Contents
What is cerebral ischemia?
cerebral ischemia – This is a disease that develops due to a lack of oxygen necessary for the brain to work. It is congenital and chronic. The first form occurs in young children. Chronic cerebral ischemia is typical for people in old age.
Hypoxia occurs when blood clots or atherosclerotic plaques form in the vessels that provide oxygen and nutrients to the brain. This process is accompanied by a change in blood pressure in large arterial trunks and arterioles. If it increases sharply, the vascular walls are destroyed and impregnated with plasma proteins. This leads to the growth of connective tissue. It fills the lumen of the vessel, causing its narrowing. Circulation becomes difficult. A complete blockage prevents blood from delivering oxygen and nutrients to brain cells. This leads to death.
Symptoms of cerebral ischemia

The first signals indicating cerebral ischemia are fatigue during mental work, forgetfulness. Older people often do not consider this a sign of a serious illness, taking into account age. But if the memory deteriorates sharply, you should consult a doctor. Patients with cerebral ischemia suffer from persistent headaches.
As the disease develops, falls and fainting, dizziness are possible. There is a sharp increase in blood pressure, nausea, turning into vomiting. In the later stages of cerebral ischemia, vision and hearing are impaired. The patient is unable to work and mental activity, self-service. He loses sleep, cannot perform complex movements, suffers from unsteadiness when walking.
An acute form of cerebral ischemia is a stroke. It is focal in nature and occurs when a plaque inside a vessel ruptures and clogs the lumen. As a result of thrombosis, blood stops flowing to the brain, which is why tissue necrosis is inevitable, that is, ischemic stroke. After it, deep neurological disorders occur: sensitivity and the ability to move independently may disappear.
Diagnosis of cerebral ischemia is based on visible symptoms, as well as on the basis of the study of cerebral and sensory function. A survey of the patient and his relatives is conducted, since patients in the later stages of the disease often suffer from dementia and memory loss. Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are needed to examine the cerebral cortex. The results of the procedures allow the doctor to see the changes that have occurred in it.
Causes of cerebral ischemia
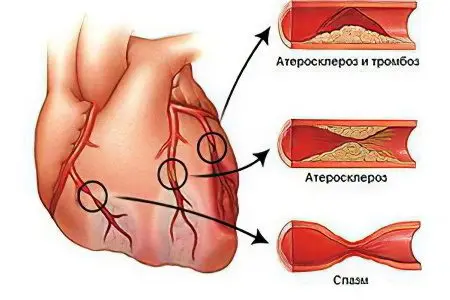
Atherosclerosis
This disease is considered chronic and affects the large blood vessels in the body. On their walls deposits of cholesterol, forming atherosclerotic plaques, accumulate. They are able to increase in size and can either significantly reduce blood flow, or completely close the lumen of the vessel. Atherosclerosis affects mainly men.
Its development is promoted by malnutrition, smoking, obesity, frequent stress and diabetes. Treatment of atherosclerosis requires not only taking medications, but also moderate physical activity and diet. Foods containing cholesterol and fats should be excluded from the diet.
They cause clogging of blood vessels, being deposited in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. Blood, moving through the arteries, can carry particles of such neoplasms. They get stuck in the narrow parts of the vessel and stop blood circulation.
Patients with atherosclerosis are advised to give up fried and fatty foods, red meat, and alcohol. It is recommended to eat wholemeal bread, cereals, foods containing Omega-3 fatty acids. It is important to maintain a normal weight, as obesity is one of the risk factors for atherosclerosis.
Arterial hypertension
This is the medical term for high blood pressure. This disease cannot be completely cured. However, it is necessary to constantly keep blood pressure under control in order to prevent various complications, including cerebral ischemia.
As in the case of atherosclerosis, men are more likely to suffer from arterial hypertension. Among the risk factors are also older age, a large amount of stress, bad habits and obesity.
An increase in blood pressure may not be accompanied by visible external signs and changes in the patient’s well-being. In this case, it can be determined using a tonometer. Sometimes a sharp increase in pressure is accompanied by dizziness and headaches. Some patients note the appearance of red dots before the eyes.
To prevent a sharp increase in blood pressure, you need to do exercises daily, reduce the consumption of salt, convenience foods, and sweets. If you have excess weight, you should get rid of it. The diet must contain foods rich in potassium. It is important to visit your doctor regularly and monitor your blood pressure levels.
Cerebral vasculitis
The disease is non-infectious in nature and manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the blood vessels. This causes their narrowing and the development of coronary disease. The exact cause of vasculitis is unknown, and it can occur at any age. Manifested by severe headaches, leg cramps, hearing or visual impairment. In the early stages of development, vasculitis can be confused with neoplastic diseases. It progresses quickly, and it is very difficult to cope with it, largely due to the difficulties in diagnosis. A biopsy can accurately determine the presence of this disease, but its implementation is most often impossible due to the threat of hemorrhage.
The causes of cerebral ischemia include pathologies and vascular anomalies, rheumatism, but they are of secondary importance. Patients with diabetes mellitus, the elderly are at risk. Smoking provokes the formation of plaques in the blood vessels, since cigarette smoke contains carbon monoxide and nicotine. Tachycardia, bradycardia, acute heart failure, increased blood viscosity caused by erythrocytosis or anemia – all this also contributes to the development of cerebral ischemia in adults.
Degrees of cerebral ischemia

Cerebral ischemia 1 degree
At this stage, the symptoms of the disease are mild. The patient suffers from headaches, heaviness in the head, gets tired quickly and experiences general weakness. Sleep is disturbed, problems with hearing, vision and memory are possible. Disorders are stable, but the formation of syndromes does not yet occur. This allows you to reduce the manifestation of symptoms or eliminate them altogether, as well as the disease as a whole. The changes relate to the psychological state of the patient: emotional lability is possible, that is, a quick change in mood without any reason.
Cerebral ischemia 2 degree
Asthenic symptoms are less common. Stage 2 cerebral ischemia is characterized by loss of memory and disability. The patient experiences constant weakness, dizziness, may experience difficulty in performing the simplest movements, for example, when walking. There are problems with vision, reflexes of oral automatism, convulsions are disturbed. The duration of the periods during which violations appear increases.
Pathological reflexes are reflected in intellectual-mnestic disorders. This means that mental work for the patient becomes impossible. As with cerebral ischemia of the 1st degree, the patient experiences psychological difficulties, emotional lability progresses.
Cerebral ischemia 3 degree
At this stage, there is an organic lesion of the brain. Patients often faint, are unable to perform simple actions on their own, and therefore need help. Circulatory disturbance manifests itself in the form of “small strokes” or a progressive “finished stroke”. At 3 degrees of cerebral ischemia, dementia, that is, dementia, is possible.
Patients have reduced cognitive ability, they can no longer carry out full-fledged intellectual activity. In addition, patients experience memory problems. This causes a sharp decline in their quality of life and social adaptation. Violation of gnosis and praxis, which are one of the main functions of the brain, leads to the inability to navigate in space, recognize familiar objects and perform complex motor acts.
Cerebral ischemia in newborns
Congenital cerebral ischemia in children develops due to hypoxia during childbirth or pregnancy. The risk of oxygen deficiency increases in proportion to the age of the mother. In young girls, the risk of cerebral ischemia in children is slightly lower than in women after 30.
However, this factor is not decisive. An important role is played by the presence of various diseases in the mother, for example, diabetes, taking various medications during pregnancy. The competent work of doctors during childbirth, when there is a danger of lack of oxygen, allows preventing the development of cerebral ischemia.
According to the degree of the disease, various symptoms are distinguished. In the early stages, cerebral ischemia manifests itself in the form of increased oppression or arousal of the child. Grade 1, which is considered the mildest, is diagnosed most often. As a rule, the disease disappears some time after birth. Cerebral ischemia of the 2nd degree is characterized by more serious brain damage.
The reason for contacting a neurologist may also be loss of appetite, frequent mood swings. The child has dystonia, impaired psychomotor and speech development, motor activity. For example, when walking, he can stand on his toes. At stage 3 of cerebral ischemia, hospitalization of a small patient is necessary.
Treatment of ischemia in newborns
Cerebral ischemia of the 1st degree in children is treated with medication and with the help of massage. Often the use of drugs is not required. The main task at this stage is to restore blood circulation and provide conditions for the normal functioning of healthy parts of the brain.
At stages 2 and 3 of cerebral ischemia, treatment is carried out with the help of vasodilators. They are necessary to improve blood circulation and restore the normal supply of oxygen to the brain. Nooropnye drugs stimulate brain activity, and vitamins have a strengthening effect on the entire body.
Timely treatment of cerebral ischemia in children can avoid many complications. The disease can cause headaches and irritability. The child has problems with sleep, is often naughty. Children with cerebral ischemia are incapable of normal learning, are silent, suffer from distracted attention, and cannot concentrate on something for a long time.
Initial symptoms develop into epilepsy and mental retardation. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose the disease during the first months of a child’s life. A mild form of cerebral ischemia is effectively treated in a short time. In most cases, by the time of discharge from the hospital, the child is no different from other babies.
Massage, which is necessary to combat cerebral ischemia, helps to relax the nervous system, has a positive effect on muscles and the general condition of the body. It should be carried out by a doctor, since careless movements can not only not bring benefits, but also harm the health of the child. During the first year of life, it is recommended to have at least 4 sessions, with a break between them of several months.









