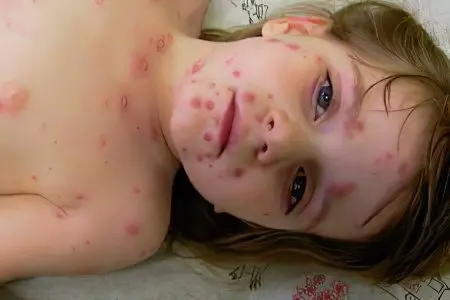
Chickenpox or chicken pox is a common disease among childhood infections.. The immunity developed after the disease is quite stable. Relapses of the disease are extremely rare. The causative agent of chickenpox dies, leaving the body. The patient is the carrier of the infection. The incubation period for varicella-zoster virus is three weeks. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, while the virus spreads in large quantities when talking, coughing, sneezing.
The disease is dangerous for those who have not had it in the period from two to seven years, especially for adults. In other cases, chickenpox passes easily. The mucous membrane serves as an entrance gate for infection, that is, when it enters the body through the upper respiratory tract, the virus multiplies there, then enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body with the bloodstream. Fixation in the upper layers of the skin and mucous membranes, allows the virus to manifest itself with a characteristic rash.
Chickenpox is easily tolerated by children, and when it enters an adult body, the virus behaves aggressively, especially if the patient has weakened immunity. Typical symptoms for chickenpox are: rashes all over the body, general loss of strength, high fever, sore throat. It is important to remember that this disease is not so much dangerous as contagious. Do not leave the house for three weeks (quarantine period) and do not contact those who have not had chickenpox, regardless of age, then you will not become a source of the spread of the disease.
Symptoms of purulent chickenpox
The initial stage of chickenpox is manifested by a blistering rash on the head (in the scalp, behind the ears), then rashes appear throughout the body, including the mucous membrane, tongue, and palate. Reddish-brown blistering rash is not limited to the skin. Often it affects the kidneys, pancreas, esophagus, ureters, bladder.
At the next stage, the rash turns into blisters up to three millimeters in diameter and is accompanied by severe itching. Scratching the blisters can lead to the formation of indentations in the skin that remain for life.
The typical course of chickenpox is an increase in temperature up to 39,5 ° C (usually at the time of an abundant manifestation of the rash), the duration of the rash is from three to five days, complications are not observed.
windmill shapes
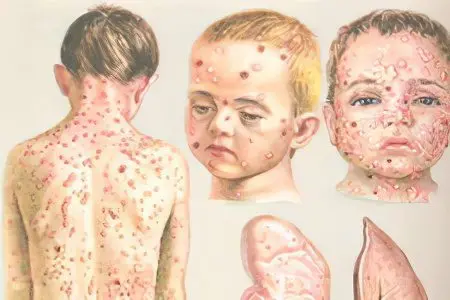
There are atypical forms of chicken pox, which occur in a mild (rudimentary) form or in a severe form (hemorrhagic, bullous, gangrenous, generalized) with unusual, possibly purulent, skin rashes. The outcome of these types of chickenpox is often fatal.
Rudimentary form manifested by single rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, without further filling with liquid and mild malaise. The hemorrhagic form is characterized by bleeding from the nose, gums, gastrointestinal tract and hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes, while the rash is filled with blood fluid.
Generalized form manifested by damage to internal organs, gives a severe course of the disease, sometimes fatal.
Bullous and gangrenous forms have purulent manifestations. Rashes with bullous chickenpox form become large, flabby blisters and are filled with a cloudy yellowish liquid. These blisters tend to enlarge along the periphery and coalesce into larger formations. Drying up, they burst, turning into long non-healing wounds with a wet surface. This process is caused by bullous streptoderma, where streptococci and staphylococci join the chickenpox virus. The disease is long-term and requires antibiotic treatment.
Progressive necrosis is an indicator of the gangrenous form of chickenpox. It is characterized by the appearance of gangrenous rims around the vesicles, spreading along the periphery.
In this case, the bubbles have a round, large appearance (a few centimeters in diameter) and are filled with a bloody-purulent fluid. After opening such a formation, a necrotic scab appears. As a result of its rejection, deep, non-healing ulcers with a purulent bottom are formed. All processes are accompanied by severe intoxication with a high probability of death. This form is observed extremely rarely, in most cases in children with reduced body reactivity.
All severe forms of chickenpox, including purulent ones, appear in people with a weakened immune system, and the presence of chronic diseases aggravates the course of the disease and increases the risk of complications. The most frequent complications can be skin lesions with the presence of purulent processes – boils, phlegmon, abscesses. The basis of these consequences is a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection. A private cause may be intensive scratching of itchy places on the skin. An open chickenpox bladder is a source of purulent infection.
Treatment of purulent chickenpox
Treatment of chickenpox requires hygiene to avoid secondary infection. Bed rest is necessary during the period of fever and rash. All elements of the rash are treated with an alcohol (aqueous 2%) solution of brilliant green.
Antibiotics are prescribed only in case of purulent complications and the presence of a secondary infection. All appointments are made by the doctor after examination and diagnosis of the disease. The main method of preventing chickenpox for adults and adolescents who did not have this infection in childhood is vaccination.









