Contents
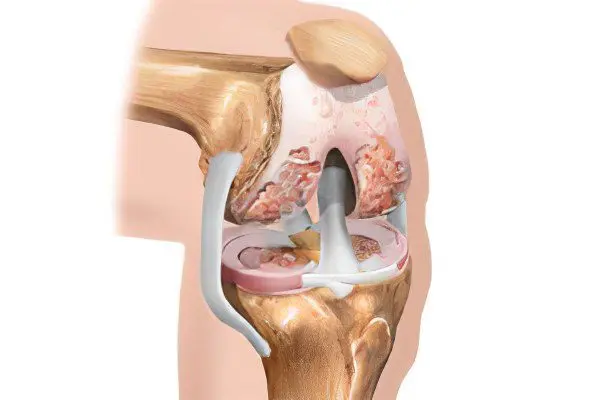
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a deformity and destruction of cartilage. The disease has a chronic degenerative character, accompanied by pains of varying strength. It can lead to its complete immobilization, loss of functionality. The disease develops more often in women than in men. Moreover, excess weight and venous disease are considered factors that increase the risk of arthrosis at times. It is no coincidence that most obese women over the age of 40 suffer from such joint problems. Most older people experience osteoarthritis. It can be bilateral or unilateral depending on whether only one leg or both are affected. At a young age, the disease is usually caused by injuries received during sports or in the process of doing physical work.
Initially, changes are observed at the molecular level, and then they affect the physicochemical properties of cartilage tissue. The cartilage becomes minty, thinner, cracked and exfoliated. All these processes can be detected in the study of cartilage tissue. If you do not carry out the necessary treatment, the cartilage will collapse completely. Eventually, this will expose the bone.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
The following causes can lead to osteoarthritis of the knee joint:
Injuries. These include fractures, dislocations, and damage to the menisci. It is after injuries that gonarthrosis develops at a young age. When the knee joint is damaged, it becomes impossible to perform flexion-extension movements. Treatment of injury in this case involves temporary fixation of the limb, which leads to poor blood circulation. This causes the development of post-traumatic arthrosis of the knee joint.
The menisci are of particular importance. Their damage provokes the “cycling” of the knee. If a patient has a meniscus removed, then in 9 out of 10 cases this leads to arthrosis of the knee joint.
Heavy loads. Sports activities should be carried out taking into account the age of the patient. Very often, people in old age tend to train as actively as in their youth. In most cases, this is a direct path to injuries: fractures, sprains. Sometimes there are microtraumas. They are not felt, but cause serious damage to the joints. Therefore, playing sports after 40 should involve moderate exercise. In old age, the joints cannot cope with the load that was easily tolerated in youth, because the cartilage tissue wears out over time, becomes thinner. For this reason, during sports, all movements should be smooth. The greatest damage to the knee joints is caused by running on asphalt and squats. These exercises should be replaced with other types of physical activity.
Overweight and obesity. This cause in itself does not lead to damage to the cartilage tissue of the joint, but it contributes to injury to the menisci. Obese people endure such injuries hard, and the knee joint after that is difficult to recover. Injuries to the meniscus, as a rule, culminate in the development of arthrosis of the knee joint. In addition, the legs receive an additional load due to the presence of excess weight, and it lies on the knees. The most difficult situation is when obesity is combined with varicose veins. In this case, the most severe form of arthrosis of the knee joint can develop.
Weak ligament. This phenomenon is also known as “loose” ligaments. It is usually combined with high joint mobility. At the same time, a person has a very flexible body and can perform various exercises without warming up, for example, stretching, sitting on a twine. However, such physical activity leads to microtrauma of the knees, and eventually to arthrosis, if the damage becomes too much. Along with a weak ligamentous apparatus, joint mobility can be caused by a violation of the sensitivity of the legs. A person does not experience severe pain when injured, so he does not notice it.
Diseases of the joints. Most often, osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a consequence of arthritis. It can be rheumatoid, psoriatic, reactive. In arthritis, inflammation leads to the accumulation of synovial fluid in the joint cavity, a tumor. As a result of all these processes, cartilage tissue is destroyed. This leads to osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
Violation of metabolic processes in the body. As a result, tissues do not receive the necessary substances and minerals. Calcium deficiency affects the condition of bone and cartilage tissue.
Stress. Even constant nervous tension and mood swings affect the health of the joints. It is recommended to change the environment more often, to alternate physical activity with mental activity, to rest more to avoid the development of arthrosis. In most cases, women over the age of 40 suffering from this disease had accumulated emotional fatigue, which led to poor circulation in the legs, swelling and inflammation.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee
Pain sensations
Pain does not occur suddenly, as a rule, in the early stages of the development of arthrosis of the knee joint, the pain is felt weakly. This condition can last for months and even years, until an exacerbation of the disease occurs. Weak pain occurs during active physical exertion, while running, walking. A sudden onset of discomfort cannot be a symptom of arthrosis. Most likely, the pain in this case is caused by trauma: pinched meniscus, dislocation, fracture.
With arthrosis of the knee joint of the 2nd degree, discomfort is felt much more strongly. If earlier the pain arose only as a result of excessive physical exertion, now it also appears at rest. The most prolonged attacks occur after a long walk or lifting heavy things. To get rid of discomfort in the knee joint, you need to rest for a long time. However, if physical movements are resumed after this, the pain returns.
knee deformity
It becomes noticeable in the later stages of the development of arthrosis. When the first symptoms appear, the knee may look swollen, but retains its normal shape.
Synovitis
This term in medicine refers to the accumulation of joint fluid in the joint cavity. When its amount exceeds the permissible norm, a phenomenon such as a Baker’s cyst occurs. This is the appearance of a dense elastic formation on the back wall of the knee joint. The most noticeable Baker’s cyst is in an extended state. It is successfully treated and does not require surgery.
characteristic crunch
It appears with arthrosis of the knee joint of 2 and 3 degrees. This crunch must be distinguished from the sounds that are heard when the knees are bent in a healthy person. The crunch with arthrosis is sharp and accompanied by pain. In all other cases, it is due to weakness of the ligamentous apparatus or excessive joint mobility.
Limited mobility of the knee joint
This symptom also manifests itself in the later stages of the development of arthrosis. The patient cannot freely bend and straighten the leg. Attempts to make such movements are accompanied by severe pain. You can only bend your leg at a right angle. Further movement causes severe pain. Simultaneously with the restriction of mobility, the deformation of the joint occurs. It is well expressed externally.
At stage 3 arthrosis, the knee may be completely immobile. Because of this, some patients move on half-bent legs. Pain in the knee joint is often caused by changing weather conditions. They have a aching character, occur both during movement and at rest. Patients often cannot sleep because of the pain, so they have to resort to the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Degrees of arthrosis of the knee joint
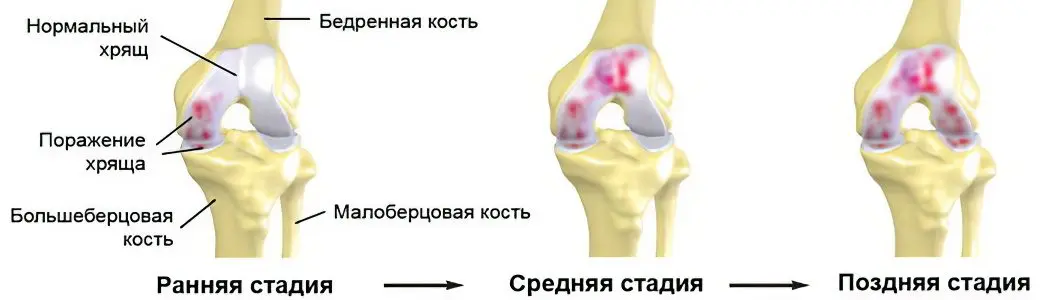
Arthrosis of the knee joint 1 degree
In this case, the disease is characterized by minor pain during active movements. Synovial fluid may accumulate in the joint cavity, leading to the formation of a Baker’s cyst. Pain occurs during movement, but immediately disappears at rest. Cartilage tissue is damaged, but outwardly the deformation of the joint is not noticeable.
With the help of radiography at this stage of the development of arthrosis, it is difficult to make a diagnosis; additional examination methods are required.
Arthrosis of the knee joint 2 degree
There is a narrowing of the joint space, the cartilage tissue is damaged to a large extent. In the picture obtained during the x-ray, you can see the growth of the bone. Acute pain is accompanied by any movement in which the knee joint takes part. At rest, discomfort disappears, but then reappears. A characteristic crunch is added to the pain when performing flexion-extensor movements.
Gradually, the function of the joint becomes impossible. The knee ceases to bend and unbend. Externally, the doctor can determine the deformation of the bones.
Arthrosis of the knee joint 3 degree
In places, the cartilaginous tissue becomes thinner completely, and exposed areas of the bone are formed. On the radiograph, a large number of osteophytes are clearly visible – salt deposits in the joint cavity. In addition, loose bodies may be found there.
External changes are becoming more and more noticeable. To cope with the pain, stopping the movement, now fails. It persists during physical stress on the joint, and at rest.
Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint
Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint is caused by the deposition of salts. They are more likely to affect overweight women. In the early stages, the disease affects the inside of the joint, in the later stages it also affects the outside.
The main symptoms of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint are acute pain and a characteristic crunch. Treatment of this disease must begin at an early stage. In this case, the chance to save cartilage tissue is higher.
How to treat osteoarthritis of the knee joint?
Along with drug treatment in modern medicine, methods such as:
Ozone therapy. This is an effect on a sore knee joint with the help of ozone. With this method of physiotherapy treatment, the substance can be injected or used externally. Ozone therapy allows you to achieve the maximum effect, while its use is possible in most cases. Treatment with intramuscular and subcutaneous injections of ozonized saline, ozone-based ointments and creams has practically no contraindications and side effects. Ozone therapy has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, restores blood circulation in the knee joint. Strengthen the effect of this method allows the simultaneous use of chondoprotectors and glucocorticosteroid drugs.
Kinesitherapy. In this case, the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is carried out with the help of special exercises. The load is selected in accordance with the degree of development of the disease and the physical fitness of the patient individually. When performing some exercises, special devices or simulators are used. In this case, not only muscles, tendons and joints are involved, but also other organ systems in the body: endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive. It is very important to breathe correctly when performing a set of exercises. Therefore, it is recommended to exercise under the supervision of a doctor.
Exercises allow you to improve blood circulation in the knee joint, restore the elasticity of the ligaments, improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue cells, and contribute to its restoration. Such a load positively affects not only the physical, but also the psychological state of the patient, since hormones of joy – endorphins – are produced in the process.
[Video] Traumatologist, orthopedist Zubikov V.S. How to treat deforming arthrosis of the knee joint:









