Contents
What is vaginitis?
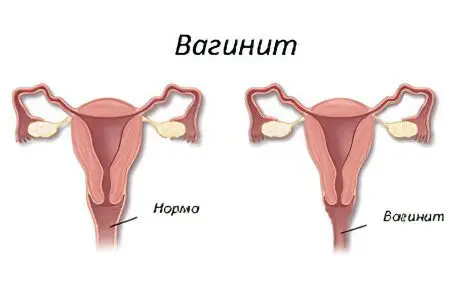
Vaginitis – this is an inflammation of the entire mucous membrane of the vagina, which is caused by the activity of pathogenic microbes. Vaginitis is the most common disease in gynecology. Unfortunately, today the number of patients with vaginitis is increasing. As statistics tells us, every third woman of childbearing age suffers from vaginitis.
According to recent studies, the development of vaginitis is directly related to sexual activity and is considered a sexually transmitted disease.
Favorable factors for the development of vaginitis are the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms (gonococci, Trichomonas, pinworms) into the vagina from dirty clothes and unwashed hands, non-observance of personal hygiene rules. Often the disease develops with prolonged mechanical irritation of the mucous membrane. Girls 5–12 years old can get vaginitis when they get an infection with the bloodstream with influenza, scarlet fever.
During puberty, allergic and bacterial vaginitis is often observed. This disease should not be ignored, as it can cause negative consequences for women’s health.
Causes of vaginitis
The vagina is represented by a muscular tube, which is lined from the inside with a multi-layered epithelium. The upper layer of the epidermis contains a lot of glycogen. They feed on bacteria that are normally always present in the vagina. Beneficial flora include Dederlein sticks and lactic acid bacteria.
These microbes break down glycogen and release lactic acid. Thus, the vagina will be protected from both sides. Dederlein’s sticks line its epithelium with a dense layer, and lactic acid bacteria produce an acidic secret. Pathogenic flora cannot multiply in it. Another reliable factor in protecting the vagina is its ability to self-cleanse. The cells of the organ secrete mucus, which flows down the walls of the vagina and comes out. Together with it, desquamated epithelial particles and dead microbes leave it.
The level of sex hormones determines the level of glycogen in the cells of the vagina. Estrogens stimulate its accumulation, and progesterones slow it down. Most progesterone in the blood is found before the next menstruation. It is not surprising that it is during this period that women often turn to a gynecologist with a complaint of acute vaginitis, or a relapse of the chronic form of the disease.
Risk groups
The following factors can provoke the development of the disease:
Vaginal injuries received during labor. Because of this, its walls lose their ability to close. The opening in the vagina always remains open. A similar situation can be observed after surgery on the genitals.
Hormonal imbalance in the body: postponed childbirth, pregnancy, abortion. Many women experience vaginitis during postmenopause.
Stress, experiencing strong emotions, serious illnesses and infectious processes in the body can provoke a decrease in immunity.
Violation of hygiene rules. Pathogenic flora rapidly increases in menstrual blood and other vaginal secretions.
Diabetes. This process causes excessive deposition of glycogen in the walls of the vagina, causing itching and poor nutrition.
Bacteria that cause genital infections are capable of provoking vaginitis. Infection occurs through unprotected intercourse.
The mechanism of development of vaginitis
Vaginitis is always characterized by inflammation, but pathogenic microorganisms do not always cause it. Sometimes a violation develops when the walls of the vagina are injured. This can occur with inaccurate douching, with rough intercourse, with the use of personal hygiene products that are distinguished by an aggressive composition. Sometimes vaginitis develops as a result of an allergization of the body. It can occur on lubricants, on contraceptives, on tampons.
In the vagina, the infection can get from the external environment, that is, by ascending. In this case, bacteria are introduced into the body from the labia, from the urethra or anus. The second route of infection spread is downward. In this case, bacteria enter the vagina from a focus of chronic infection that exists in the body. Such a focus can be tonsils, carious teeth, inflamed kidneys. The bacteria reach the vagina through the bloodstream.
The destroyed cells of the vaginal mucosa will produce certain biological substances. They lead to vasodilation, which causes the blood to stagnate. White blood cells and plasma seep out of the capillary walls. This leads to swelling at the local level.
Since the mucous membrane of the vagina is permeated with nerve endings, its edema provokes their irritation. This leads to discomfort. It is manifested by pain and itching.
Epithelial glands, in response to irritation, begin to produce more mucus in order to wash off the pathogenic flora from the surface of the vaginal walls. When leukocytes die en masse, the discharge becomes purulent. The capillaries are destroyed, so blood can be seen in the mucus. If infectious agents have become the cause of inflammation, then the discharge acquires an unpleasant odor. It indicates specific inflammation.
Varieties of vaginitis
Depending on how long the inflammation lasts for a woman, the following types of vaginitis are distinguished:
Acute inflammation. It lasts no more than 8 weeks.
More acute inflammation. It lasts longer than 8 weeks, but not more than 6 months.
Chronic inflammation. It lasts over half a year. Periods of exacerbation are replaced by phases of remission.
Depending on the nature of the inflammation, the following types of vaginitis are distinguished:
Purulent vaginitis. The discharge will be thick, with an unpleasant odor. Their color varies from yellow to green.
Mucous vaginitis. The discharge is cloudy, thick and viscous.
Serous vaginitis. The discharge is liquid and clear.
Symptoms of vaginitis

Depending on the cause that led to the development of vaginitis, its symptoms will vary. In this case, the disease rarely leads to a deterioration in the general well-being of a woman. Body temperature does not exceed subfebrile marks. If it rises to high values, and intense pain occurs in the vaginal area, then this indicates a severe inflammatory process with spread to the uterus and fatty tissue.
Symptoms of bacterial vaginitis
This inflammation is caused by opportunistic aerobic bacteria. Such microbes do not need oxygen in order to reproduce. Normally, they are always present on the surface of the skin, but their number is small. When the female body is weakened, these bacteria increase. They are able to penetrate the vagina and begin to actively multiply there. At the same time, the patient develops purulent discharge, which has a yellow-green color and an unpleasant odor.
During the examination of the organ, the doctor visualizes areas of redness and swollen walls. They are covered with purulent mucus. The smear will reveal epithelial cells that are surrounded by a dense layer of bacteria. The number of Dederlein sticks has been reduced. Sometimes they are missing. The disease often becomes chronic. Over the years, a woman will notice a slight yellowish discharge.
Symptoms of trichomonas vaginitis
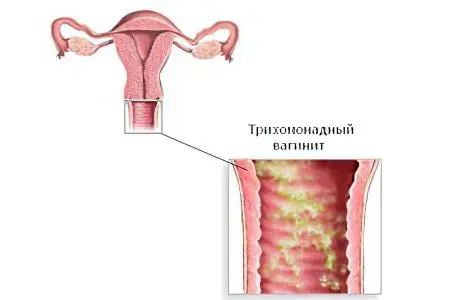
Vaginitis caused by Trichomonas develops a few days after intercourse without a condom (provided that the partner was infected). Sometimes before the onset of the first symptoms of the disease, 3 days pass, and sometimes a month. As soon as there are many bacteria in the vagina, corresponding clinical signs will appear.
Discharges are frothy. They give off an unpleasant odor. Their color may be whitish or yellow. The woman experiences itching in the perineum and pain in the lower abdomen.
Trichomonas have flagella with which they can move. If the disease is not treated, then the bacteria will spread to the uterus, ovaries and even the abdominal cavity. The symptoms of the disease will increase in intensity. The pain will become unbearable. Body temperature will rise to feverish levels. Menses become irregular.
When examining the vagina, the doctor visualizes inflamed and red walls, which are covered with foamy secretions. The latent course of a disease is less often observed. In this case, vaginitis reveals itself only as a slight inflammation of the epithelium of the organ.
Symptoms of gonorrheal vaginitis
Gonococci are sexually transmitted. Inflammation develops 3 days after unprotected intimacy. The woman feels pain and burning in the vaginal area, the discharge becomes purulent. White films can be seen in them. They are represented by areas of the epithelium of the mucous membrane, which, with gonorrheal vaginitis, begins to exfoliate.
The walls of the vagina are edematous, have a bright color. They have views of raspberry papillae. When the disease has a severe course, films will be visible on the surface of the organ. If you remove them, then erosion is visible under them, which bleed and do not heal.
Symptoms of candidal vaginitis
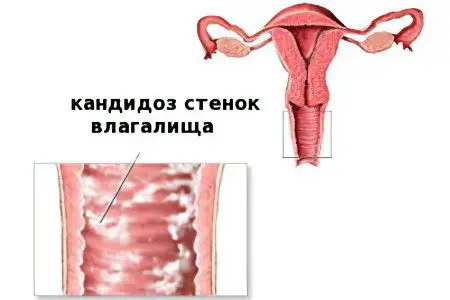
This vaginitis is provoked by fungi of the genus Candida. They are sown in a smear in every fifth woman. Inflammation develops only in those patients whose immunity fails. The impetus for the manifestation of the disease is metabolic failures and hormonal imbalance.
The first symptom of candidal vaginitis is dryness and itching of the vagina. The external genitalia become edematous, which indicates developing vulvovaginitis. A few days later, the woman notices that the nature of the discharge is changing. Curd clots appear in them, which resemble grains of cottage cheese. Mucus has a sour smell. Sometimes there are a lot of secretions, and sometimes they are absent.
Vaginitis of this type often develops before the next menstruation or during childbearing. Often the disease becomes chronic.
Symptoms of atrophic vaginitis
This vaginitis is a companion of women who have entered the menopausal period. Patients complain of intense itching. The vagina becomes dry, the discharge is odorless, there are very few of them.
The doctor visualizes the pale mucous membrane of the vagina, which gives off yellowness. There are bruises on its surface. The disease may be accompanied by the formation of adhesions.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of vaginitis appear, you should consult a gynecologist. The doctor will examine the woman using mirrors. He will then assess the acidity level of the vagina. This test is performed using a litmus strip. Violation of the microflora of the vagina is diagnosed at a pH above 5.
A smear taken by the doctor from the walls of the vagina is sent to the laboratory. There it is examined on various nutrient media. Overgrown colonies of bacteria allow you to make a diagnosis and choose a treatment. If there is a suspicion of sexual infections, then a PCR test is performed.
Treatment of vaginitis
Treatment is carried out at home. A sick leave is not issued to a woman; she can continue to go to work. If the disease was provoked by a sexual infection, then both partners should receive therapy.
At the time of treatment, you need to refrain from intimacy. In addition to eliminating the inflammatory reaction, it will be necessary to restore the vaginal microflora and eliminate the cause of vaginitis. For this, all chronic infections are treated. It is important to stop using aggressive personal care products that can provoke an allergic reaction. Patients with diabetes should receive appropriate insulin therapy. Treatment can be carried out both with local preparations and by taking medicines inside.
When antibiotic treatment is completed, the patient is prescribed suppositories with beneficial bacteria to restore the microflora of the vagina. The second stage in the form of a probiotic is essential for thrush in order to restore the intimate microflora and reduce the risk of repeated exacerbations, as well as maintain local immunity. If you do not make a quick recovery, activation of conditionally pathogenic microflora is possible, which will lead to an exacerbation of thrush or bacterial infections. For the same reason, antifungal therapy for thrush may not be effective enough. Therefore, after the first stage of treatment aimed at eradicating the infection, it is important to carry out the second stage – to restore the balance of beneficial microflora.
Douching (a glass of water + 2 teaspoons of soda) may also be recommended for a woman.
The most difficult thing is to cope with vaginitis, which has become chronic. Such patients are shown undergoing physiotherapy (UHF, electrophoresis, magnetotherapy). They are also prescribed immunomodulators and vitamins. A woman can be sent to a specialized sanatorium.
[Video] Obstetrician, gynecologist Kuznetsova Tatyana Semenova from the Moscow Doctor clinic talks about vaginitis:









