Contents
Diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma
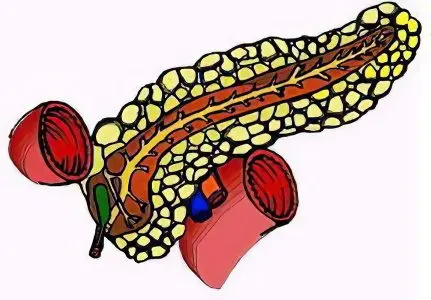
The pancreas is a large organ of internal and external secretion. It is located on the posterior abdominal wall in the retroperitoneal zone, consists of a head, body, tail, and is partially covered by the stomach in front. In the thickness of the pancreas there is its duct directed from the tail to the head. The gland produces pancreatic juice containing enzymes that help digest proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
The pancreas contains endocrine glands that produce insulin for glucose uptake. A healthy pancreas has a homogeneous tissue, large contours. The cause of diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma, according to doctors, is acute and chronic pancreatitis, elevated blood sugar.
Often, diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma are diagnosed in elderly people, with various problems of the cardiovascular system, diseases of the liver and biliary tract, and the digestive tract. The reason for the change in the parenchyma of the pancreas can also be infectious and inflammatory diseases of the internal organs that contribute to metabolic disorders.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma
When conducting ultrasound diagnostics, you can find out the density of internal organs. If a decreased or increased echogenicity of the pancreas is detected, then this is a serious reason for undergoing an extensive examination that provides an accurate diagnosis and determines methods for eliminating problems.
Increased echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is detected during inflammation with the formation of fibrosis that develops against the background of metabolic disorders, when healthy parenchyma tissue is replaced by fat, in acute pancreatitis and relapse of chronic inflammation that changes the density of the parenchyma.
The value of the absorption coefficient of ultrasonic radiation depends on the increased echogenicity of the parenchyma. Malignant tumors that form in the parenchyma have a higher absorption coefficient of ultrasonic energy than benign tumors.
Thickening of the pancreatic parenchyma
Methods for studying the pancreatic parenchyma include questioning and examination of the patient, laboratory, instrumental and radiological methods. Thickening of the parenchyma can be the result of various diseases of the pancreas.
Symptoms include pain in the epigastric region and the left hypochondrium, disorders of the digestive system that cause a person to feel discomfort, general weakness, and severe weight loss. The mode and nature of nutrition, the presence of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, and cystic fibrosis have a certain influence on the appearance of compaction of the parenchyma of the organ.
Heterogeneous structure of the pancreatic parenchyma
The pancreas of a healthy person has a homogeneous structure, the same echogenicity, well-visible contours, an uncinate process, the correct position and normal sizes of the head and tail. Deviation from the norm is determined by an increase in the size of individual parts of the pancreas and the heterogeneity of the structure of its tissues.
Heterogeneity of the pancreas is evidence of the presence of various diseases, including pancreatitis and diabetes. This pathology can be found in any part of this organ. Diffuse-heterogeneous changes can be caused by edema, inflammation and the formation of pseudocysts.
Reactive changes in the pancreatic parenchyma
Reactive changes in the parenchyma are a consequence of inflammation of the pancreas due to the aggressive effects of the liver and gallbladder on it. This causes pain, dyspepsia and an increase in blood sugar levels and occurs because the glandular tissue of the parenchyma with a reactive pancreas produces pancreatic juice and hormones in insufficient quantities. One of the most common causes of reactive changes in the parenchyma can be an allergic reaction.
Diffuse changes in an important organ contribute to a reactive change that spreads evenly throughout the pancreas without the presence of local foci indicative of neoplasms or stone formation. The treatment of this pathology is one of the topical issues of modern gastroenterology.
The combination of medicines prescribed by the attending physician and properly organized nutrition can prevent the development of various complications. It must be remembered that a timely visit to the doctor and careful implementation of the prescriptions can be a guarantee of successful treatment.
[Video] Surgeon Vladimir Pavlenko – What foods does the pancreas like or dislike:









