What is gallstone disease?
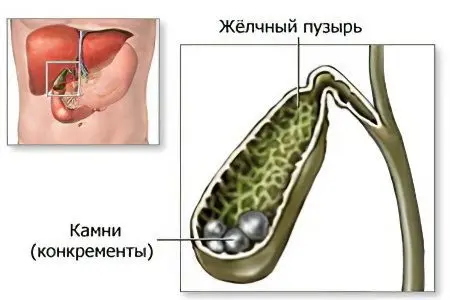
Gallstone disease (GSD) – This is a disease characterized by the formation of stones in the gallbladder and its ducts due to a violation of certain metabolic processes. Another name for the disease is cholelithiasis.
The gallbladder is an organ adjacent to the liver and acts as a reservoir for liquid bile produced by the liver. Gallstones, or calculi, can be found both in the gallbladder itself and in its ducts, as well as in the liver and the trunk of the hepatic duct. They differ in composition and can have different sizes and shapes. Gallstone disease often provokes the development of cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), as the stones irritate its walls.
Calculi in the gallbladder are formed from cholesterol crystals or calcium pigment-lime salts (in more rare cases). Gallstone colic occurs when one of the stones blocks the duct that carries bile from the gallbladder to the small intestine.
The formation of stones in the gallbladder is a fairly common disease that affects about 10% of the adult population in Russia, Western Europe and the United States, and in the age group over 70 years this figure reaches 30%.
In the second half of the twentieth century, the frequency of surgical interventions performed on the gallbladder surpassed the frequency of surgical operations to remove appendicitis.
Gallstone disease is predominantly found among the population of industrialized countries, where people consume a large amount of food rich in animal proteins and fats. According to statistics, cholelithiasis is diagnosed in women 3-8 times more often than in men.
Symptoms of gallstones
In most cases, gallstone disease is asymptomatic and has no clinical manifestations for several (usually five to ten) years. The appearance of symptoms depends on the number of stones, their size and location.
The main features of GSD are:
Paroxysmal drilling or stabbing pains in the liver and right hypochondrium;
Nausea, in some cases vomiting;
Bitter taste in the mouth due to flow of bile into the stomach, eructation of air;
flatulence, stool problems (constipation, diarrhea), stool discoloration;
Weakness, general malaise;
Temperature increase;
Jaundice.
Hepatic (biliary) colic usually develops after eating fatty, heavy foods, spicy and fried foods, alcohol, as well as under conditions of increased physical or stressful stress. Pain sensations begin on the right under the ribs, can be given to the right arm (shoulder and forearm), shoulder blade, lower back, right half of the neck. Sometimes the pain can extend beyond the sternum, which is similar to an angina attack.
The pain appears due to a spasm of the muscles of the gallbladder and its ducts, which occurs in response to irritation of the walls of the bladder with stones, or due to excessive stretching of the walls of the bladder as a result of an excess of bile accumulated in it.
A strong pain syndrome is also noted when stones move along the biliary tract and blockage of the bile duct lumen by stones. Complete blockage leads to an increase in the liver and stretching of its capsule, which causes constant dull pain and a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium. In this case, obstructive jaundice develops (the skin and sclera of the eyes become yellow), which is accompanied by discoloration of the feces. Other symptoms of a complete blockage of the duct may include high fever, excessive sweating, fever, and seizures.
Sometimes biliary colic resolves on its own after the stone passes through the bile duct into the small intestine. Usually the attack lasts no more than 6 hours. To relieve pain, you can apply a heating pad to the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe right hypochondrium. If the stone is too large, it cannot leave the bile duct itself, further outflow of bile becomes impossible and the pain intensifies, immediate surgical intervention is required.
A common symptom of cholelithiasis is vomiting with an admixture of bile, which does not bring a feeling of relief, since it is a reflex response to irritation of certain areas of the duodenum.
An increase in temperature to subfebrile values u37bu37,5b(not higher than XNUMX ° – XNUMX ° C) indicates the attachment of an infection and the development of an inflammatory process in the gallbladder. The development of cholecystitis is accompanied by a decrease in appetite and increased fatigue.
The first symptoms of gallbladder problems that should not be ignored are:
Prevention of gallstone disease
To prevent the formation of gallstones, you should:
Avoid rich foods high in fat and cholesterol;
If you are overweight or obese, follow a low-calorie diet and exercise so that the weight decreases gradually;
Normalize metabolic processes: reduce liver production of cholesterol and stimulate the secretion of bile acids. For this, drugs such as zixorin, liobil are prescribed.









