Contents
- What does a polyp in the uterus mean?
- Causes of cervical polyps
- Symptoms of a polyp in the uterus
- Why are polyps in the uterus dangerous?
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of cervical polyps
- Removal of a polyp in the uterus: types of operations, description
- Rehabilitation treatment after removal of polyps in the uterus
- What can not be done to a woman after surgery to remove polyps?
- Answers to popular questions: pregnancy, removal, menstruation
- Is it necessary to remove polyps in the uterus?
- Can a uterine polyp resolve on its own?
- Is it possible to get pregnant with a polyp in the uterus?
- Is it possible to give birth with a polyp in the uterus?
- Can the growth of polyps in the uterus lead to a miscarriage?
- Do uterine polyps affect the development of infertility?
- When can I get pregnant after removing a polyp in the uterus?
- Are polyps removed in the uterus without hospitalization?
- How long do you need to lie down after removal of a polyp in the uterus?
- When is sex possible after removal of a polyp in the uterus?
- Can a polyp come out with menstruation?
- Can a cervical polyp turn into cancer?
What does a polyp in the uterus mean?
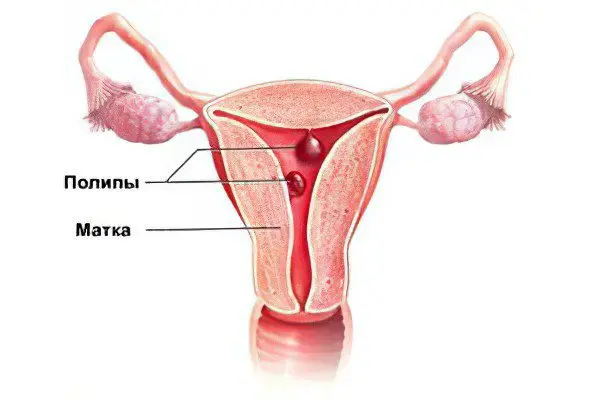
Polyps in the uterus are mushroom-shaped formations on a stalk in the lumen of the cervical canal of an organ, which occur due to the growth of epithelial tissues. The reason for this process may be malfunctions of the immune system, hormonal imbalances, excessive production of estrogen, as well as stressful conditions of the body.
Polyps account for approximately 25% of all diagnosed benign changes in the cervix, among which there are also papillomas, erosions, condylomas, erythro- and leukoplakia. Chronic infection, psycho-emotional stress, crisis periods of the reproductive system – puberty, pregnancy and childbirth, menopause can provoke their occurrence.
By themselves, polyps in the uterus are not dangerous, although they can cause serous discharge and pain. But in case of impaired immunity or hormonal failures, there is a risk of pathological degeneration of cells and the onset of a malignant process. Therefore, women with polyps in the uterus should be regularly examined by a gynecologist to monitor the condition of the neoplasms.
Causes of cervical polyps
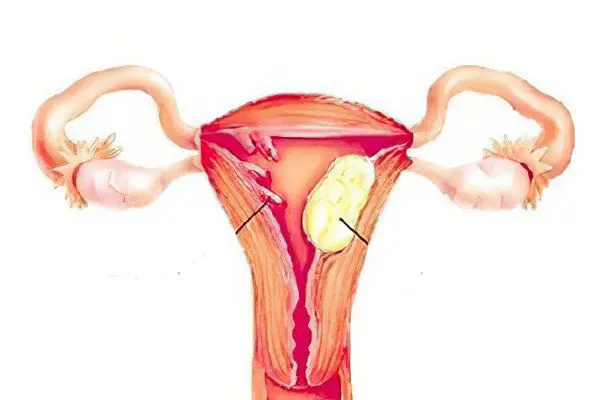
There is no single reason for the formation of polyps, the mechanism of endometrial growth can be triggered by a number of factors, including age-related changes associated with hormonal surges, gynecological diseases, systemic diseases, and hormonal regulation disorders.
Reasons for the development of polyps in the uterus:
Endometriosis, ovarian dysfunction, cyst, uterine fibroids and other gynecological diseases;
A period of age-related hormonal surges and declines – puberty or menopause with comorbidities such as chronic infections, diabetes mellitus or thyroid dysfunction;
Overwork and psycho-emotional overstrain, depression, stress;
Injury to the uterus during diagnostic manipulations, such as curettage or hysteroscopy;
Inflammatory processes of the uterine mucosa, endocervicitis;
Injury to the cervix during childbirth or during a surgical abortion;
Dysbacteriosis, thrush, chlamydia and infectious processes of the genital organs associated with inflammation.
Concomitant pathologies are erosion, ectopia, leukoplakia, cervicitis and atrophic colpitis. At least one health problem from this list is observed in 70% of cases of endometrial polyposis.
Do hormonal changes contribute to the formation of uterine polyps?
The mucous membrane of the uterus is very sensitive to hormonal changes, and in response to a violation of the hormonal balance, the endometrium may begin to thicken, certain groups of cells begin to divide uncontrollably, and polyposis occurs. In order for the surgical treatment of uterine polyps to be successful, the woman’s hormonal balance must first be restored.
Causes of hormonal imbalance:
Ovarian cysts and other tumor-like formations. An ovarian cyst prevents the release of an egg during ovulation, in response to this, the amount of estrogen produced in the body increases, which increases the risk of developing polyposis. In addition, ovarian tumors have cells that can themselves produce estrogen, creating additional prerequisites for endometrial hyperplasia;
Pathology of the pituitary gland. Gonadotropic hormone, which is produced in the pituitary gland, affects the synthesis of estrogen. If, as a result of a skull injury, tissue hypoxia, severe poisoning, or damage during brain surgery, the pituitary gland produces too much of this hormone, then estrogen is released in large quantities, which stimulates the formation of polyps in the uterus;
Adrenal dysfunction. The adrenal glands secrete hormones that regulate the vital activity of the whole organism, including those that affect the concentration of sex hormones in the blood;
The use of hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives. Means that affect the hormonal balance of the body should be prescribed by a doctor individually for each patient. The mechanism of action of oral contraceptives is based on the effect on the balance of estrogen and progesterone. If the dosage or individual reaction to the drug is violated, there may be a risk of adenomatous polyps, which are very dangerous because they can turn into malignant tumors in the process of malignancy.
At what age is the most likely to develop uterine polyps?
Since this disease of the uterus is directly related to hormonal changes in the body, the risk of polyps increases when a woman’s hormonal background is the least stable.
Three crisis periods are noted during which the hormonal background changes due to the restructuring of the organs of the reproductive system:
The period of puberty. Hormonal changes in the body during puberty can lead to increased production of estrogen, which is necessary to start the menstrual cycle. Estrogens can act on the endometrium, stimulating its division and the formation of polyps. But the young body has strong protective mechanisms that prevent pathological growths in the uterus, if there are no concomitant diseases – diabetes mellitus, infections of the genitourinary system, thyroid dysfunction, ovarian cysts;
Pregnancy and breastfeeding period. The hormonal background in pregnant women varies greatly, since the reproductive system must support the development of the fetus for all nine months. And then hormonal changes associated with lactation can cause the growth of these formations in the uterus, including placental polyps, which occur only in the postpartum period;
Menopause. Menopause is characterized by the extinction of ovarian function and a decrease in the concentration of sex hormones in the blood. The menopause period usually begins at the age of 45-50, and at this time, against the background of hormonal changes, the risk of developing neoplasms in the uterus may also increase. Hormonal drugs that women take to mitigate the negative manifestations of menopause can stimulate the growth of the endometrium, which also increases the likelihood of pathology.
Symptoms of a polyp in the uterus

Small growths and solitary polyps in the uterus usually do not manifest themselves as unpleasant symptoms, and often their detection occurs by chance during a routine examination.
Only mechanical damage to the polyp or infection can lead to noticeable symptoms:
Pathological discharge from the vagina;
Drawing pain in the lower abdomen;
Uterine bleeding not associated with menstruation.
In addition, it is possible to determine the presence of this disease by indirect symptoms – difficulty in conception up to infertility, a violation of the monthly cycle, which is often observed with cervical polyps.
When can polyps cause cervical cancer?
The process of malignancy consists of three stages:
Growth of the endometrium or hyperplasia, the formation of polyps;
The transformation of one type of epithelial cells into another, or metaplasia;
Dysplasia – characterized by the appearance of malignantly degenerate cells that can provoke an oncological disease.
The risk of degeneration of endometrial polyps into a malignant tumor is low, this is observed in only 1,5% of clinical cases, however, any neoplasm requires a thorough examination.
Polyposis can cause reflex irritation of the uterus, thereby increasing the risk of termination and complications of pregnancy.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for:
Scanty periods or brown discharge;
Bloody discharge in women during menopause, if menstruation has not been for several months or longer;
Difficulty conceiving in women of childbearing age;
Bloody discharge during or after intercourse;
Bloody discharge, not associated with menstruation, which can be caused by uterine bleeding.
Can cervical polyps be asymptomatic?
This pathology is characterized by an asymptomatic course, therefore it is possible to detect uterine polyps at an early stage only if they arose against the background of hormonal changes in the body, and an appropriate diagnosis was made.
In the following cases, the disease is asymptomatic:
Chronic infections of the genitourinary system. In this case, the formations grow slowly and do not have pronounced symptoms. Small polyps are also difficult to detect, since pathological signs appear only when the size reaches 1 cm;
Menopause. Since one of the symptoms of this condition is a violation of the menstrual cycle, it is difficult to detect neoplasms during the menopause without special diagnostics. Against the background of hormonal changes during menopause, the frequency of formation of polyps in the uterus increases, this is also facilitated by the lack of regular renewal of the endometrium during menstruation;
Fibrous polyps. The growths of connective tissue, which does not contain blood vessels, cannot cause uterine bleeding, and therefore often remain undiagnosed. At the same time, education can reach a significant size and develop over several years, without causing inconvenience and pain to a woman.
Surgical removal of endometrial polyps that do not show unpleasant symptoms is not necessary. But the patient must regularly undergo examinations to prevent malignant degeneration of the neoplasm. Hormonal agents used in non-surgical treatment can stimulate their growth and exacerbate the course of the disease.
Why are polyps in the uterus dangerous?
The danger of such formations in the uterus is primarily associated with their possible malignancy or malignant degeneration. Even polyps that have been growing for many years without showing negative symptoms can turn into cancer at any time.
What complications can occur in the absence of treatment of uterine polyps:
Violation of the normal course of pregnancy. In addition to the difficulty of conception that occurs if a large area of the endometrium is occupied by polyps, the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases, which leads to rupture of the fallopian tubes and serious pathologies. In later pregnancy, uterine growths can provoke placental abruption, which leads to spontaneous abortion;
Uterine bleeding. As the size of the polyp increases, blood vessels appear in it. In such vessels, the walls are characterized by increased permeability, which can lead to periodic bleeding. In this case, blood loss is usually small, blood accumulates in the uterine cavity or is mixed with urine in small portions, bleeding begins and ends spontaneously without outside interference. Sometimes it is possible to detect uterine bleeding only by the symptoms of anemia, which occur due to the loss of hemoglobin. These signs include a general decrease in immunity, pallor of the skin, drowsiness, fatigue, dry mouth. Bleeding that does not stop for a long time and requires the intervention of a doctor is most likely caused by malignant processes;
Difficulties in conception. A large number of such formations in the uterine cavity or one polyp, reaching a significant size, is a mechanical obstacle to the attachment of the embryo to the walls of the endometrium. Therefore, conception can be difficult;
Malignant transformation of cells. Malignancy most often occurs in adenomatous polyps. According to statistics, this process is observed in 1,5% of cases. Malignant degeneration of cells leads to the destruction of healthy tissues, profuse blood loss and growth of the neoplasm. Bleeding during malignancy of the polyp can even lead to the death of the patient. That is why with uterine polyps, even if they are asymptomatic, it is necessary to regularly undergo a diagnosis by a doctor who classifies the type of growth and prescribes a treatment regimen;
The emergence of a chronic focus of infection. Normally, there are protective factors on the uterine mucosa that prevent the development of infection. Polyps, on the other hand, are usually formed from connective tissue, which does not contain protective factors, and because of this is very vulnerable to pathogenic bacteria. Since a polyp without treatment can reach a large size, this increases the risk of a chronic focus of infection in the uterine cavity.
Diagnostics
To diagnose growths in the uterus, a number of tests are performed:
General and biochemical blood test. A complete blood count shows the number and shape of blood cells – erythrocytes, platelets and leukocytes, which determine the quality of blood and change under the influence of diseases. So, with a decrease in the number of red blood cells, we can talk about uterine bleeding, even if they are insignificant and invisible to the eye. An increase in the number of leukocytes – white blood cells – indicates the development of an infection in the body, including a genitourinary infection, which is a risk factor for the formation of polyps. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection and reduce the risk of new polyps. Platelets provide blood clotting, therefore, with a decrease in their number, the blood coagulates weakly, which contributes to bleeding;
Analysis of urine. The state of the liver and kidneys is examined, in the presence of blood in the urine, uterine bleeding can be diagnosed. (read also: urinalysis according to Nicheporenko);
Histology of polyp tissue helps to determine the type of overgrowth. The doctor takes a biopsy, takes a sample and traces its constituent cells, after which he can classify the tumor. If an adenomatous polyp is diagnosed, its surgical treatment is recommended in order to prevent malignant degeneration of cells;
bacteriological analysis. For its implementation, a swab is taken from the vagina and cervix and examined for the presence of pathogens. The analysis helps to identify chronic infections that lead to the formation of polyps, while this type of study is more effective than counting white blood cells. Together with bacteriological analysis, an antibiogram is carried out, determining the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to drugs;
Hormone analysis. The state of the endometrium is very dependent on the concentration of certain hormones in the blood. If polyps are found in the uterus, it is necessary to determine the cause of their occurrence, and it often lies in hormonal disorders. To determine the hormonal status of the patient at different times of the menstrual cycle, blood is taken for analysis, the amount of estrogen, progesterone, androgens, and gonadotropic hormone is determined. If the hormonal balance is disturbed, the doctor may prescribe drugs to correct it, which helps to remove the negative manifestations of endometrial polyposis and prevent neoplasms.
Methods for diagnosing cervical polyps
This disease is diagnosed by instrumental methods – ultrasound, colposcopy, hysteroscopy, metrography, CT and MRI. A thorough examination of neoplasms is necessary in order to correctly prescribe a treatment regimen and draw conclusions about the need for surgery. It is not enough just to detect uterine polyposis, it is necessary to classify polyps and determine how high the risk of malignancy is. Errors at the stage of diagnosis can lead to a malignant process and various pathologies of the reproductive system.
So, to determine the presence of polyps in the uterine cavity, use:
Ultrasonography. Ultrasound is performed in two ways – through the abdominal wall and transvaginally. The first method is used during the diagnosis of polyps in the organ cavity, and the introduction of a scanner into the vagina is necessary to detect cervical polyps. Ultrasound examination allows diagnosing polyps with a size of one centimeter, smaller neoplasms require special equipment. In addition to the presence of polyps and determining their type, ultrasound allows us to draw conclusions about the type, growth rate of neoplasms and the likelihood of malignancy. Thus, polyps that grow into the wall of the uterus are more prone to malignant transformation;
Colposcopy. The study of the cervical canal using a gynecological mirror allows you to determine the number of polyps, to examine the surface of large cervical neoplasms. Large growths can fall into the vagina, but their base is located in the cervical canal. Colposcopy allows you to explore the structure of these polyps in more detail, but it is possible to draw conclusions about the cause of their occurrence only after a histological analysis;
Hysteroscopy. During hysteroscopy, a fiberscope is inserted into the vagina – a long flexible tube with a camera located at the end, if an obstacle is encountered in its path, a polyp is diagnosed. The growths of the cervix close the lumen of the cervical canal, so it is quite easy to detect them. The study of the uterine mucosa using hysteroscopy methods allows you to accurately determine not only the presence of formations and their number, but also the place of attachment of the leg, inflammatory processes and the risk of malignancy. At the initial stage of malignant degeneration, the surface of the formation is uneven, has small nodes;
Hysterography – a less accurate method of research, a contrast agent is injected into the uterine cavity and cervical canal, after which an x-ray is taken. Dark areas in the picture indicate the presence of polyps, but the technique cannot provide information about their type and structure;
CT and MRI. These methods provide the most accurate data on the location of the polyp, the degree of its ingrowth and cell malignancy. Since these diagnostic procedures are expensive, they are usually prescribed in case of suspected oncology. Computed tomography allows you to determine the presence of metastases and their spread throughout the organs, which is necessary for the doctor to draw up an effective treatment regimen.
Additional methods for diagnosing uterine polyps
Other diagnostic procedures include:
Cytological study. A special apparatus collects fluid from the uterine cavity (aspirate) and examines the smear for the presence of pathologically degenerated cells. This method is not as accurate as a biopsy, so it is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods.
Biopsy of tissues for analysis – one of the most accurate ways to determine the type, structure and cause of polyps, the study of the material selected during the biopsy is carried out in the laboratory.
Tests for hormonal status – a necessary procedure, since in most cases the mechanism of the development of the disease is triggered precisely because of a violation of the hormonal balance. Based on the data obtained, the doctor can prescribe an individual drug treatment regimen.
Treatment of cervical polyps
If the diagnosed polyp has a low probability of malignant degeneration, then instead of removal, the doctor may recommend symptomatic treatment, which is aimed at eliminating unpleasant manifestations.
Symptomatic treatment helps prevent spotting and pain in the lower abdomen, which often cause inconvenience to patients.
If the pain does not subside after taking painkillers, then you should immediately consult a doctor, as surgical removal of the polyp is required. When it grows, its size can increase by more than 1 cm, it can cause severe pain and must be removed.
To prevent the development of infection, which can complicate the treatment process and contribute to the growth of polyps, it is necessary to observe the hygiene of the genital organs. Rinsing with weak solutions of antiseptics helps to prevent the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms and infection.
Is it possible to get rid of uterine polyps without surgery?
Drug treatment helps prevent new growths and remove the symptoms of already present neoplasms, but they do not affect the cause of the pain syndrome.
For this, hormone replacement therapy is used to help adjust the ratio of estrogen and progesterone. Drug treatment helps to solve the problem of infertility, bloody and mucous discharge, which are often observed with such formations in the uterus.
In addition, surgery is necessary if the risk of malignant degeneration is increased, as is the case with adenomatous polyps. In this case, drug treatment can only be used to prevent recurrence of the disease.
Removal of a polyp in the uterus: types of operations, description
The removal of such an education in most modern medical institutions is carried out using one of the most common methods – hysteroscopy. Hysteroscopy is a gentle operation with simultaneous examination of the uterine cavity and curettage of the cervical canal. Thanks to the possibilities of modern technologies, polypectomy and curettage are carried out quickly and without consequences, and the biological material obtained as a result of hysteroscopy undergoes a histological analysis, thanks to which the treatment carried out by doctors is corrected and improved.
There are different tactics for getting rid of endometrial polyposis, depending on several factors in the development of the disease: its cause, the presence of concomitant diseases of hormonal regulation, the distinguishing features of the endometrium, the size of the polyp planned for removal, the age of the patient.
As a result of the research, the following general rules are derived:
In the presence of fibrous polyps their removal is mandatory;
Polyp glandular-fibrous type suggests that hormonal changes occur in the course of the disease. This does not affect the form and purpose of the surgical intervention in any way, but in the postoperative period, hormonal therapy will be required to correct violations of the endocrine glands;
Detection of an adenomatous polyp, which often occurs in premenopausal women, is an indication for an operation to remove the uterus. Polyps that can provoke oncology are most guaranteed to be eliminated with the help of complex operations: extirpation of the uterus, supravaginal amputation with an accompanying revision of the ovaries, sometimes together with appendages.
Hysteroscopy – polyp removal
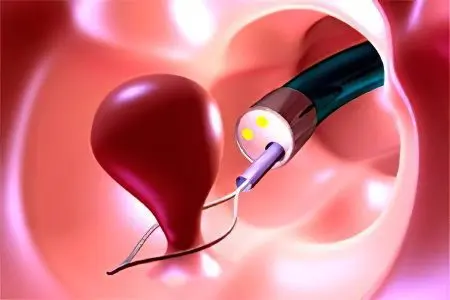
Only an experienced doctor is capable of performing hysteroscopy at a high level, so do not neglect the services of medical institutions using equipment based on modern high technologies. This significantly increases the reliability of the surgeon, on whose professionalism the health of the patient will depend.
Hysteroscopy is used not only to eliminate the formation itself, but also for an incidental study of the uterine cavity, which provokes a minimum of complications. Removal of a polyp using this method can hardly be called a surgical operation, since it takes place without internal intervention (violation of the integrity of the covering tissues). However, careful and accurate cutting of the pathological tissue with a special tool through a natural opening (in this case, the vagina and cervical canal) avoids any serious consequences that are typical for abdominal operations.
The whole procedure is carefully controlled by the surgeon, who controls the movement of the hysteroscope (a tube with a camera and a device for removing a polyp at the end) inserted into the cervix. Using a video camera, the uterine cavity is examined, and the pathological tissue is removed after assessing the polyps in terms of size, location, and number.
On the part of the patient, in order to improve the working conditions of the surgeon and, as a result, the results of the operation, one should adhere to the fasting regimen – this will help to avoid postoperative nausea. Also, hysteroscopy should be performed only after menstruation, on one of the first ten days of the cycle – this is necessary for better visualization of the organ under study.
Office hysteroscopy
This is a method of thorough diagnostics, which is carried out by a hysteroscope without instruments, which eliminates the need for anesthesia, that is, there is no injury. The technique gives the doctor the opportunity to conduct an examination of the uterus with the subsequent choice of therapy together with the patient. Minihysteroscopy, in addition to polyposis, allows you to diagnose fibromyoma, synechia, endometrial hyperplasia and other diseases of the female genital organs.
Diagnostic curettage
Curettage is one of the oldest operations performed on the uterus, but even now you can find medical facilities where it is performed due to the lack of educated staff and technical support for hysteroscopy. Diagnostic curettage can also be prescribed in addition to hysteroscopy to obtain endometrial samples, according to which, after histological analysis, it will be possible to say whether pathological cells remain in the tissues that can provoke a relapse.
Even after a successful hysteroscopy, 30% of patients return to the doctor to treat a recurrent polyp. This is due to the complexity of the treatment of the bed (laser, cryogenic coagulation), as well as the possible trauma of the operation itself. What can we say about curettage, during which the surgeon has to blindly remove the neoplasm and its leg.
But in some cases, such an operation is due to urgent indications, such as severe uterine bleeding. Curettage helps prevent blood loss that occurs against the background of endometrial hyperplasia. In this case, bleeding usually appears unexpectedly, and requires urgent assistance. Thus, in modern medicine, diagnostic curettage is assigned the role of an operation to preserve hemostasis, and not a method for removing uterine polyps.
Curettage is performed using a cervical dilator, which keeps it in this position all the time while the surgeon works with a special curette (metal loop). With this tool, excess tissues with polyps are scraped off the walls of the uterus and cervical canal, which become samples for laboratory analysis.
Removal of polyps in the uterus with a laser
The most modern way to remove polyps from the cervix is laser burning. Its advantage lies in the unprecedented accuracy of high-tech equipment, which allows to reduce the trauma of the operation to get rid of polyps to almost zero. Targeted destruction of pathological tissues with a laser is carried out quickly and without scarring, and with full preservation of the possibility of fertilization, which is so important for women who are still planning to have children.
For women who have undergone routine surgery to remove any type of polyp, laser burning would seem like fantasy. In the latest medical centers with the appropriate equipment, a full cycle of cervical polyp treatment (examination, analysis of results, preparation of an operation program and, in fact, laser removal) can be done in just three hours! No hospital stay, disability or rehabilitation due to trauma to the uterus and surrounding tissues.
What is the discharge from the vagina after removal of uterine polyps?

The postoperative period for patients consists of two scheduled gynecological examinations within a week, followed by the appointment of rehabilitation procedures. The nature of rehabilitation therapy depends on age, the cause of the disease and its characteristic features.
Do not worry if after hysteroscopy are found:
Pain in the abdomen, similar to pain from contraction of the uterus during menstruation;
Constant discharge for two to three weeks after surgery.
The above phenomena are considered normal and indicate a successful completion of treatment. By the nature of the discharge after the removal of polyps, the doctor can judge whether the healing processes are normal. Allocations are observed in most patients after surgery, their type depends on the shape and size of the polyps, the degree of their vascularization, the presence or absence of infection, and also on the method of their removal.
Factors affecting the intensity of postoperative discharge, and their type:
bacterial infections. If the formations developed against the background of a chronic infection, or if the infection occurred during the operation, the healing process takes longer and may be accompanied by purulent discharge from the vagina;
Removal method. Cryodestruction and laser removal of a polyp are considered less traumatic methods of surgical treatment than curettage or twisting of the leg, so the healing process after them is faster, and the intensity of the discharge is less;
Blood supply of the neoplasm. Each anatomical formation and organ has its own degree of blood supply intensity, has its own blood vessels. The type of vascularization of the neoplasm, the number of blood vessels and their size determine the intensity of discharge after surgery. Fibrous formations are less vascularized than glandular-fibrous and adenomatous polyps, respectively, and there is less discharge after their removal;
Depth of ingrowth, its size and shape. The larger the polyp, the more vascularized it is. Polyps with large vessels on a thick stalk after surgical treatment provoke bloody discharge from the vagina. In addition, if the leg of the polyp grows deep enough, then in the process of its removal, the risk of damage to the uterus’s own blood vessels may increase, which slows down the healing and rehabilitation process.
In general, there are 4 types of discharge in the postoperative period:
Bloody. The release of clotted blood clots can be observed when blood enters the uterine cavity during surgery. The discharge of fresh blood can last 1-2 days after the operation, during which the blood vessels of the uterus were damaged;
Physiological secretions. Normally, postoperative discharge lasts no more than two days or up to 2 weeks when the uterus is scraped, their volume is up to 50 ml. They are transparent, may contain ichor. After the wound has healed, the discharge disappears;
Purulent discharge observed with a bacterial infection, among the pathogens of which are staphylococci, streptococci and other microorganisms. The discharge is yellow or greenish in color. In the absence of treatment, the infection can cause a purulent abscess with complications up to infertility;
Putrid secretions may be a sign of a secondary infection. One of the postoperative complications is the ingress of Clostridium into the uterine cavity. These microorganisms can multiply in the absence of air, causing foamy discharge with an unpleasant odor.
What complications can occur after surgical removal of uterine polyps?
There are four most common ways of surgical treatment of this disease:
Excision of the legs of the polyp by hysteroscopy methods – used to treat solitary neoplasms with a long stem;
Cryodestruction polyp – treatment of the neoplasm with liquid nitrogen, after which it is separated from healthy tissues with tweezers;
curettage – removal of a part of the mucous membrane of the uterus or cervical canal with a vacuum device or a surgical instrument;
Laser burning – one of the most minimally invasive methods with the lowest risk of complications in the form of bleeding and infections.
Among the complications of surgical treatment of endometrial polyposis are:
perforation of the uterus – a through hole in the wall of the organ, which communicates its cavity with the abdominal cavity, which can lead to severe infectious and inflammatory processes. Perforation can occur during blind curettage or during surgery on areas of the endometrium with scars and adhesions. A severe consequence of perforation may be inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum due to microorganisms that have entered there from the uterine cavity. Treatment is with antibiotics and additional surgery;
Hematometer – the accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity, caused by a spasm of its neck, which makes the evacuation process difficult. This complication is very dangerous, because clotted blood is an environment for the development of pathogenic microorganisms, which can cause infection. For treatment, antispasmodics are used, which relax the cervix and promote the release of blood in a natural way. If antispasmodic drugs do not help, a probe is used to suck blood from the uterine cavity;
Scarring and adhesion formation – if the internal mucosa of the uterus is severely damaged, which often happens during curettage, the connective tissue undergoes scarring. This disrupts the function of the endometrium, the egg cannot attach to the surface with scars and adhesions, which results in infertility or ectopic pregnancy. The risk of this complication is reduced when uterine polyps are removed with a laser or cryodestruction methods;
Inflammatory processes – can be caused by infection in the uterine cavity, lead to serious consequences up to infertility, hinder the healing process. Antibiotic therapy is used for treatment. The use of antiseptic agents during the operation, cauterization of the wound helps to prevent this complication. Laser removal is considered the safest, since during it infection is unlikely due to the lack of direct contact of the instruments with the uterine membrane;
Malignization – malignant degeneration of tissues, from which the oncological process begins;
Disease recurrence – re-formation of polyps caused by mechanical damage to the uterine mucosa. In addition, it is impossible to guarantee the absence of new polyps, even if the operation was without complications. To prevent their occurrence, it is recommended to undergo regular examinations and provide treatment for chronic diseases of the endocrine system, infectious and inflammatory processes.
What is the likelihood of recurrence of uterine polyps?
In 10% of cases, after removal of uterine polyps, neoplasms reappear after a while. This happens due to an incorrectly performed operation, the individual characteristics of the organism, or the malignant nature of the formation.
With incomplete removal of polyp tissues it can grow back in the same place. This happens after an operation performed poorly. Often, new polyps in the uterus develop after twisting the legs of the old one, if parts of tissues or neoplasm cells remain. Polyps reappear if cauterization of the wound has not been performed.
The cause of new polyps in the uterus are other diseases – this is a fairly common cause of relapse, since such neoplasms rarely appear on their own, hormonal disorders of the body contribute to their occurrence. Among the reasons causing the growth of new polyps may be hormonal agents that disrupt the balance of estrogen and progesterone, thyroid disease, diabetes, genitourinary infections and chronic diseases of the reproductive system.
Hereditary predisposition. The patient needs to undergo frequent preventive examinations, and all polyps detected at an early stage should be cauterized by laser surgery.
postoperative stress by itself can create the preconditions for a relapse of the disease. Therefore, during the rehabilitation period, it is important to provide the patient with peace, not subject her to psycho-emotional stress and conduct general strengthening therapy in order to increase the body’s defenses.
To prevent the recurrence of endometrial polyposis, the gynecologist usually prescribes antibiotics and progestin preparations to correct the hormonal background.
Rehabilitation treatment after removal of polyps in the uterus
After an operation to remove such neoplasms using hysteroscopy or laser surgery, the risk of complications associated with traumatic tissue damage and infectious processes is minimal.
But for preventive purposes, the doctor may prescribe antispasmodics, hormonal drugs and antibiotic therapy:
Antispasmodics taken on the day after surgery to relieve spasm of the cervix, which can provoke an accumulation of blood in the organ cavity;
Antibiotics prescribed if the cause of polyps was the infectious processes of the genitourinary system, as well as for the prevention of secondary infection. Antibiotics are necessary after operations with an increased risk of tissue injury (curettage, excision and unscrewing of the polyp stem);
Hormonal preparations prescribed to patients in whom neoplasms have arisen due to an unstable hormonal background, with surges and drops in the level of sex hormones, or with excessive production of estrogen. This helps prevent the recurrence of fibrous polyps.
In order to maintain the immune system and stabilize the hormonal background, phytotherapeutists may recommend an infusion of a boron uterus, celandine, and other remedies based on medicinal plants. In addition, vitamin complexes are prescribed to strengthen the body’s immune barrier, in particular, powerful antioxidants – vitamins A, C and E.
What can not be done to a woman after surgery to remove polyps?
As mentioned earlier, from 14 to 20 days after hysteroscopy, most patients experience bleeding in small amounts. This indicates the effectiveness of the healing processes.
In order not to interfere with normal tissue regeneration, you need to follow a few rules:
Do not overheat your body, as this increases blood pressure and increases the risk of bleeding. Within a month after the operation, hot baths, baths, saunas should be avoided, and hyperthermia should be prevented by any means;
It is better not to take drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin, Citramon, Upsarin, Cardiopyrin, Tomapirin, etc.), as they impair blood clotting and contribute to bleeding;
Physical overexertion, especially associated with heavy lifting, is prohibited. Any sports, dancing, gymnastics and outdoor activities are also prohibited;
During the month of rehabilitation, physical and chemical interventions in the reproductive system (sexual intercourse, douching, etc.) are also prohibited;
It may seem obvious, but some patients have to be reminded of the need for careful observance of intimate hygiene, and not only after surgery, but all the time.
Answers to popular questions: pregnancy, removal, menstruation
Is it necessary to remove polyps in the uterus?
The methods of modern medicine allow you to quickly and painlessly remove any neoplasms, but, in the end, the choice remains with the patient. Removal is definitely recommended if medical treatment does not help to get rid of unpleasant symptoms, or if the polyps do not stop growing. Adenomatous polyps have a high potential for malignant transformation, and therefore must also be removed.
Can a uterine polyp resolve on its own?
A polyp is an anatomical formation of overgrown connective tissue, which is difficult to external influences. Therefore, it is impossible to get rid of the polyp in a non-surgical way, hormone therapy only helps to stop its growth and prevent new growths. These are quite effective methods for treating small polyps with a low risk of malignant transformation. However, if these neoplasms put pressure on the uterus, cause pain and prevent pregnancy, they must be removed.
Is it possible to get pregnant with a polyp in the uterus?
Pregnancy with a polyp in the uterus is possible, but if the polyp is large (1-2 cm) or there are a lot of them in the uterine cavity, then attachment of the embryo can be difficult. If it is impossible to attach an egg to the endometrium, the risk of an ectopic pregnancy increases with all the ensuing complications.
Is it possible to give birth with a polyp in the uterus?
Pregnancy and childbirth can be difficult if there is such a growth in the uterus. Among the frequent complications of pregnancy are placental abruption at the site of localization of the focus of polyposis, uterine bleeding, impaired fetal development due to mechanical pressure exerted by the polyp. Complications during childbirth: violation of the elasticity of the walls of the uterus due to growths, deterioration of uterine contractility, the risk of mechanical damage to the polyp and blood loss as a result of uterine bleeding.
Can the growth of polyps in the uterus lead to a miscarriage?
Yes, the chance of miscarriage increases if there are polyps in the uterus. The main cause of miscarriage in this disease is placental abruption. Normally, the placenta is attached to the areas of the internal mucous membrane of the organ and implements air exchange and nutrition of the fetus through the mother’s body. In areas of the endothelium with polyps and growths, the placenta is poorly attached, fetal nutrition is difficult and the risk of detachment increases. Other causes of miscarriage in endometrial polyposis: a malignant process that begins with malignancy of polyp cells, as well as malformations and abnormalities in the course of pregnancy due to the mechanical pressure exerted on the fetus by large neoplasms.
Do uterine polyps affect the development of infertility?
Small solitary polyps do not interfere with reproductive function. The danger is represented by multiple growths that occupy a large area of the inner surface of the uterus and interfere with the attachment of the egg. Large formations on the bottom of the uterus can also provoke infertility, as they block the fallopian tubes and prevent the penetration of the egg. In addition, even small growths can block the cervical canal, making it difficult for sperm to enter the uterine cavity from the vagina and, thereby, make conception impossible. Malignancy or degeneration of polyp cells into malignant cells also leads to reproductive dysfunction and infertility.
When can I get pregnant after removing a polyp in the uterus?
Removal of polyps is a safe and fast operation, which in most cases passes without complications, which makes pregnancy possible already in the first month after treatment. An obstacle to pregnancy after removal of polyps can be infection during surgery, the occurrence of adhesions and scars at the site of removed tumors, hormonal instability and uterine bleeding, as well as relapse of the disease.
Are polyps removed in the uterus without hospitalization?
Hospitalization for removal of polyps takes an average of 1 to 3 days. If there are no complications and pain, then the patient can go home in the evening of the same day when the operation was performed.
How long do you need to lie down after removal of a polyp in the uterus?
Two hours after the operation, if there is no pain and weakness, you can get out of bed and go about your daily activities.
When is sex possible after removal of a polyp in the uterus?
You can not have sex after the operation until the healing process is completed. On average, this happens after six weeks. A woman should not have bloody or brown discharge not associated with menstruation, anemia and weakness. If sex happens before the rehabilitation period ends, there is a high chance of microtrauma and infection.
Can a polyp come out with menstruation?
Polyps respond very poorly to non-surgical treatment. Hormonal drugs can remove unpleasant symptoms and stop the growth of a polyp, but they cannot reduce it in size, separate it from the uterine wall and remove it from the body. Therefore, the stories that polyps come out with menstruation after taking a certain remedy are a fraud in order to sell the drug more profitably or a delusion common among illiterate people in the gynecological field.
Can a cervical polyp turn into cancer?
This disease may well give rise to the development of a malignant tumor. The transformation of a polyp into cancer occurs in about 1,5% of cases.









