as a result of incorrectly chosen tactics for the treatment of acute salpingo-oophoritis. The characteristic features of the chronic form of the disease are a sluggish course with recurrent exacerbations, the need for more complex and prolonged treatment.
According to ICD-10, the chronic form of the disease has the code N70.1 (chronic salpingitis and oophoritis).
Symptoms of chronic adnexitis

There are acute and chronic forms of inflammation of the appendages, which have a different clinical picture. To differentiate the chronic form of adnexitis from the acute type of the disease, you need to know their characteristic features.
Acute adnexitis
Clinical manifestations of acute inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries are always very pronounced. From the very beginning of the process, the temperature rises significantly, its values u38bu39breach XNUMX-XNUMX °, the woman feels chills. Sharp, sharp pains are felt in the lower abdomen. They are localized on one or both sides in the iliac part of the peritoneum. Pain is given to the sacrum, rectum, leg.
On palpation of the abdomen, symptoms of peritoneal irritation, its soreness and tension are diagnosed. Urination may become frequent and accompanied by a burning sensation. A woman feels a headache, as a symptom of intoxication, there is no appetite.
During a gynecological examination, a serous-purulent or purulent secretion from the opening of the cervical canal is recorded in the mirrors. The size and shape of the appendages is very difficult to determine, they are enlarged, have limited mobility. When conducting laboratory studies, an acceleration of the ESR, an excess of the number of leukocytes, the amount of C-reactive protein is revealed.
Chronic adnexitis
With poor-quality treatment or in its absence, acute adnexitis becomes chronic. Its clinical manifestations are erased, exacerbations of the disease occur during the off-season. The introduction of the infectious component occurs in the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube. The process then spreads to muscle tissue, causing swelling of one or both tubes.
The tube lengthens and increases in volume, it is easy to detect on palpation. Together with the tubal fluid, the infection spreads into the serous membrane and into the tissues of the peritoneum. The result of this is purulent inflammation in the appendages, there is a risk of developing peritonitis and the formation of a tubo-ovarian abscess.
With the development of the inflammatory process, the walls of the tubes stick together, fibrous bands are formed, exudation is observed, and a hydrosalpinx may appear. A tubal obstruction often results in an ectopic pregnancy.
Chronic inflammation in the pelvic organs leads to the formation of a large number of adhesions not only in the reproductive system, but also in the intestines, including the appendix, and also in the peritoneum. Since the inflammatory process is sluggish, the clinical picture of chronic adnexitis is not pronounced, most of the symptoms are hidden, they appear only during relapses.
Symptoms of chronic adnexitis
A woman experiences aching pains in the lower abdomen, radiating to the vagina and to the lumbar region.
On palpation, the abdominal wall is moderately painful.
Due to functional changes in the ovaries, expressed in a decrease in estrogen production and the absence of ovulation, the menstrual cycle is disturbed in women. Menstruation becomes too scarce, or, conversely, abundant, they proceed accompanied by a pain syndrome (algomenorrhea).
Sexual intercourse with chronic adnexitis is painful, libido is reduced.
The disease complicates the work of the digestive, endocrine, urinary and nervous systems, provoking the occurrence of colitis, enterocolitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, and depression. A woman cannot fully work, the quality of life suffers.
Exacerbations are accompanied by hyperthermia up to 38 °, increased pain. During a gynecological examination, purulent discharge from the cervix, soreness of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, limitation of their mobility and tissue sclerosis (formation of strands, adhesions) are recorded in the mirrors.
The onset of relapse can be determined by the appearance of chills, pain in the lower abdomen at rest and during urination. On palpation, the appendages are not felt clearly enough, but pain is noticeable in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbtheir location. A laboratory blood test shows an acceleration of ESR and an increase in the number of leukocytes.
Symptoms of adnexitis outside periods of exacerbations:
Constant subfebrile temperature (about 37 °);
Dull or weakly throbbing pain in the lower right or left of the navel, aggravated before menstruation and during the alleged ovulation;
Pain during sexual intercourse, after physical exertion, hypothermia or stress;
Menstrual disorders associated with the volume of menstrual flow and the duration of menstruation;
Headache and weakness as symptoms of intoxication.
The clinical picture of the disease, which lasts for many years, often has very poor manifestations. The fact that a woman has chronic adnexitis, the doctor finds out when she complains about the inability to conceive a child.
Causes of chronic adnexitis
The onset of the disease is provoked by pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms. The causative agents of specific adnexitis are tuberculosis bacillus, gonococci, diphtheria bacillus. Nonspecific adnexitis is triggered by the activity of chlamydia, mycoplasma, staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli, fungi and viruses, or their associations.
Ways of penetration of infection into the reproductive system:
Ascending – from the cervix, from the vagina;
Descending – from the organs in which the inflammatory process occurs (for example, appendicitis);
Lymphogenic – with lymph flow;
Hematogenous – with blood flow (typical for tuberculous adnexitis).
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
hypothermia;
Stress;
Promiscuous unprotected sex;
Violations of intimate hygiene;
Intrauterine manipulations – abortion, hysteroscopy, diagnostic curettage, removal and insertion of an intrauterine device, metrosalpingography;
Complicated childbirth;
Removal of the appendix;
Decreased immunity due to an infectious or somatic disease, HIV infection.
The development of chronic adnexitis is based on untreated or not treated acute and subacute adnexitis at all.
Chronic adnexitis and pregnancy

Obstruction of the fallopian tubes is a common complication of this disease, therefore, when planning a pregnancy, you should get rid of chronic adnexitis. At the end of therapy, you need to undergo an examination that allows you to assess the patency of the fallopian tubes and the possibility of conceiving a healthy baby.
If the diagnosis of “chronic adnexitis” is made during pregnancy, the doctor prescribes therapy with drugs that are as harmless as possible to the unborn child. Antibiotic treatment of pregnant women is usually not practiced in order to avoid negative consequences for the child, the doctor chooses safe drugs from other pharmaceutical groups. However, it is very dangerous to leave a focus of inflammation in the reproductive system of a pregnant woman untreated, because the risk of abortion or fetal fading increases.
Consequences and complications of chronic adnexitis
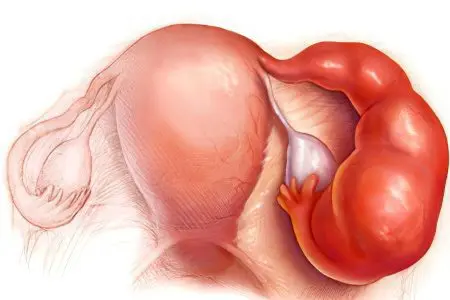
As a result of a chronic inflammatory process occurring in the ovaries, their functionality is impaired. In this case, conception becomes impossible, as the egg loses its ability to fertilize. Due to the disruption of the ovaries, the menstrual cycles become irregular.
Infertility as a result of tubal obstruction is the most severe consequence of chronic adnexitis. Clumped tissues of the fallopian tubes completely block the ability for the sperm to reach the egg. In addition, the inflammatory process disrupts the function of the ciliated epithelium to promote the fertilized egg to the uterus for implantation. Since in this case the movement through the tube is difficult, implantation can occur directly in the fallopian tube. In this case, an ectopic pregnancy occurs – another serious complication of chronic adnexitis.
Inflammation of the appendages, or salpingo-oophoritis, causes the following complications:
Infertility, as a result of the adhesive process, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, ovulation disorders;
Transition to a chronic form;
Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy;
The development of tubo-ovarian formation (purulent fusion of the fallopian tube and ovary with the formation of an abscess).
Chronic pain directly affects a woman’s libido, reducing it. Sexual contacts become undesirable, a woman feels weak, irritable, her mood often changes.
When a child is conceived by a patient with a chronic form of adnexitis, she may develop an intrauterine infection, start a spontaneous abortion, and premature birth.
Diagnosis of chronic adnexitis
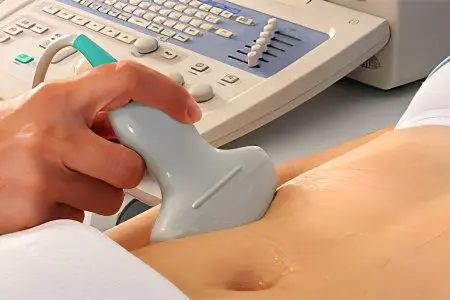
To diagnose salpingoophoritis, you should contact a gynecologist. The doctor will study the history, conduct a gynecological examination, during which painful and inactive appendages are fixed.
What interests the doctor during the collection of anamnesis:
Whether the patient had abortions and complicated childbirth;
Has a uterine device ever been placed?
Whether intrauterine procedures and salpingography were carried out.
To determine the type of infectious agent that caused inflammation and assess its sensitivity to antibiotics, bacterioscopy and bacteriological examination of smears from the vagina, cervical canal and urethra are performed. A general blood test in this case is not informative enough – only an increase in ESR can indicate the presence of inflammation.
Instrumental research methods:
vaginal ultrasound;
CT, MRI of the reproductive system;
Sonography to determine the presence or absence of an adhesive process;
X-ray of the uterus and ovaries;
Hysterosalpingography to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Treatment of chronic adnexitis
The treatment of this disease proceeds for a long time, however, with the exact implementation of the doctor’s recommendations, a positive trend is most often recorded. After determining the sensitivity of the causative agent of the inflammatory process to antibacterial drugs, the doctor prescribes a treatment regimen. It is based on antibiotic therapy, with the exception of which is pregnancy.
The best result is obtained in the treatment of adnexitis during an exacerbation, since active bacteria are more sensitive to the effects of antibacterial drugs. Treatment of chronic adnexitis is carried out in a complex, using medical and physiotherapeutic methods.
Therapy of salpingoophoritis is carried out in bed rest in a gynecological hospital. A woman is prescribed a special diet with restriction of seasonings and carbohydrates. It is recommended to apply cold to the abdomen to relieve pain and inflammation.
Drug therapy includes broad-spectrum antibiotics, a combination of two or more drugs:
Clindamycin (2 g twice a day) + Gentamicin;
Klaforan IM (1-0,5 g twice a day) + Gentamicin IM (80 mg three times a day);
Lincomycin IM (0,6 g three times a day);
Cefobid IM (1 g twice a day) + Gentamicin;
Cefazolin IM (1 g twice a day) + Ciprofloxacin IV (100 ml twice a day).
At the same time, Metronidazole is administered orally at a dose of 0,5 g three times a day. If an anaerobic infection is suspected, a woman is given intravenous injections of Metrogyl (100 ml twice a day).
For detoxification, drip administration of glucose, Reopoliglyukin, Gemodez, saline solutions with a volume of 2-3 liters is prescribed.
NSAIDs are used as painkillers orally, in the form of rectal suppositories or in the form of injections:
Ibuprofen (Nurofen, Faspik, Ibuklin);
Ketorolak (Ketorol, Ketanov);
Diclofenac (Voltaren, Ortofen, Diklak, Naclofen).
Additionally, antihistamines (Cetrin, Suprastin, Pipolfen) are prescribed for the prevention of an allergic reaction, vitamin complexes.
For the treatment of adnexitis outside the period of exacerbations, physiotherapy procedures are used:
Electrophoresis with iodine or lidase;
Ultrasound treatment;
Electrophoresis with copper and zinc on the phases of the menstrual cycle;
Treatment with pulsed currents of high frequency.
To restore well-being, autohemotherapy, treatment with immunomodulators, injections of aloe, Longidase, FIBS are used. Excellent results are obtained by spa treatment with mud, paraffin baths, baths and douches.
Treatment of adnexitis with candles
Vaginal and rectal suppositories are extremely effective in the treatment of this disease, because they act in close proximity to the site of inflammation. Candles relieve pain, their components actively resist the action of bacteria.
The most frequently prescribed:
Movalis – analgesic, used for 5-7 days;
Fluomizin – is used once a day at bedtime, as an antibacterial agent;
Polygynax – suppositories with anti-inflammatory effect, used for 10-14 days;
Voltaren – have an analgesic effect;
Hexicon – approved for use during pregnancy as an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent;
Indomethacin – rectal suppositories with anti-inflammatory effect;
Candles with belladonna extract – effective against pain.
Do not use suppositories without a doctor’s prescription, which will take into account the characteristics of the course of the disease and possible contraindications.
Prevention of chronic adnexitis

To prevent the acute form of the disease from transforming into chronic adnexitis, it is necessary to carry out a course of treatment in a timely manner under the guidance of the attending physician with strict adherence to his recommendations. To prevent exacerbations, it is recommended to periodically conduct courses of therapy with therapeutic mud, spa treatment. In order not to provoke the inflammatory process, stressful situations, hypothermia should be avoided.
Sexual relations with a regular partner, the use of condoms will help to avoid infection of the reproductive system with sexually transmitted diseases.
You should not swim in cold water and sit on cool surfaces, refuse warm underwear in winter.
The rules of intimate hygiene must be strictly observed:
It is recommended to wash daily with warm water;
Shower regularly;
Mandatory frequent change of sanitary pads during menstruation;
It is advisable to refuse the use of hygienic tampons for the duration of treatment.
At the first manifestations of diseases of the reproductive system, the appearance of pain and atypical discharge, you should immediately contact your doctor, without waiting for complications.
Prognosis of the disease
If the therapy of chronic adnexitis is carried out in a timely manner and in full under the guidance of a qualified doctor, the disease has a favorable prognosis and does not threaten the patient’s life. Failure to comply with preventive measures and ignoring the recommendations of the gynecologist increases the risk of infertility, menstrual irregularities, and the appearance of an ectopic pregnancy.









