Contents
Among the cosmetic procedures aimed at maintaining the beauty of the body and creating an ideal figure, anti-cellulite measures are very popular. Cellulite or “orange peel” is a common problem among women. To solve it, there are many ways, including special cosmetics, vacuum massage, ultrasound treatment procedures and electrical stimulation of tissues.
What is cellulite?
Cellulite is an inflammatory disease of the subcutaneous adipose tissue. The everyday meaning of this word implies a cosmetic defect associated with the deposition of fat in the form of tubercles under the skin, which makes its surface embossed, violating the aesthetic appeal. What is called cellulite in women’s glossy magazines and beauty salon brochures has the scientific name “gynoid lipodystrophy”. However, the term “cellulite” has taken root in this sense so much that for ease of perception in our article it will be used in the generally accepted sense.
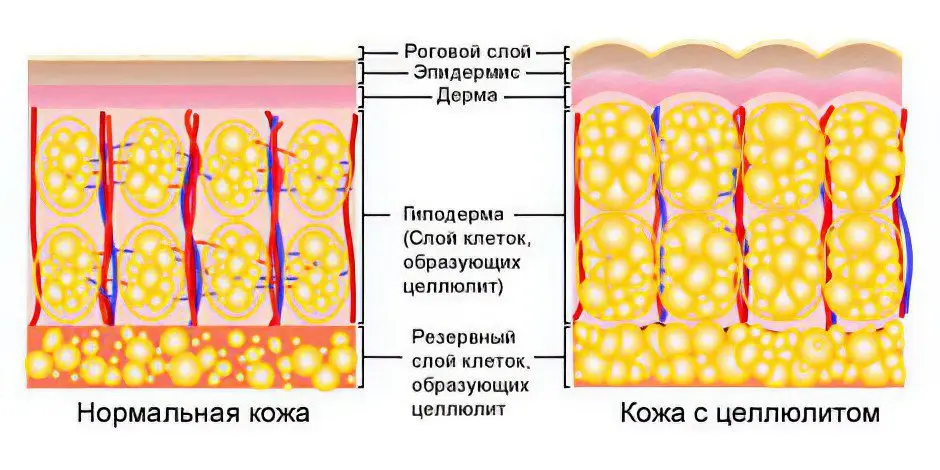
Another name for the defect – “orange peel” – is common due to the fact that as a result of a violation of fat metabolism and the formation of edema, the skin acquires an uneven surface and feels like a citrus peel to the touch.
An important role in the development of cellulite is played by estrogen – a group of female sex hormones, which are present in small quantities in men. However, in a healthy woman, the concentration of estrogen is several times higher than in a healthy man, so cellulite is considered an exclusively female problem. Cellulite is found only in women also because of the specific structure of their fatty tissue.
The mechanism of development of gynoid lipodystrophy begins with uneven accumulation of fat in adipocytes. Adipocytes are fat cells that all people have, even very thin girls, so it cannot be said that cellulite is a problem associated exclusively with obesity, although this is a common belief.
In violation of fat metabolism, adipocytes increase unevenly under the influence of excess fat, pathological changes affect nearby cells – fibroblasts. Fibroblasts synthesize collagen fibers, the purpose of which is to delimit areas of connective tissue. With gynoid lipodystrophy, collagen bridges compress the enlarged fat lobules, resulting in the formation of dense capsules, protrusions into the dermis appear, which visually manifests itself in the unevenness, tuberosity of the skin relief.
This is not all the consequences of the pathological process – due to constant compression, blood supply and lymphatic drainage of tissues are disturbed, which leads to the formation of edema. With the progression of gynoid lipodystrophy, nerve endings are pinched, which can cause pain in areas of the body covered with cellulite.
Causes of cellulite

The causes of cellulite are varied, they are made up of many factors, and if you have several of them, then you are at risk. You should take preventive measures, but about them later.
Predisposing factors for cellulite:
Gender, race and heredity play an important role in the pathogenesis of gynoid lipodystrophy. Thus, Caucasian women are more prone to cellulite than blacks and Asians. The probability of manifestation of this defect in white women is much greater due to the specific structure of the subcutaneous adipose tissue and hormonal predisposition. If cellulite is a common problem in a girl’s family, it is observed in her mother, grandmother and other blood relatives, it is likely that she herself will have this problem with age;
Hormonal imbalances create the prerequisites for the formation of cellulite, therefore, when treating it, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist. Hormonal disorders may be associated with the use of oral contraceptives, the functional state of the thyroid and pancreas, ovaries and adrenal cortex. Age peaks in hormonal status – adolescence, pregnancy, menopause – can provoke gynoid lipodystrophy with manifestations in the form of “orange peel” on the thighs and buttocks. So, due to disruption of the endocrine glands, the balance of fat metabolism can shift towards lipogenesis with reduced lipolysis. Excess fats will accumulate in adipocytes, which is where gynoid lipodystrophy begins;
Vascular pathologies, circulatory and lymphatic disorders, as a result of which toxins accumulate in the hypodermis, and metabolism slows down;
Obesity, sedentary lifestyle also lead to the accumulation of excess fat in adipocytes;
Bad habits, in particular smoking, suppress the processes of lipolysis (fat breakdown).
Stress, lack of sleep lead to a slowdown in metabolism, vasospasm, which leads to circulatory disorders and the accumulation of excess fluid in the form of edema. With chronic stress, the work of the endocrine system can be disrupted, which is also a factor predisposing to the development of cellulite. See also: symptoms and causes of stress;
Unfavorable environmental situation – with an abundance of toxins in the air and water, the body is constantly under stress, forced to bring them out. With chronic exposure, negative environmental factors can provoke hormonal imbalance, lipid metabolism disorders, and all this creates prerequisites for gynoid lipodystrophy;
Sudden weight loss or weight gain. In the first case, the loss of kilograms can occur due to proteins, not fat, as often happens with strict diets. The lack of protein leads to thinning of the collagen fibers that make up the connective tissue bridges. Rapid weight gain turns into excessive accumulation of fat in problem areas, creating the preconditions for the appearance of cellulite;
Unbalanced Diet – with a lack of natural proteins and polyunsaturated fatty acids, tissue metabolism and the synthesis of connective tissue bridges can be disturbed. It is important to monitor the amount of fiber in the diet – it contributes to the timely removal of toxins and speeds up the metabolism. The abundance of products such as carbonated drinks, sweets, flour, fast food and convenience foods leads to the formation of excess subcutaneous fat.
Features of the anatomical zones predisposed to cellulite in women
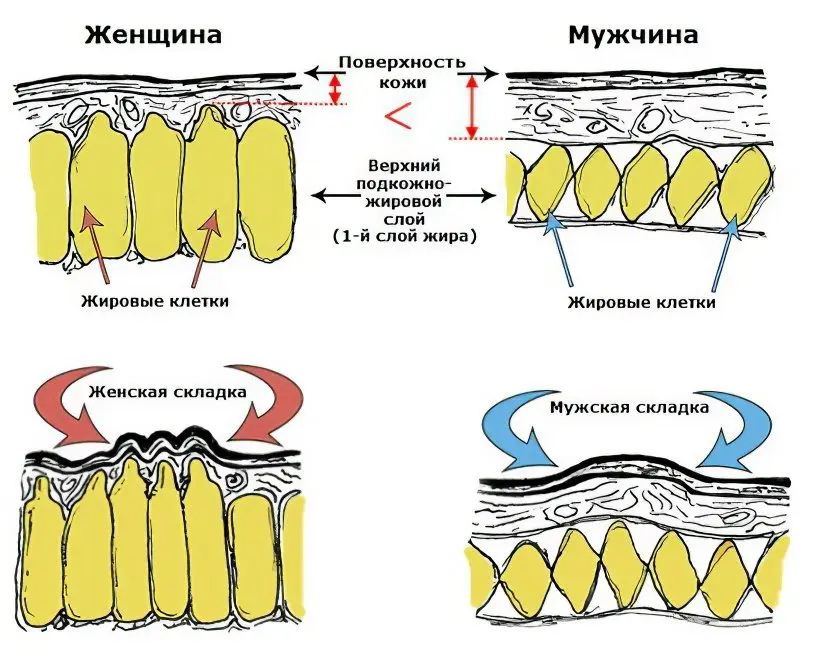
genetic aspect. Men and women from the beginning of the action of puberty hormones are differently prone to fullness. If in men fat deposits are concentrated in the upper part of the body and form a “beer belly” with an excessive amount, then in women fat is deposited on the hips, buttocks and lower abdomen. Such a distribution is necessary for the normal course of pregnancy, but is always observed, even in nulliparous women.
The structure and location of connective tissue partitions. The epidermis and dermis are the layers that make up the skin. In men, they are thicker, while the fat layer, on the contrary, is thinner than in women. Another difference lies in the structure of the connective tissue bridges – these partitions are made of protein and are woven into the dermis on one side, and attached to the muscle fascia on the other in such a way that a structure of cells is formed, inside which there are fat cells. There are differences both in the method of attachment (diagonally in women and at right angles to the skin in men) and in the number of septa. In men, there are more of them, and the fat lobules themselves are usually smaller, so that their growth is constrained by connective tissue structures. In addition, there are more collagen and elastin fibers in the skin itself, so that even with significantly enlarged adipocytes, the skin does not look uneven from the outside, so cellulite as a cosmetic defect does not bother men to the same extent as women. In women, the structure of the skin and connective tissue may vary depending on heredity, age, hormonal status and the presence of diseases. So, with connective tissue dysplasia, the skin loses elasticity and tone, can sag and cannot withstand stretching – striae appear on it. It is clear that with such a disease in a thin woman, cellulite can appear with the same success as in an obese woman. Otherwise, it is difficult to determine “by eye” who is more likely to have cellulite, since a lot depends on the state of metabolism and the current hormonal status.
Structure and function of fat cells. Gynoid lipodystrophy develops due to an imbalance in the processes of lipogenesis and lipolysis. That is, much more fat is formed than is burned, the permeability of the adipocyte membrane is disrupted, as a result of which fat accumulates inside the cell, but even changes in the diet and regular physical activity cannot remove the “orange peel” at this stage, although they bring significant improvements. with excess weight. Alpha and beta receptors are present on the surface of adipocytes. The former are necessary for the processes of lipogenesis, and the latter are involved in the processes of fat breakdown. In women, the number of alpha receptors is six times greater than in men, which is why cellulite occurs only among the fair sex. Due to the fact that such a ratio of receptors mainly concerns the thighs, buttocks and abdomen, weight loss in other areas during intense physical exertion occurs at a normal rate. But in these parts of the body, fat is formed most actively and breaks down very slowly, which creates the conditions for the appearance of cellulite.
Hormones that affect the processes of lipogenesis and lipolysis
The mechanism of lipogenesis consists in the penetration of fatty acids, glucose and glycerol into the adipocyte cell, where triglycerides are synthesized from them. During lipolysis, fatty acids and glycerol, on the contrary, are removed from the cell. If the balance of these processes is not observed, fats accumulate inside the cell, due to which it increases in size.
What is the role of hormones in the regulation of lipogenesis and lipolysis? First of all, insulin (a hormone produced in the pancreas) is involved in lipid metabolism, it starts a chain of reactions, as a result of which lipogenesis increases and lipolysis stops.
Elevated blood glucose leads to an increase in insulin concentration, so that lipolysis slows down, and a large amount of fat is formed in adipocytes. The level of glucose in the blood can increase with certain diseases (for example, with diabetes), as well as with the constant use of flour and sweet, the so-called “fast” carbohydrates.
Another group of hormones involved in lipid metabolism is the catecholamines. They are produced in the adrenal cortex, and when bound to adipocyte receptors, they can activate both the processes of lipolysis and lipogenesis. It depends on the type of receptors with which catecholamines interact – when bound to alpha receptors, the processes of production and accumulation of fats are activated, when bound to beta receptors, respectively, the breakdown and excretion of fats are stimulated. However, this group of hormones has a high affinity for alpha receptors, so it binds to them willingly and spontaneously. That is, while alpha receptors are free, catecholamines will interact with them, and only then with beta receptors, activating the processes of lipolysis.
In practice, this means that if the hormones of this group are not enough, then the processes of lipolysis will occur very slowly, since all catecholamines are occupied by alpha receptors. The content of these hormones in the blood increases during physical exertion, with short-term stress, exposure to cold, hypertonicity of the sympathetic nervous system.
The process of losing weight does not correlate well with the state of cellulite fat deposits, since the ratio of alpha and beta receptors in different parts of the body is not the same. For example, with increased physical activity and a balanced diet, you can lose 7 kilograms, while weight loss will occur mainly due to those areas where there are fewer alpha receptors. And if we take into account that beta-adrenergic receptors are the least in relation to alpha receptors in the areas of the “breeches zone” and the lower abdomen, then splitting will affect these parts of the body the least. But it is there that cellulite forms most actively.
Glucocorticoids are another group of hormones produced by the adrenal glands that increase blood glucose levels. In addition, they can change the number of active alpha and beta receptors in favor of the former. As a result, the processes of lipogenesis are enhanced, which leads to the formation of cellulite deposits. Chronic stress, insomnia and overwork also increase the concentration of these hormones in the blood.
Glucagon is a pancreatic hormone that can bind to receptors on the surface of adipocytes and trigger lipolysis. An increased concentration of this hormone is observed with low blood sugar levels, during sports training and carbohydrate-free diets.
Other hormones involved in lipid metabolism, in particular those promoting increased lipolysis: thyroid hormone; male sex hormone testosterone; growth hormones produced by the pituitary gland; adrenocorticotropic hormone.
The connection between hormones and adipocytes is so close that the enzymes of fat cells affect the concentration of hormones of a certain group in the blood. So, adipocytes contain a special enzyme called aromatase P450, which stimulates the conversion of testosterone (male sex hormone) into estradiol (female sex hormone of the estrogen group).
Thus, even in men with an excess of adipose tissue, the level of female hormones rises (normally, a small amount of estrogen is present in men), and female-type obesity occurs, respectively, there is a likelihood of developing cellulite, but this cosmetic defect will still not be so noticeable, like women. See also: obesity – degrees and causes.
cellulite stages
Classification of cellulite by stages
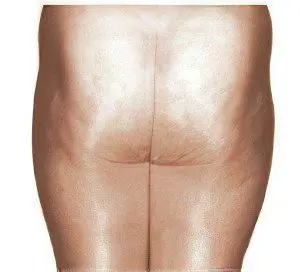
1 stage cellulite | The skin is even, but there is mild swelling. Injuries (abrasions, hematomas, burns) in the problem area regenerate more slowly than in other parts of the body. The layer of subcutaneous fat is soft on palpation. These manifestations indicate a violation of blood circulation in the capillary network, stagnation of lymph and fluid in the cell matrix. The transformation of the first stage into the second occurs when cellulite prevention is not observed. |
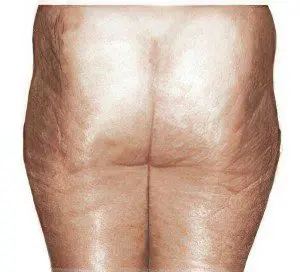
2 stage cellulite | The tuberosity of the skin becomes noticeable if you collect it in a fold, swelling increases. When probing, the subcutaneous fat layer becomes harder in comparison with the state at the first stage, the unevenness of the skin relief is slightly noticeable even in a calm state. These phenomena are associated with stagnation of the lymph, the venous circulatory system can not cope with the removal of excess fluid. If appropriate measures are not taken at the second stage, pathological changes affect the connective tissue septa and the lobular structure of fatty deposits, which provokes the third stage of cellulite. |
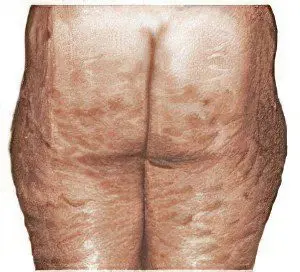
3rd stage of cellulite (lobulated) | At this stage, irregularities in the form of an “orange peel” are distinguishable in a calm state, and if the skin is slightly pulled up, the relief of its surface becomes bumpy: fibrous formations are located in place of the pits under the skin, and fatty deposits are located in place of the tubercles. The venous system in problem areas cannot cope with the task, which leads to the formation of edema, circulatory disorders, spontaneous hematomas, and delayed skin regeneration after damage. The skin in this area is pale and dry, cold to the touch due to problems with microcirculation. Another important symptom of the third stage of gynoid lipodystrophy is dense nodes under the skin, which are found on palpation. The formation of hematomas is associated with a violation of the permeability of blood vessels, due to which blood penetrates into the tissues. The connective tissue grows, forming a mesh with cells, sclerosed and thickened, which externally manifests itself as bumps and pits on the skin. |
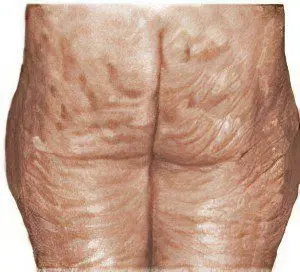
Stage 4 cellulite (nadular) | At this stage of cellulite, the tuberosity of the skin is pronounced even in a calm state without muscle tension, when you try to fold the skin into a fold, painful uncomfortable sensations appear, a venous network is visible through the skin. When probing, large nodular formations are distinguishable. At the final stage, not only connective tissue septa are sclerosed, but also fat cells. Pain may appear in the area of cellulite localization, because sclerosed formations compress the nerves. Another name for the fourth stage of cellulite (macronodular stage) is given by the name of its main symptom – the formation of a large macronodule from many micronodules. |
In some cases, two more stages of cellulite are distinguished – the fifth and sixth, they do not differ in external and internal manifestations from the fourth, but pathological changes in this case extend to atypical areas of the body and occupy a large area.
Classification of cellulite by clinical varieties
The clinical form of cellulitis has two varieties – plaque and nodular cellulitis:
With nodular cellulitis, many nodes form under the skin, which can be soft or hard when probing;
Plaque cellulitis differs from nodular cellulitis in that multiple nodules and lumpy formations merge to form chronic cellulite foci, the appearance of the skin is uneven, and there is a depression in the center of such a focus.
Classification of cellulite according to skin characteristics
hard cellulite often occurs in women who play sports and lead an active lifestyle. The defect is characterized by the presence of dense small formations under the skin, solid when palpated, not changing their position when the skin is stretched. Hard cellulite can be detected only by pressing on the skin; in the normal state, the “orange peel” is not visible. As concomitant symptoms, striae, varicose veins and other vascular pathologies may appear. With the progression of the disease after a few years, it passes into another form – flaccid cellulite;
Flaccid cellulite also called soft, since the affected areas of the skin are soft to the touch, shake and change their position when moving. This form of cellulite is also characterized by vascular pathologies – varicose veins, telangiectasias. Often found among women of the older age group, losing weight dramatically due to illness or due to a strict diet, leading a sedentary lifestyle;
Edematous cellulitis. The main symptom of this form of pathology is a sharp increase in the lower extremities with signs of cellulite in volume due to the accumulation of excess fluid. If you press the skin, an indentation forms on the spot, while the skin is pale, the vessels are translucent;
Mixed cellulite – this form of gynoid lipodystrophy is most common. The defect manifests itself in different parts of the body and, depending on the position, can proceed in a solid, flaccid or edematous form.
Cellulite diagnostics

Methods for diagnosing cellulite:
Anthropometric data. To assess the predisposition to cellulite, data on height, mass index, body volume are needed. External examination allows you to detect the localization of fat deposits and the thickness of fatty tissue. This type of diagnosis is more often used to determine obesity and its degree, and thin women can also have cellulite, so this method is usually not enough;
Bioelectrical impedance measurement. Electrodes are placed on the body and, according to the current resistance, the ratio of fat and water is determined in areas most prone to cellulite. The method is based on the physical properties of various tissues and structures of the body – water conducts electricity better than fat, therefore, according to the data from the devices about the area studied, conclusions can be drawn about its structure and the amount of body fat;
Anode thermography. The cellulite stage is assessed on the basis of the data of the anode, which transmits a signal on the skin temperature to the screen. The fact is that with gynoid lipodystrophy, skin areas with cellulite in the later stages differ in temperature, which looks like black holes on the screen. This is a fairly accurate and informative diagnostic method, but its drawbacks are in the nuances of application. So, it is necessary to create a calm environment in which the patient will not be nervous, as well as normal conditions for the operation of the sensor – constant temperature, humidity and lighting. Changes in the body associated with the menstrual cycle, fever and smoking can distort the data and make the study unreliable;
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance scanning more often used to assess the degree of obesity, but in the diagnosis of cellulite can also be used. Using these methods, it is possible to determine the thickness of adipose tissue, but they do not provide information about microcirculation in the superficial vessels and skin tissues;
Doppler ultrasound unlike the methods described above, it allows you to determine the state of microcirculation in the subcutaneous adipose tissue, to assess the state of blood vessels in the area under study, which makes the procedure very informative in terms of diagnosing cellulite;
Xerography. This method of X-ray examination allows you to assess the location and thickness of the layer of skin, adipose tissue and muscles, while it does not provide data on microcirculation and the state of blood vessels. Another drawback is the need to expose the body to radiation;
XNUMXD echography. One of the most informative methods for diagnosing cellulite is carried out using wave radiation with a frequency of 7,5-10 MHz and higher. Allows you to determine the number of nodular formations and their size, the state of nearby tissues, the presence and location of edema and microcirculation disorders;
Histological examination. It requires a tissue sample taken at a depth of 4 mm under the skin. The sample is stained with different dyes, according to the purpose of the study. For the analysis of polysaccharides, alcian blue is needed, the study of collagen and muscle fibers is carried out using fucorcin. Despite the fact that this is the most informative diagnostic method, it is not used so often due to the need to violate the integrity of the skin for sampling.
Cellulite treatment methods
It is quite difficult to completely get rid of this defect, a complex of therapeutic measures is needed, including massage and cosmetic procedures, products for external and internal use. But even after the “orange peel” disappears, it will be necessary to follow the rules of cellulite prevention, otherwise it will appear again.
Getting rid of cellulite is not an easy task, it is best not to wait for the appearance of a bright cosmetic defect, but to start preventive measures in advance. If it manifests itself, then you should contact a cosmetologist who will develop an individual cellulite correction program for you. It should include various hardware cosmetic procedures.
Ways to fight cellulite
Among the various approaches to solving the problem of cellulite, the following categories can be distinguished:
Pharmaceuticals acting from within.
Medicines for external use.
Physiotherapy.
Operative (surgical) intervention.
Cellulite prevention.
Modern methods of cellulite treatment are as follows:
Activation of beta receptors, launching and accelerating the breakdown of existing fats;
Inhibition of the work of alpha receptors, inhibition of the synthesis and deposition of new fats;
Formation of the outflow of lymph and metabolic products from tissues;
Acceleration of blood flow in the capillaries of the skin, healing of blood vessels;
Destruction of capsules in which fat is deposited, a decrease in the density of fibrous fibers in the deep layers of the skin;
Activation of muscle contractions;
Rejuvenation of the skin, increasing its elasticity.
Preparations for cellulite internal action
Active substances and trace elements acting at the molecular level: retinol, tocopherol, ascorbic, nicotinic and lipoic acids, coenzyme Q10, carotenoids, a complex under the outdated name “vitamin F” (linolenic, linoleic, oleic and arachidonic acids);
Seaweeds are natural iodine-containing lipolytics that also help maintain salt balance. First of all, we mean kelp and fucus;
Various products containing natural flavonoids:
Accelerators of blood flow in the capillaries of the skin (extracts from grape seeds, hawthorn berries).
Skin health products (horse chestnut extract, evening primrose oil).
Digestive stimulants (turmeric or rosemary).
Substances that promote the excretion of fluid (extracts of horsetail and dandelion).
Antioxidants and detoxifying products (activated charcoal, mate and Eubicor teas, ginger, fiber).
Pharmaceutical preparations against cellulite: Detralex, Ascorutin, Venorutin and Rutin, Troxevasin. They can be prescribed by a doctor according to indications.
External preparations

From the side of the skin, not every remedy can affect cellulite. Basically, these are cosmetic, not medical products, so topical preparations play an auxiliary role in the treatment of cellulite.
Various oils of vegetable origin used in cupping massage: sage, primrose, shea, wheat germ and others;
Essential anti-cellulite oils of citrus and coniferous plants, bergamot, chamomile, etc. When mixing oils, one must adhere to the principle of similarity: wood only with wood, citrus with citrus, flower with flower;
Extracts that stimulate the outflow of fluid: grapefruit, ivy, arnica, horsetail, cowberry, lotus;
Substances with lipolytic properties: capsaicin, menthol, caffeine, mate tea, guarana and gotu kola extracts;
Mud and algae preparations used for lotions and wraps. Produce the effect of tightening, nourishing and improving skin elasticity;
Honey in the fight against cellulite most clearly shows healing properties with manual massage: removing fluid, toxins and metabolic products, healing and nourishing the skin, as well as reducing the amount of fat.
Methods of physical influence
Consider the various procedures aimed at the treatment of cellulite:
Cellulite massage. Several types of anti-cellulite massage have been developed:
Manual – has a lymphatic drainage effect, has a positive effect on blood flow and is able to soften fatty deposits;
Vacuum – improves blood circulation and stimulates the excretion of fluid due to the creation of pressure drops;
Cupping – performs enhanced lymphatic drainage of problem areas of the body. Can be static when cups stay in one place, or kinetic when cups are moved across the skin;
Vibrovacuum – is an analogue of cupping massage, performed by a special apparatus. As a result, edema is removed and the rate of metabolic processes increases;
Pressotherapy – massage with the use of a device that puts pressure on problem areas, with the help of which they achieve the activation of metabolic processes, the removal of metabolic products and excess fluid, the stimulation of the breakdown of adipocytes and the improvement of the vascular system.
Electromyostimulation for cellulite. The essence of the procedure is to stimulate muscle contractions in areas with cellulite. This accelerates blood flow and nutrition of the skin, tones the blood vessels and promotes lymph outflow. Electromyostimulation is used only as an aid in the complex therapy of cellulite.
Microcurrent therapy or microcurrents for cellulite. This procedure is necessary to stimulate biochemical reactions in epithelial cells. Microcurrents of scanty strength (40-1000 μA) and frequencies of 0,1-500 Hz penetrate shallowly and act weakly, but with prolonged exposure they can stimulate recovery processes, lymph outflow and local immunity. It is used in the complex treatment of cellulite as an auxiliary procedure.
Electrolipolysis for cellulite. The procedure acts on fat cells. With the help of electricity, lipolysis is started, triglycerides are broken down and excreted. There are two varieties of this method – needle and electrode electrolipolysis. The procedure gives the best results in combination with lymphatic drainage massage, so excess fluid and metabolites are excreted faster.
Ultrasound or cavitation for cellulite. Ultrasound destroys fibrous formations around fat cells, normalizes lymph outflow and blood circulation in problem areas. This is the only method that acts directly on adipocytes, destroying the fibrous scaffold and releasing triglycerides from fat cells. Despite the high efficiency, it is used with caution, as it has many contraindications, they are basically the same as for other ultrasound procedures.
RF-therapy (radiofrequency therapy) for cellulite. During the procedure, the skin is heated, high-frequency electrical impulses pass through it, as a result, the processes of lipolysis, tissue regeneration, and the synthesis of new collagen fibers are stimulated. The method has two directions – thermolifting and lipolysis. Thermal lifting occurs with skin heating, as a result, excess fluid is removed, swelling is removed, and the synthesis of new collagen and elastin fibers is stimulated. After several thermal lifting procedures, the skin looks younger, becomes firmer and more elastic. Actually, RF-lipolysis leads to the destruction of the fibrous framework of fat cells, the removal of excess deposits of subcutaneous fat.
Mesodissolution and mesotherapy for cellulite. During mesotherapy, medicinal preparations are injected at a shallow depth under the skin, where they act locally on problem areas, facilitating lymph flow and removing edema, also strengthen blood vessels and improve microcirculation in tissues. The processes of tissue metabolism, the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers, the production of hyaluronic acid, which is necessary to moisturize the skin and maintain its turgor, are stimulated. Mesodissolution produces a destructive effect on fat cells, the procedure is used for local correction of cellulite and excess fat deposits on the face and other parts of the body.
Ozone therapy for cellulite. During ozone therapy, a mixture of ozone and oxygen is injected subcutaneously, which stimulates the processes of lipolysis, the destruction of the fibrin framework, and also improves blood circulation and tissue metabolism in the problem area.
Cryotherapy and cryolipolysis. Cryotherapy methods include all methods of exposure to the body or its parts with cold for medicinal purposes. It has a general tonic and strengthening effect on the immune, endocrine, nervous and cardiovascular systems. Cryolipolysis is a local temperature effect on areas with cellulite and excess fat deposits. Adipocytes at a temperature of -5 ° C go into energy starvation mode, which leads to apoptosis – programmed cell death.
Hydrotherapy or hydrotherapy. Among the procedures of this group are hydromassage, salt baths, hydrocolonotherapy, Charcot’s shower, contrast douches. They are aimed at stimulating tissue metabolism, improving lymph flow, have a general tonic effect, strengthening the immune system and improving the appearance of the skin.
Surgical methods
Surgical treatment of cellulite is carried out with the help of liposuction – this is an operation to remove excess fat deposits, helps to correct the contours of the body, also called lipoplasty. In addition to correcting the appearance of the skin, lipoplasty allows you to reduce the size of the body, bring it to the desired proportions.
It should be borne in mind that the operation cannot be performed on thin women, even with pronounced cellulite. In addition, given that liposuction is usually performed in the fourth and later stages of cellulite, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist. With a progressive pathology, there is a possibility of fat deposition in places atypical for cellulite and a relapse of the disease.
[Video] Dr. Berg – How to get rid of cellulite on thighs? Why does cellulite appear?