Contents
- Chest X-ray
- When should a chest X-ray be performed?
- Chest X-ray – how to prepare for the examination?
- Chest X-ray – what does the examination equipment look like?
- Why are the bones white and the lungs black?
- Chest X-ray – how is the examination done?
- Well-being during and after the X-ray examination
- What are the benefits and risks of the study?
- Chest X-ray – are there any limitations?
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
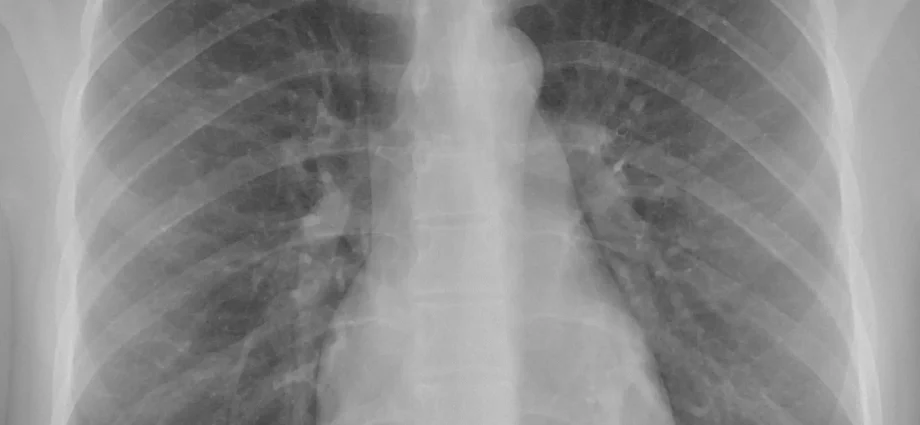
Chest X-ray is the most commonly used imaging test. Thanks to the use of X rays (on film or in digital quality), the heart, lungs, respiratory tract, vessels and bones of the chest, as well as fragments of the spine are imaged in a non-invasive way. Performing an X-ray examination exposes the body to a small dose of ionizing radiation.
Chest X-ray
A chest X-ray is an imaging test that involves short-term exposure to X-rays. Thanks to the X-ray examination, it is possible to visualize the respiratory tract, lungs, parts of the spine, heart and chest bones. Irradiation creates an image of the chest and internal organs located in this area of the body. Radiation is absorbed in various amounts, depending on the amount of water, air, bones, blood and muscles in the body’s tissue. Even bones absorb a lot of radiation. X-ray examination is recommended every 2 years, while heavy smokers should do it once a year.
When should a chest X-ray be performed?
Chest X-rays are most often performed when the following symptoms appear:
- shortness of breath
- a disturbing or persistent cough,
- chest pain or injury,
- chest injury,
- bleeding when coughing
- bleeding from the esophagus.
X-ray examination is performed as a diagnostic test in family medicine, cardiology and pulmonology. Chest X-ray is helpful in the diagnosis and assessment of the effectiveness of the treatment used:
- pneumonia
- heart failure and other heart diseases,
- rozedmy,
- lung cancer
- interstitial changes,
- neoplastic changes in the lungs (malignant and benign),
- tumor metastasis from other organs,
- tuberculosis
Chest X-ray is performed only on the recommendation of a doctor (a referral is required), both in public and private medical facilities.
Who should do a chest X-ray?
- Adults – during periodic examinations every 2 years.
- People working in harmful conditions – once a year.
- Smokers – once a year.
Note: Chest X-ray examinations are forbidden in pregnant women as there is a possibility of harm to the fetus. If it is necessary to perform a test in this group of patients, special safety measures are applied to protect the fetus from harmful radiation.
Chest X-ray – how to prepare for the examination?
Chest X-ray does not require any special preparation (you do not need to be on an empty stomach).
The tester may ask you to remove your clothes (blouse, bra) and jewelry (chain), glasses, or any metal that may interfere with the X-ray transmission.
Women should inform the doctor who orders the test or the person who carries it out if they are suspected of being pregnant.
Chest X-ray – what does the examination equipment look like?
The equipment usually consists of a wall mounted one apparatus in the shape of a large box containing a radiopaque plate or a special plate that records the radiological image in digital quality, and tubeswhich is located a few meters from the plate and emits X rays. The tube can also be hung over the bed on which the tested person is lying.
There are also portable X-ray machines. They are usually used in hospitals for the so-called bedside X-ray for more severely recumbent patients. A plate recording radiation emitted by the tube at the end of the arm above the patient, protruding from the apparatus, is placed under the body of the examined person.
Why are the bones white and the lungs black?
X radiation is a type of wave, somewhat reminiscent of radio waves. The rays pass through obstacles in their path. After directing the tube (source of rays) to the appropriate part of the body, a beam of rays is sent, penetrating the skin, organs and bones. Individual parts of the body absorb radiation to varying degrees. Due to their high density, bones absorb more radiation than soft tissues (liver, kidneys). In turn, muscles, adipose tissue and internal organs allow the rays to penetrate freely. As a result, dense areas appear bright, soft tissue dark / gray, and air black.
Chest X-ray – how is the examination done?
Usually, the examination is performed in two projections (positions): anterior-posterior and lateral. This means that you must first face the indicated plate, and then stand sideways to it (with your hands up). The person who will conduct the examination (most often it is a radiological technician) will instruct you thoroughly and show you how to position yourself and which parts of the body should be adjacent to the radiation recording plate. Participants should remember that one side of the chest should not stick more to the cassette than the other, and that the hands should rest on special grips. Before taking a picture, take a deep breath and hold it in the air. Ignoring this recommendation may result in distorted images. Before performing the test, you can ask to wear a lead apron to protect the pelvic area (this is especially recommended for women) and the neck (thyroid protection). In patients who are unable to stand independently, the test may be performed in the supine position.
After determining the optimal position for the test, stay in it for several seconds. The technician will leave the room for the duration of the examination and will control the apparatus from another room.
After the x-ray is done, you may be asked to stay in the office for a while until the radiologist confirms that all the necessary images have been obtained.
A chest X-ray usually takes up to 15 minutes and is completely painless.
The obtained results are read by the radiologist. The old technique of analyzing the results of a chest X-ray is to place the image next to a light source. In the age of today’s medicine and progress, analyzing the results is much more convenient. X-rays are placed on the computer screen, thanks to which they can be simultaneously saved on the disk. However, thanks to the access to older photos, you can easily compare test results taken at a long time interval.
Well-being during and after the X-ray examination
X-ray examination is completely painless.
The feeling of discomfort may appear due to the lower temperature in the office where the X-ray examination is performed, as well as the cold plate to which the chest must adhere for several seconds. People with degenerative changes in the joints of the hands or with injuries to the chest may experience pain due to the need to assume the correct position and remain in it during the examination.
What are the benefits and risks of the study?
A comprehensive chest X-ray allows you to assess the organs and bones located above the diaphragm muscle. In most patients, the heart and lungs are the most visible.
1. Chest X-ray – benefits
- After the test, the rays do not remain in the body.
- Usually the test does not cause any side effects.
- Due to the low price, the test is widely available in health care facilities.
- X-ray is an easy and quick examination, especially useful in emergencies, where every minute counts.
2. Chest X-ray – risk
- In case of frequent exposure to high doses of radiation, there is a small risk of developing cancer. However, contemporary chest X-rays are associated with exposure to very low doses of radiation.
- Women should always tell the doctor or the tester if there is any chance they are pregnant.
Chest X-ray – are there any limitations?
Chest X-ray is very helpful, but it is not always possible to diagnose the disease on its basis. In classic X-ray, it is impossible to detect small neoplastic changes or blockages in the pulmonary vessels. In such cases, more detailed diagnostics is necessary, e.g. chest computed tomography.
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website. Do you need a medical consultation or an e-prescription? Go to halodoctor.pl, where you will get online help – quickly, safely and without leaving your home.