Contents
- Breast cancer symptoms
- Recommendations for self-examination of the breast
- I. Inspection should be carried out in a standing position, facing the mirror, in two positions of the hands – down and up:
- II. Feeling (palpation) of the chest should be done while standing. With a large size of the mammary gland, additionally, in the supine position. There are six positions for palpation of the chest on one side.
- Determination of symptoms by tumor markers
- Recommendations for self-examination of the breast
- Causes of Breast Cancer
- Stages of breast cancer
- Breast Cancer Diagnosis
- Breast Cancer Treatment
Breast cancer – this is a malignant degeneration and uncontrolled growth of breast epithelial cells, one of the most dangerous and common diseases of women, rarely detected in men.
The high incidence of women is associated with the role of estrogen, progesterone, and other hormones at the stages from menarche to menopause, pregnancy, and lactation. The risk of developing cancer does not depend on the size of the breast
Breast cancer symptoms
Nonspecific signs of breast cancer, in case of which it is advisable not to delay contacting a medical institution for consultations:
Progressive weight loss. How to determine? Weight loss persists, for more than three months in a row (Attention! The dynamics of weight loss is individual for each person), against the background of habitual physical activity, without the use of low-calorie diets.
Persistent and stable rashes, peeling on the chest.
How to determine? Allergic, infectious, parasitic rashes or peeling, in contrast to rashes of unclear etiology, are characterized by:
dynamic development of rashes;
itching;
different stages of the rash (beginning, mature, healing);
decrease or vice versa increase in their number.
Changing the shape of the nipple. The norm is only during lactation, with breastfeeding.
Enlarging moles in the chest area. You should be wary if you find growing moles, combined with discharge from the nipples.
Pain in the armpit. One of the causes is inflammation of the lymph node, it is advisable to exclude the cause.
Almost always, breast cancer is associated with the development of nodular seals, neoplasms. Indeed, it is. However, some forms, accompanied by seals in the chest, are not oncology, although some are capable of malignancy (malignant degeneration). There are forms that do not manifest themselves as neoplasms for a long time.
Previously, mastitis, nodular, diffuse mastopathy, fibroadenomas were mentioned in which focal or diffuse lesions of the breast tissues are formed.
Other pathologies are known, with damage to the gland, also diagnosed at different stages and periods:
During the lactation period:
Galactocele or milk cyst. It is formed after blockage of the milk duct, as a result of acute mastitis. Stagnant milk accumulates in the cyst, a jelly-like (fluctuating) swelling is formed.
Chest injury. It means an insect bite, a scratch or the like. It manifests itself with improper attachment of the baby, infection. Accompanied by the formation of a hematoma (bruise).
At any stage of life, more often in the older age group:
Lipoma or wen. Benign tumor of subcutaneous connective tissue. A low risk of malignancy (malignant degeneration) is characteristic.
Intraductal papilloma. A benign tumor in the form of outgrowths of the epithelium of the milk ducts. When tender papillomas are traumatized, bloody discharge from the nipples is possible; on palpation of the chest, they are felt in the form of small seals. There is a high risk of malignancy.
In this article, we will focus on the method of self-examination of the breast. It should be known and used by women, especially over the age of 25 (hereditary risk group), after 40-45 years, all females. The technique has a high diagnostic value at the preclinical (pre-medical) stage of disease detection.
Recommendations for self-examination of the breast

For women of childbearing age, only in the first week after the end of the menstrual cycle. Similar studies during pregnancy, menopause to carry out at any time.
The sequence of the procedure is not strictly mandatory. However, compliance with it disciplines, increases attentiveness, and reduces the risk of missing dangerous symptoms. There are two consecutive diagnostic stages: inspection, palpation.
I. Inspection should be carried out in a standing position, facing the mirror, in two positions of the hands – down and up:
Hands vertically down. Pay attention to visible deviations:
symmetry of the glands, nipples of the left and right sides (asymmetry is normal during breastfeeding);
deformations (exclude lipomas, unsuccessful mammoplasty);
focal retractions of the skin (one of the signs of cancer);
peeling, changes in the structure of the skin (exclude allergies, skin diseases);
ulcers, erosions, crusts (exclude healing of primary rashes, wounds);
skin color (exclude rubbing, erysipelas).
Hands vertically up. Pay attention to visible deviations in the armpit when the breast is shifted upwards, as well as:
symmetry;
swelling;
color of the skin.
Examination of the inside of the bra fabric. The wetting of the fabric of linen with spots of various colors, more often brown, red or colorless, not associated with lactation, sticky, mucous, watery consistency, odorless, with a smell, including fetid, should be alarming.
II. Feeling (palpation) of the chest should be done while standing. With a large size of the mammary gland, additionally, in the supine position. There are six positions for palpation of the chest on one side.
Description of the technique on the example of the right mammary gland:
Right hand vertically down. The palm of the left hand covers the right breast, the nipple rests on the center of the palm. Circular stroking and deep palpation, by squeezing the palm of the left hand, helps to identify seals in the body of the gland from the outside and the depth of the tissue.
Right arm vertically up. The palm of the left hand is pressed against the chest wall from below, the fingertips touch its outer side. Deep palpation is carried out by pressing during the period of movement from the bottom up, squeezing the palm.
Right hand vertically down. The position of the palm of the left hand on the upper wall of the chest surface. By squeezing, stroking the palm, eliminate seals, nodes under the skin of the upper chest.
Right hand vertically down. With the fingers of the left hand, feel the thoracic descent, determine the formations inside, invaginations, swelling, increased, decreased sensitivity to touch, cold, heat, pain, discharge.
Right hand vertically down. The palm of the left hand in the armpit. Feel the fingers of the hand, the thumb on the outside, the rest on the inside. With sliding squeezing movements of the fingers, examine the state of the lymph nodes of the axillary zone (normally, axial or axillary lymph nodes are not detected).
The position of the right hand is arbitrary. Fingers of the left hand in position on the right supraclavicular fossa. Feel, sub-and supraclavicular zone, around it, in order to determine the lymph nodes (normally, subclavian, supraclavicular nodes are not determined).
The study in the supine position is carried out similarly. Repeat the self-examination procedure on the other side of the body, as breast cancer can be unilateral and/or bilateral. Consider any neoplasms, seals, changes on the skin as suspicious.
The identified changes are evaluated according to the following parameters:
shape, size of breasts, nipples, areola;
the size and shape of the package of lymph nodes, seals, defects, neoplasms;
the nature of the surface of the neoplasm or lymph node is smooth, rough;
the mobility of the tumor and / or lymph node, that is, during the examination, it is possible to move from the place of the main localization;
sensitivity, soreness of the lymph node or neoplasms to touch, pinch.
Report them to a mammologist who will evaluate the diagnostic value of the symptoms from the standpoint of the risk of developing oncology. Previously, we gave a clinical description of seals that are presumably symptoms of cancer, including: nodular, diffuse forms (see here).
Suspicions of preclinical and clinical examination results are confirmed by instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods.
Earlier, it was described in more detail about the symptoms detected by instrumental methods, their diagnostic value (see here), including:
radiation (mammography, CT);
ultrasonic and magnetic radiation (ultrasound, MRI).
The main disadvantage is the subjectivity, evaluation of the results of x-ray mammography and ultrasound, depending on the qualifications of doctors. The quality of the results on CT is much higher – a type of X-ray examination, and MRI – a type of magnetic radiation.
In recent years, the high efficiency of diagnosing early stages has been reported, using methods:
contrast MSCT (multispiral computed tomography) – 3D image, topographic binding of the tumor to the anatomical formations, examination of the whole body, which allows the doctor to choose a treatment program.
PET-CT (positron emission tomography and computed tomography) – combines the advantages of X-ray examination with topographic reference and identification of the nature of pathophysiological processes in the tumor and around.
Infrared mammography – the method is based on the increased sensitivity of cancer cells, in comparison with healthy tissues, to penetrating heat rays, building, on this basis, a three-dimensional image of the breast with foci of cancer cells. It is reported about the high sensitivity of the method, up to 90% of correct diagnoses of the first stage of breast cancer.
The methods have an increased, in comparison with other methods, diagnostic value. They are not painful procedures, have a minimal effect on the body, the results of an objective analysis are presented in the form of a three-dimensional image, the results are carried out and processed within a short time, recorded on any media, including computer ones.
The disadvantage is the relatively high cost of examinations, including abroad, the queue for quotas for free examinations.
Differentiation of forms of breast cancer at the cellular and tissue level. Methods applied:
cytological (tumor cells) study;
histological (ultrathin sections of tumor tissue) studies.
Samples are obtained as a result of a biopsy – intravital excision of pieces of breast tissue.
Determination of the microscopic characteristics of the tumor is necessary to establish:
forms of pathology (forms of breast cancer differ in the aggressiveness of growth);
tactics (programs) of therapeutic measures (they differ in sensitivity to the effects of drugs);
prognosis of the probable outcome of the disease (differ in the likelihood of relapses).
Determination of symptoms by tumor markers
Early symptoms can be determined long before the clinical manifestations of the disease using immunological methods.
Determination of tumor markers using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is an in vitro (in vitro) technology to help find complementary to each other:
antibodies – (a standardized DNA fragment of a breast tumor molecule – a tumor marker, its commercial designation is CA 15-3);
antigens – (native breast cancer cells circulate in the blood of a sick person, have capture receptors for CA 15-3).
As a result of the PC technology, when mixed, in the wells of the device plates containing samples (CA15-3 + human blood), the following results are possible, confirming or excluding the disease:
Cancer confirmation. An antibody-antigen complex is formed.
Cancer exclusion. The immune complex “antibody-antigen” is not formed.
The results are easy to read using the detectors built into the instrument’s hardware.
Using PCR, tissue tumor markers of tumor growth are also isolated:
ER – estrogen receptor;
PR, progesterone receptor;
HER 1 or HER 2 are receptors for cancer cell growth factors.
The problem is that not all forms of cancer are willing to obey the simplified laws of immunology – the complementarity of receptors for specific antigens and antibodies. There are reports of false positive and false negative results. Cancer cells successfully fight the immune system of a sick person, suppressing it, directing the response down the wrong trail. This is the insidiousness of most forms of cancer.
Breast cancer is classified according to different principles. In this text, we will not specify the forms of cancer.
The main forms of pathology have been previously described:
hormone-dependent;
triple negative;
luminal cancer;
infiltrating.
Read more here. This is not an exhaustive list of breast cancers.
It is almost impossible to determine the exact form of oncology by clinical symptoms and morphological description of the tumor.
The symptoms characteristic of different types of oncology are established on the basis of a complex of in-depth studies. However, this is outside the scope of the popular article in the health education series.
Causes of Breast Cancer
Hormonal changes in the body are an integral part of female physiology. Starting from menarche, the body rebuilds every month. After fertilization of the egg, the woman’s body adapts to the bearing of the fetus, birth, lactation. The effect continues with menopause, menopause. In men, sexual physiology functions, an order of magnitude, easier.
Every second, the cells of the breast gland of a woman are under the influence of a variety of physiological impulses that stimulate the active regeneration of cells of the fatty, glandular, and connective tissue of the breast. The greater the load, the greater the likelihood of failures (cancer cell mutations).
Male mammary gland cells, of course, participate in metabolic processes, but are not subjected to significant pressure in the form of rhythmic or arrhythmic bursts. Hormonal disruptions of the genital area are mainly characteristic of the male menopause. This period, after the age of fifty, coincides with the peak incidence of breast cancer in men. However, even during this period, the level of male oncology is no more than one percent of a similar oncology of the opposite sex.
More significant causes of breast cancer, especially in women, are internal and external pathological factors.
Summarizing the known causes of breast cancer (see here) formulate the principles of breast cancer prevention.
Active prevention:
increased cancer alertness in oncogenic risk groups (genetic predisposition to cancer, hormonal diseases, etc.);
regular self-examination of the breast for women over 25 years of age (risk groups);
screening examinations after 40 years, in women, regardless of the nature of the risks, the minimum recommended examination (mammography, determination of estrogen levels, detection of tumor markers).
Passive Prevention:
careful attitude to the breast (protection from injuries, regular wearing of comfortable bras, a positive attitude towards breastfeeding);
giving up bad habits that are considered the causes of cancer (smoking, alcohol);
harmonization of sexual relations in stable couples;
reducing the risks of the negative impact of environmental factors on the body, especially exposure to ultraviolet radiation, sunlight, in solariums.
Stages of breast cancer
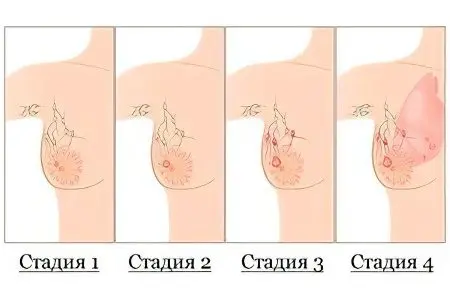
Previously, the stages of cancer accepted in official medicine were described using alphabetic and numerical designations for the stages of cancer. In this publication, we will focus on a simplified description of the stages, based on the clinical symptoms of the patient, a description of the tumor clinic.
breast cancer stage 1
When determining the initial stages of the disease, there are difficulties associated with the small size of the tumor (up to 20 mm). The neoplasm is difficult to grope in a large chest. Seals of a transitional form, carcinoma in situ, close to the first stage, are easily confused with diseases of non-oncological etiology or cannot be identified at all.
This stage is considered to be the initial – non-invasive. The opinion is based on the fact that visible carcinogenesis does not extend beyond the breast. The regional lymph nodes of the thoracic zone of the body are in a normal state, that is, they are not palpable.
Pathological changes at the subclinical level, characteristic of the first stage of oncology, can be determined exclusively by modern diagnostic methods. The most informative is a comprehensive examination, which includes several complementary methods during the screening examination.
breast cancer stage 2
The size of the tumor does not increase much in comparison with the first stage of the disease. It is generally accepted to consider the size of the neoplasm of the second stage in the range of 20 – 50 mm.
A characteristic sign of this stage is the palpation of one or two lymph nodes in the axillary (axillary), supraclavicular, and other areas near the chest. Normally, the sentinel lymph nodes of the breast are not palpable.
Self-diagnosis is becoming a more important method of detecting signs of disease. In order to increase the effectiveness of the examination, let’s pay attention to the signs of damage to the lymph nodes available during self-examination of the breast.
Signs of damage to the lymph nodes:
Pain. Usually in the axillary (axillary) zone, this is the earliest possible sign.
Hyperplasia. Enlargement of lymph nodes to a size palpable on the surface of the skin;
Lymphadenitis. Inflammation of the lymph nodes.
The names of the packets of sentinel lymph nodes located near the chest, which are part of the system of lymphatic vessels flowing from the mammary gland.
It is easy to determine their location on their own by the name of well-known anatomical landmarks:
axillary (axillary), usually affected first, and then;
subclavian, supraclavicular;
peristernal (prarasternal) – the center of the chest in the hollow between the glands.
The most common method for detecting oncology in the lymph nodes is a biopsy for the purpose of examining pathological material under a microscope.
breast cancer stage 3
The size of the tumor reaches a diameter of more than 50 mm.
A characteristic feature is the definition of the lymph nodes of the axillary, clavicular zones in the form of packages (groups). Feels like a bunch of small or medium sized berries. It is possible to damage the lymph nodes of the parasternal zone, without affecting the nodes in other areas.
At this stage, the likelihood of distant metastasis increases significantly. The greatest probability of distant metastases is localized in bone structures. The probability of bone metastasis is up to 90%. Bone metastases, according to the latest scientific data, can be detected even at the first stage of the disease. However, it does not exceed 5% when the disease is detected at the first stage.
breast cancer stage 4
It is accompanied by moderate and severe clinical symptoms localized in the chest area (ulcers, erosion, crusts), manifested by signs of bone damage (ache, pain). The clinical indicators of the body, the patient’s well-being, in the absence of a therapeutic effect, is steadily regressing.
During this period, the size of the tumor does not matter. Lymph nodes are palpated with packets on both sides; distant groups of lymph nodes may be affected. Characterized by multiple metastases in the bones and liver.
Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Various diagnostic programs are offered. One of them includes physical examinations, including: screening and follow-up examinations. When signs of oncology are identified, they are differentiated. The last stage of diagnosis is a specialized consultation. (See here for more details).
In addition, we list the methods of standard research used in the clinical practice of diagnosing breast cancer, namely:
primary registration of the patient, collection of an anamnesis of life and illness, traditional methods of examination (examination, palpation, percussion, auscultation, thermometry);
x-ray examination (mammography and chest x-ray);
Ultrasound of the mammary glands in various modifications with additional examination (liver);
Scincigraphy is a method of radioisotope visual diagnostics of metastases in bone tissue, the use of the technique for other medical purposes is known;
Other diagnostic methods are prescribed according to indications, taking into account the technical capabilities of the medical institution. Laboratory studies of biological fluids (whole, stabilized blood, serum, other) for morphological, biochemical, and other indicators are of an auxiliary nature, mainly to clarify the state of the patient’s body.
Breast Cancer Treatment
The most promising treatment of the early stages of the disease. During this period, it is possible to predict a complete recovery.
The likelihood of metastasis and return of the disease is possible in the later stages:
Surgical treatment in the form of resection of the total, partial with the possibility of breast plastic surgery.
Hormonotherapy
Chemotherapy – adjuvant (enhanced) and non-adjuvant.
Radiation therapy.
Targeted (targeted) therapy.









