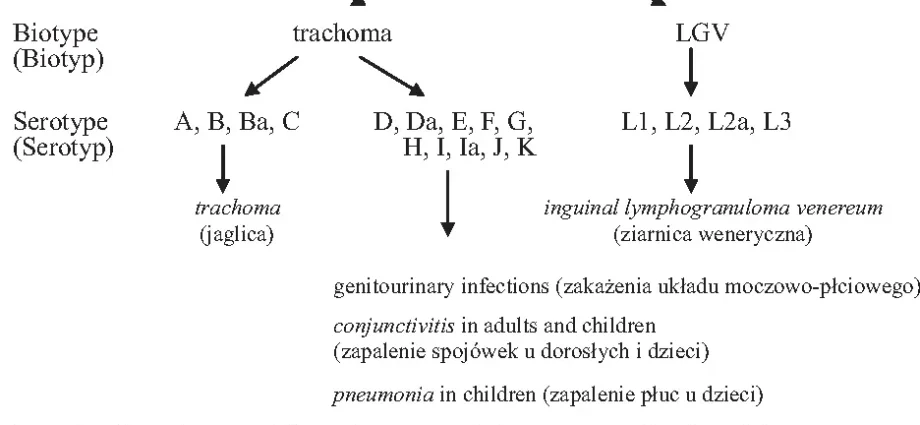
Within this species, several serological types have been distinguished.
Types A, B, Ba, C cause endemic conjunctivitis (trachoma). Types B, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K can cause inflammation of the lower urinary tract and their complications, as well as conjunctivitis and pneumonia in newborns.
DK types cause non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU) in men, epididymitis or, less commonly, prostatitis, and in infants conjunctivitis, pneumonia, and possibly otitis media. In women, DK types cause cervicitis, urethritis, endometritis, Bartholinits, adnexitis, or pelvic infl ammatory disease (PID) ).
In both sexes, Ch. trachomatis can cause proctitis, asymptomatic pharyngitis, Reiter’s syndrome, Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (perihepatitis). Types L1, L2 and L3 cause inguinal Hodgkin (LGV) and proctitis.
DL: Cell culture on McCoy cells, (Fig. C-4) enzyme immunoassay (EIA), direct immunofluorescence (DIF) and many methods for detecting chlamydial DNA, such as polymerase chain reaction – PCR) or ligase chain reaction (LCR).
DIG. C-4. Non-gonococcal urethritis. Slight mucous discharge from the urethra.