Italian Renaissance artists often depicted women with an enlarged thyroid gland in their paintings, apparently at that distant time – this phenomenon was so common that it was the norm.
Also, over the past decades, there has been a steady increase in the incidence of thyroid pathologies in the population.
Among endocrine diseases in terms of occurrence, they approach diabetes mellitus. The reason for such high rates is poor ecology, low-quality food and lack of iodine in water and food.
What is a multinodular goiter?
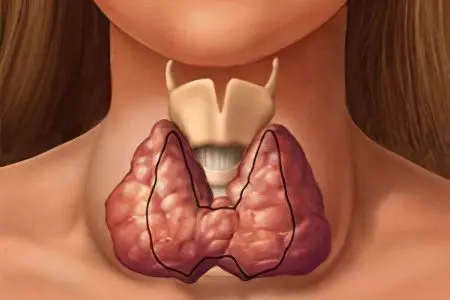
Multinodular goiter is a disease that combines all formations in the thyroid gland in the form of nodes that have a different origin, structure and size of more than 10 mm.
Nodes can be of different nature:
Follicular;
cystic;
Colloidal and others.
In some cases, a combination of several types of nodes in one patient is simultaneously observed.
Depending on the structural changes in the structure of the gland, multinodular goiter is divided into 3 types:
nodal: diagnosed with uneven enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is caused by its excessive activity.
Diffuse: occurs with a uniform growth of the gland tissue, which indicates a decrease in its secretory function.
Mixed: quite rare and is called “endemic nodular goiter.” At the same time, the thyroid gland is unevenly enlarged, but some of its parts remain homogeneous.
If more than two nodes are found, the size of which exceeds 1 cm in diameter, a thyroid puncture is recommended. The vast majority of identified thyroid nodules are benign. As a rule, such neoplasms do not affect its function and, with a similar development of the disease, they speak of a multinodular euthyroid goiter. Only 5% of the nodes found are malignant.
The mechanism of development of cancerous malignant and benign neoplasms is different. Tumor nodes are formed by abnormal rapid division of one of the cells of the gland due to damage to its genetic code. Malignant nodes do not replace healthy cells of the gland, but penetrate between them. In a benign pathological process, the node grows and compresses the surrounding tissues.
Despite the fact that the presence of nodes in the thyroid gland may not affect its normal functioning, the disease requires mandatory treatment. In some cases, ignoring such a problem is a threat to life.
Symptoms of multinodular thyroid goiter

Multinodular goiter may not affect the function of the thyroid gland for many years, and the patient does not experience discomfort and complaints. Until the node reaches a size of 1–2 cm in diameter, it is rather problematic to see it outwardly. With this course of the disease, nodes are often detected during preventive examinations on an ultrasound machine. If you do not pay attention to this problem in time, hyperthyroidism, or hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, may develop over time.
The clinic for multinodular goiter resembles a toxic diffuse goiter, but there is no ophthalmopathy and myxidema. The patient may be disturbed by excessive sweating, irritability, deterioration in general well-being with an increase in outdoor temperature, frequent heartbeat and arterial hypertension. Sometimes the patient may complain of tingling in the heart and shoulder blades, as well as increased appetite, constant thirst, diarrhea and weight loss. In addition, there is trembling of the fingers on the hands, tongue and whole body. At night, such people are haunted by a feeling of heat, they are characterized by fear and anxiety. Against the background of such symptoms, potency and sexual desire are significantly reduced.
Sometimes the thyroid gland grows and takes on irregular shapes that are noticeable not only to the doctor, but also to his patient. Usually, by this time, the gland is so large that it compresses nearby organs. In this case, there is a change in voice, difficulty in swallowing, breathing, a feeling of constriction or suffocation in the neck, this feeling is especially clear in the supine position.
You can try to find a node on the thyroid gland yourself. A healthy gland is homogeneous and elastic, if dense areas are found during probing, these can be nodes. They are usually not attached to the skin and are mobile when swallowed.
Multinodular goiter, which does not manifest itself outwardly, is detected during examination on an ultrasound machine. After that, a hormonal examination is prescribed and, if necessary, a study of the cells of the node. The purpose of further treatment depends on the result of these tests.
[Video] Endocrinologist Ph.D. Vinogradskaya O. I. — Symptoms and causes of the appearance of nodes in the thyroid gland:









