Contents
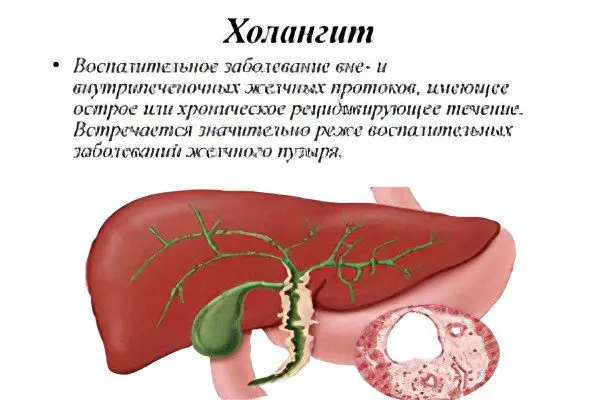
Cholangitis is an inflammation of the bile ducts. Various factors can provoke it, but with this disease, stagnation of bile is always observed. Sometimes the pathology is manifested by acute symptoms and leads to the development of serious complications. The manifestations of the disease depend on its form and stage of development.
Cholangitis should be treated by a doctor after a thorough diagnosis. Therapy is predominantly medical. Most often, women suffer from cholangitis. At risk are the elderly (50-60 years). In children, inflammation of the bile ducts is rarely diagnosed.
What is cholangitis?
Cholangitis is a pathology accompanied by a violation of the liver and inflammation of the bile ducts. When the disease occurs, stagnation of bile occurs. This can be caused by various reasons. Often the disease develops against the background of a bacterial infection.
With cholangitis, the function of the gastrointestinal tract as a whole suffers. The patient can be diagnosed with hepatitis, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis.
Types and forms of the disease
Depending on the cause of the violation, the following forms of cholangitis are distinguished:
Bacterial.
Viral.
Parasitic.
Autoimmune.
Oncological.
Depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease, the following varieties are distinguished:
Acute cholangitis. The disorder has a vivid clinical picture. The patient’s condition worsens significantly.
Chronic cholangitis. The disease sometimes worsens, sometimes it goes into remission. Once the acute phase has passed, the person will not experience any symptoms of the disorder.
Acute cholangitis
Acute cholangitis is infectious. Violation develops unexpectedly for the patient himself. The bile ducts become inflamed and bile begins to accumulate in them. Sometimes there is a complete blockage of the paths. If the disease has a mild course, then it is possible to cope with it with medical methods. Surgery is resorted to when complications develop.
Acute cholangitis occurs in various forms, including:
Catarrhal cholangitis. Such a lesion of the bile ducts is considered the easiest. The mucous membrane of the biliary tract turns red and swells. The symptoms of the disorder in the patient are mild, there is no treatment. Therefore, it is catarrhal cholangitis that often acquires a chronic course.
Diphtheric cholangitis. The mucous membrane of the biliary tract is covered with ulcers, on which a film forms. Under them, areas of necrosis begin to grow rapidly. Often, diphtheria cholangitis passes from the biliary tract to the liver.
Purulent cholangitis. Pus begins to accumulate in the bile ducts. Inflammation progresses rapidly, spreads to nearby tissues and organs.
Necrotic cholangitis. The bile ducts undergo necrosis, as enzymes produced by the pancreas penetrate into them. It is they who begin to corrode the ducts from the inside. This form of cholangitis is the most dangerous, as it can cause inflammation of the peritoneum or liver.
Chronic form of cholangitis
If we consider cholangitis in the general structure of diseases of the hepatobiliary system, then it is not often diagnosed. Inflammation of the bile ducts is predominantly a secondary disorder that occurs against the background of other pathologies of the digestive tract. Of particular danger in this regard is the defeat of the gallbladder and liver. In 1/3 of patients, cholangitis is a consequence of the removal of the gallbladder.
Cholangitis can have a different course:
latent form. In this case, the symptoms of pathology are completely absent.
relapsing form. The disease gets worse and then subsides.
septic form. Pus accumulates in the ducts. The disease has a severe course and can lead to the death of the patient.
Abscess form. Abscess areas filled with purulent masses form in the bile ducts.
Separately, it is necessary to highlight such a form of the disease as primary sclerosing cholangitis. In this disorder, the inflammation is non-infectious. As the pathology progresses, the biliary tract narrows, the outflow of bile is disturbed. At the terminal stage of the disease, they completely overgrow, the patient develops cirrhosis of the liver.
Sclerotic cholangitis is a severe pathology. It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease. For 10 years, these patients develop irreversible changes in the liver.
Types of cholangitis, depending on the location of the inflammatory process:
Choledochitis. Inflammation of the common bile duct, called the common bile duct.
Angiocholitis. Inflammation of the small bile ducts.
Papillitis. Inflammation of the papilla of Vater. It is located where the common bile duct enters the duodenum.
Total inflammation of the biliary tract.
Causes
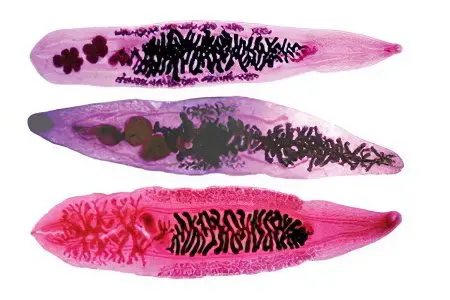
The main cause of the development of cholangitis is considered to be an infectious process. The most common pathogens are Escherichia coli, Proteus and Enterococcus. If a patient develops purulent inflammation, then during the analysis of bile, several representatives of the infectious flora are sown in it at once. Such an analysis is of no small importance, since according to its results it will be possible to choose the optimal treatment.
Infection can enter the bile ducts in several ways:
Ascending. Bacteria rise into the bile ducts from the duodenum through the mucous membranes.
By blood, through the portal vein.
Through the lymphatic vessels. The source of infection can be the pancreas, intestines and gallbladder.
Sometimes the bile ducts become inflamed due to the entry of pancreatic enzymes into them. They have an aggressive effect, so the walls of the ducts corrode, their necrosis occurs. In this case, experts point to aseptic inflammation.
Sclerosing cholangitis is an autoimmune disease. With it, the own cells of the immune system begin to produce antibodies that destroy the tissues of the bile ducts.
Symptoms of cholangitis
Diagnosing cholangitis is not easy, since each patient has a different course of this disease and gives a variety of symptoms. Often inflammation of the bile ducts can be confused with other diseases. In some cases, cholangitis does not manifest itself at all. However, there are certain signs that make it possible to suspect a lesion of the bile ducts.
Different symptoms are given by acute, chronic and sclerosing cholangitis.
For acute cholangitis

Symptoms of acute cholangitis:
The pain is concentrated in the chest on the right side. She gives in the stomach, in the shoulder and in the shoulder blade.
The body temperature rises to 40 ° C, the patient is shivering.
The person is nauseated and vomits.
Arterial pressure drops sharply.
Weakness increases.
There is itching.
The dermis and mucous membranes acquire a yellow color.
Consciousness becomes clouded.
There is a possibility of developing hepatic coma.
For chronic cholangitis
Chronic cholangitis is accompanied by symptoms such as:
Weak pain. It can be intense only when there are stones in the gallbladder.
Itching itch.
Pressing or bursting feeling in the right hypochondrium.
Weakness.
Increase in body temperature. It jumps from time to time.
Increased fatigue.
Hyperemia of the palms, thickening of the fingers.
In case of sclerosing cholangiocarcinoma
Sclerosing cholangitis:
Pain in the right hypochondrium and in the abdomen (mainly in its upper part).
Diarrhea.
Skin itching and yellowing of the skin.
An increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C.
Diagnostics

To diagnose cholangitis, it will be necessary not only to analyze the existing symptoms, but also instrumental, as well as laboratory examination.
Primary diagnostic procedures:
Interrogation of the patient.
Studying the patient’s history.
Examination of the skin and mucous membranes, palpation of the abdominal wall, the area of the right hypochondrium.
Collection of laboratory data:
Blood test (general and biochemical). Patients with cholangitis will have increased levels of bilirubin, transaminases, and alkaline phosphatase.
Bacterial culture of bile. Its fence is carried out during duodenal sounding.
Microscopy of feces. This test will rule out parasite infestation.
The instrumental methods of examination include:
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity.
CT scan.
Ultrasonography of the bile ducts.
Cholecystography.
Electronic holography.
MRPCHG. This method allows diagnosing obstruction of the biliary tract.
Cholangitis gives similar symptoms with various diseases.
Therefore, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with such disorders as:
Cholelithiasis.
Non-calculous cholecystitis.
Viral hepatitis.
Primary biliary cirrhosis.
Pleural empyema.
Pneumonia affecting the right lung.
Which doctor should I go to?
Cholangitis is treated by a gastroenterologist. Also, a person may need the help of a nutritionist, physiotherapist, surgeon. During the examination, it will be necessary to visit an endoscopist and an ultrasound diagnostician.
Treatment of cholangitis
A patient with cholangitis is hospitalized. He must be under the constant supervision of specialists, since at any time he may need the help of a surgeon. Therapy depends on the severity of the pathological process.
The main tasks that face the doctor:
Relief of inflammation.
Removal of intoxication from the body.
Unloading of the biliary tract.
Conservative treatment of cholangitis
The conservative treatment regimen is based on the following points:
Compliance with bed rest.
The diet should be as light as possible. The patient should receive puree soups, pureed vegetables, minced meat, fermented milk drinks, etc.
Antibiotics and drugs to rid the body of parasites.
Drugs for the relief of inflammation.
Antispasmodics for pain relief.
Infusion therapy is carried out to remove intoxication from the body. The patient is injected with electrolytes, proteins, salt preparations, glucose, blood cells.
Hepatoprotectors are designed to protect liver cells from destruction.
Plasmapheresis. The procedure for cleansing the blood is carried out with severe intoxication of the body.
Medical treatment of cholangitis
A patient with cholangitis is prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics. They are selected individually. The duration of treatment is 14 days.
In addition to antibiotics, painkillers, antispasmodics, hepatoprotective drugs, cholagogues, and ursodeoxycholic acid are used. All medicines are prescribed by the doctor after the examination.
Physiotherapy
When the acute stage of cholangitis can be overcome, the patient is referred for physiotherapy.
He can be assigned procedures such as:
UHF The body is affected by electromagnetic fields.
Diathermy. Treatment with alternating currents.
Electrophoresis. The body is affected by electrical impulses.
Inductometry. Treatment with high-frequency magnetic fields.
Mud applications. Warm mud treatment.
Microwave therapy. The body is influenced by electromagnetic fields.
Ozonekeritotherapy. The human body is influenced by heated ozocerite. This is an oil based substance.
Paraffin therapy.
Reception of mineral baths.
Surgical treatment of cholangitis
If necessary, the patient is prepared for surgery.
These may include procedures such as:
Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy. During the procedure, the Vater papilla, which has been narrowed, is dissected.
Removal of stones from the biliary tract using an endoscope.
Choledochus stenting using endoscopic equipment. A special device is inserted into the bile duct, which prevents it from narrowing.
Percutaneous transhepatic drainage of the biliary tract. Bile is brought out, for which direct drainage is installed.
Doctors prefer minimally invasive techniques using an endoscope. This procedure allows you to carry out all the necessary manipulations without making large incisions in the abdominal cavity. The use of an endoscope makes it possible to avoid massive blood loss and quickly recover the patient after surgery. However, with the development of a purulent complication, abdominal intervention is indicated.
Diet in the acute period of cholangitis

In the acute course of cholangitis, the patient is transferred to the treatment table at number 5A. With chronic inflammation, you need to stick to table number 5.
Diet number 5. requires the following recommendations:
You need to eat 5 times a day, in small portions.
Refuse to eat before bed. Only a light snack is allowed.
Under the ban are spicy and spicy dishes, garlic, horseradish, radish. .
The daily calorie content is 3500 kcal, where proteins account for 100 g, fats 100 g, carbohydrates 400 g.
The menu should include products such as: buckwheat, cottage cheese, oatmeal, low-fat meat and fish.
After feeling better, you can add vegetable and milk soups, baked and fresh vegetables, dried bread to the menu.
Diet No. 5A involves the following rules:
You can eat any cereal, but they need to be boiled.
Meat and fish are steamed.
Frying, as a method of cooking, is prohibited.
Fresh fruits and vegetables should not be included in the diet.
Rye bread is prohibited.
It is recommended to spend fasting days on cottage cheese and apples.
To avoid constipation, a person should eat beets, vegetable juices, dried fruits.
Complications and consequences
If there is no treatment for cholangitis, then the likelihood of developing complications such as:
Cholecystopancreatitis.
Inflammation of the liver tissue.
Biliary cirrhosis of the liver.
Liver abscess.
Peritonitis.
Sepsis.
Infectious-toxic shock.
Liver failure.
Hepatic encephalopathy with brain damage.
Coma.
Video: the program Live Healthy – “bile will bring to cirrhosis”:









