Contents
What is mechanical jaundice?
Obstructive jaundice is a pathological syndrome consisting in a violation of the outflow of hepatic bile through the biliary tract into the duodenum due to mechanical obstructions.
Synonyms of the disease: obstructive jaundice, subhepatic jaundice, acholic jaundice, resorption jaundice, extrahepatic cholestasis.
Mechanical obstruction of the biliary tract develops as a complication of a large group of diseases of the pancreas and biliary system (the system of bile ducts and sphincters that regulate the flow of bile) and is accompanied by such general symptoms as icteric coloration of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera, dark urine, discoloration of feces, skin itching, abdominal pain.
The consequence of progressive jaundice can be liver failure, kidney failure, purulent cholangitis, sepsis, biliary cirrhosis or cholangitis liver abscess, in especially severe cases and in the absence of qualified medical care – death.
Among the most common causes of obstructive jaundice, cholelithiasis (29% of cases) and malignant tumors (67% of cases) are distinguished. At the age of 30 years, cholelithiasis predominates; in the age group of 30-40 years, tumors and cholelithiasis as the causes of jaundice are equally common. In patients older than 40, tumor neoplasms predominate.
In general, obstructive jaundice is more often diagnosed in women (82%). However, tumor obstruction of the biliary tract is more common in men (54%).
Causes of obstructive jaundice
To date, the causes of obstructive jaundice due to compression of the biliary tract are well understood.
Depending on the etiological factors, they are divided into 5 groups:
congenital anomalies development of the biliary system: hypoplasia and atresia of the biliary tract;
Benign changes in the biliary system and pancreas, caused by cholelithiasis: stones (stones) in the bile ducts; diverticulum (protrusion of the wall) of the duodenum and stenosis of the major duodenal papilla (BDS), located inside the descending part of the duodenum; cicatricial structures of the ducts; cysts; chronic indurative pancreatitis; sclerosing cholangitis;
Strictures of the main bile ducts as a consequence of surgery (formed as a result of accidental damage to the ducts or improper suturing);
Primary and secondary (metastatic) tumors organs of the pancreato-hepatobiliary system: cancer of the gallbladder, cancer of the head of the pancreas and OBD, as well as the presence in the liver of metastases of tumors of various localization (common gastric cancer, lymphogranulomatosis);
Damage to the liver and biliary tract by parasites (alveococcosis, echinococcal cyst, etc.).
The most common cause of obstructive jaundice is tumor neoplasms (of the liver, biliary tract, pancreatic head) and cholelithiasis. Congenital malformations of the biliary system and parasitic diseases are much less common. In old age, calculous (due to gallstones) and tumor obstruction are predominantly found, at the age of less than 40 years, cholelithiasis often becomes the cause.
Duodenal ulcer and acute appendicitis (in the case of the location of the vermiform process in the zone of the liver gate) are very rare causes of this pathological syndrome.
Cholestasis (decreased flow of bile into the duodenum) occurs most often due to the migration of stones into the ducts from the gallbladder. The formation of stones in the ducts themselves is observed much less frequently. They usually pass from the gallbladder into the choledochus (common bile duct) during an attack of hepatic colic. A blocked duct occurs when a large stone cannot pass through it. Sometimes, due to a prolonged spasm of the sphincter of Oddi (smooth muscle located in the OBD), even small stones get stuck in the terminal section of the choledochus.
Tumors of the pancreatic-hepatobiliary zone cause jaundice in 37% of cases. In the first place in terms of frequency is cancer of the head of the pancreas and OBD, in the second place – tumors of the main biliary tract and gallbladder. Tumors of the liver and its ducts are quite rare.
Symptoms of obstructive jaundice
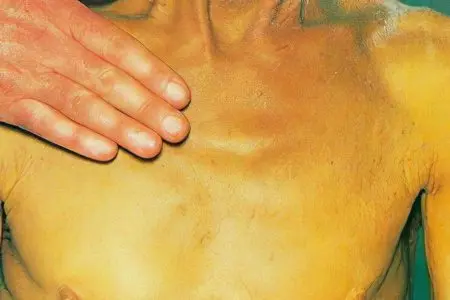
Common signs of the disease include:
Dull pain in the epigastric region and under the ribs on the right, which increase gradually;
Dark urine and discolored, loose stools;
Yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera of the eyes; icteric coloration of the skin gradually takes on an earthy hue;
Itchy skin;
Nausea, occasionally – vomiting;
Loss of appetite, weight loss
Increase in body temperature;
In some cases, yellowish cholesterol deposits on the eyelids in the form of clearly defined formations protruding above the surface of the skin;
Increase baked.
When the bile ducts are blocked by stones, the pain is spasmodic, sharp, and can radiate to the chest area, to the right armpit and shoulder blade. External signs of jaundice appear 1-2 days after the weakening of hepatic colic. Palpation of the liver area is painful. The gallbladder is not palpable. Pressing on the area to the right under the ribs causes an involuntary breath holding. Nausea and vomiting are possible.
With tumors of the pancreas, OBD, biliary tract, the pain is dull, localized in the epigastric region, and radiates to the back. On palpation, a distended gallbladder is found, pressing on which is painless. The liver is enlarged, has an elastic or dense texture, with a malignant process it has a nodular structure. The spleen is rarely palpable. External signs of jaundice are preceded by a decrease in appetite, skin itching.
Enlargement of the liver is one of the common signs of prolonged obstructive jaundice. The liver is enlarged due to its congestion with congested bile and inflammation of the biliary tract.
Skin itching often begins to bother even before the appearance of signs of jaundice, especially with the tumor genesis of the disease. It is strong, debilitating, and cannot be removed by therapeutic agents. Scratches appear on the skin, small hematomas form. Weight loss is usually observed with jaundice due to cancerous tumors.
An increase in temperature is mainly associated with infection of the biliary tract, more rarely – with the collapse of the tumor. A prolonged increase in temperature is a differential sign that distinguishes subhepatic jaundice from viral hepatitis, in which, during the period when signs of jaundice appear, the temperature drops to normal limits.
Forecast of obstructive jaundice
The duration of the disease varies over a wide range: from a few days with short-term blockage of stones in the common bile ducts to several months with tumor processes. The prognosis of obstructive jaundice is determined by the course of the underlying disease.
Diagnosis of obstructive jaundice

The preliminary diagnosis is not difficult in the presence of a neglected tumor, which is easily palpable. But with the initial manifestations of cholestasis, the diagnosis causes certain difficulties, since the patient’s complaints and general clinical symptoms can be signs of many diseases. Laboratory methods are of little use for the early diagnosis of obstructive jaundice. An increase in the level of cholesterol, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase activity is characteristic of both intrahepatic cholestasis and viral hepatitis.
Therefore, the decisive role belongs to instrumental research methods, of which the following are used:
Ultrasound diagnostics. It reveals the expansion of the bile ducts, the presence of calculi in them and focal liver damage. With the localization of stones in the gallbladder, the probability of their detection is 90%, with localization in the terminal part of the common bile duct – 25-30%. Rare errors include the identification of a gallbladder tumor as an accumulation of calculi.
Relaxation duodenography. The method is an X-ray of the duodenum in conditions of its artificial hypotension. It is used to diagnose Frostberg’s symptom (deformation of the inner surface of the descending duodenum, as a result of which its contour resembles the letter “E”) and duodenal diverticulum. Frostberg’s symptom is a sign of indurative pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer with metastases to the duodenum.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Used when ultrasound results are insufficient, when OBD blockade is suspected. In this method, a contrast agent is injected into the duct using a cannula (special tube) and then a series of x-rays are taken. ERCP allows diagnosing small tumors, conducting a cytological and histological analysis of the epithelium and the contents of the duct. This is a highly informative method, but since it is invasive, it can be accompanied by serious complications.
percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography. It is indicated for blockade of the biliary tract at the gates of the liver. In this case, under local anesthesia under ultrasound guidance, a thin needle with a contrast agent is inserted through the skin and liver tissue into one of the hepatic ducts. The number of complications with this method is greater than with ERCP (internal bleeding, bile leakage, peritonitis).
Radioisotope liver scan. It is used to diagnose tumors and parasitic lesions of the liver (alveococcosis), when it is difficult to identify a mechanical obstruction in the biliary tract in another way.
Laparoscopy. This is the most invasive method, and it is used when other methods have proved ineffective in terms of accurate diagnosis. The use of laparoscopy is advisable when detecting metastases, to determine the degree of liver damage in alveococcosis, etc.
Treatment of obstructive jaundice
The treatment of this disease is mainly surgical.
Conservative therapy
Includes a diet with an emphasis on vegetables, fruits, dairy products. Food should be fractional, dishes – boiled and mashed. It is recommended to drink as much liquid as possible (juices, water).
Treatment is carried out only in a hospital, intravenous glucose, B vitamins, hepatoprotectors, thrombolytics and other drugs are administered. If necessary, antibiotics, plasmapheresis (blood purification), enterosorption (detoxification procedure) are prescribed.
Operative therapy
Depends on the primary disease that caused obstructive jaundice. Depending on this, it can be carried out:
External drainage of the bile ducts – restoration of the outflow of bile in case of blockage of the biliary system. This is a minimally invasive method that can be applied routinely.
Endoscopic cholecystectomy – removal of the gallbladder through endoscopic holes in the abdominal wall.
Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy – removal of stones from the gallbladder.
Choledocholithotomy – carried out in conjunction with the removal of the gallbladder and consists in removing stones from the common bile duct, for which its front wall is opened.
Partial hepatectomy – removal of areas of liver tissue affected by the pathological process.









