Contents
What is cerebral edema
Cerebral edema is not an independent process. It occurs due to certain diseases, brain tumors, stroke, toxic damage to the brain, infectious diseases.
With cerebral edema, a large amount of fluid accumulates in the intercellular space and brain cells. As a rule, a person in this state is unconscious and on a ventilator.
Edema is of several types:
- vasogenic – occurs when the patient increases the permeability of cerebral vessels;
- osmotic – occurs due to an increase in the osmolarity of brain tissues;
- cytotoxic – brain cells “swell” due to the fact that the amount of fluid inside them increases;
- interstitial – occurs with increased pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
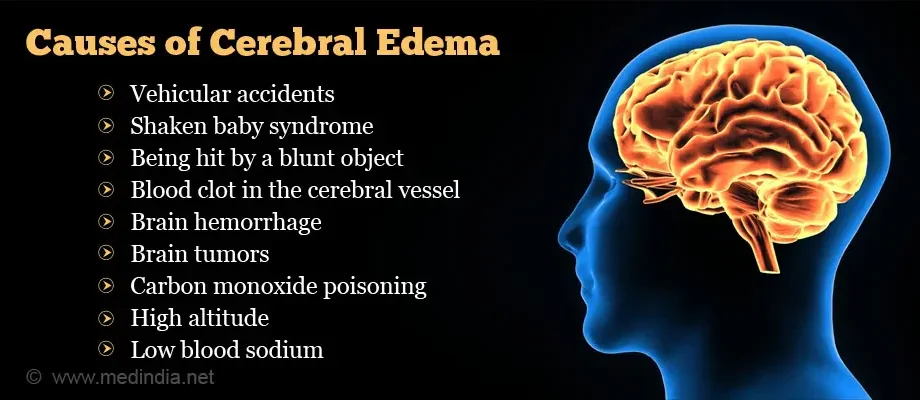
Causes of cerebral edema in adults
Neurosurgeon Pavel Trushin cites several causes of cerebral edema:
- a volumetric formation or tumor that compresses the brain and a perifocal reaction occurs around the tumor in the form of edema;
- toxic cerebral edema – as a result of the abuse of various drugs, alcohol;
- epileptic status – a condition when seizures occur one after another, and the patient does not regain consciousness in between them;
- ischemic injury – swelling of the brain after strokes.
Also, cerebral edema in adults can be caused by meningitis and encephalitis.
Symptoms of cerebral edema in adults
With a gradual increase in edema, the following symptoms appear:
- unbearable headache that does not go away;
- vomiting and nausea;
- prostration;
- deterioration of vision;
- breathing disorder;
- loss of consciousness.
Seizures can already be attributed to the symptoms of acute edema.
Treatment of cerebral edema in adults
– Edema is removed by the introduction of hormones – dexamethasone, which we actively use in neurosurgery. Also, a person is taken out of this state with the help of artificial ventilation of the lungs, the use of special preparations to protect the brain, – says neurosurgeon Pavel Trushin.
To remove excess fluid, doctors may prescribe a large dosage of diuretic drugs. If there are convulsions – anticonvulsants.
Note that a favorable outcome of cerebral edema is present only with the timely provision of medical care. You need to know that severe complications can develop due to cerebral edema. The swelling can also lead to death.
Diagnostics
A neurologist may suspect cerebral edema when the patient’s condition worsens. A CT scan or MRI will likely be needed to confirm the diagnosis of cerebral edema.
It is also possible to establish an accurate diagnosis by assessing the neurological status, according to general and biochemical blood tests. Cerebral edema is an emergency condition, so diagnosis should be carried out immediately and only in a hospital setting.
Modern treatments
During treatment, doctors need to restore oxygen metabolism in the human brain, therefore, both surgical and medical methods are combined. It all depends on the case and the condition of the patient.
Cerebral edema is mainly due to some underlying disease, so doctors use surgery in this case too. For example, swelling was caused by a brain tumor or traumatic brain injury.
There is also symptomatic therapy. With the help of it, convulsions, pain, vomiting are eliminated.
After the patient’s condition has become stable, etiotropic therapy occurs.
Prevention of cerebral edema in adults at home
As such, the prevention of cerebral edema does not exist, because it occurs due to other diseases. However, those pathologies that can lead to this condition should be prevented. It is necessary to diagnose diseases in a timely manner and treat them when detected in order to avoid undesirable outcomes.
Popular questions and answers
Answered popular questions about cerebral edema neurosurgeon of the highest category, Ph.D. Pavel Trushin.