Contents
What is purulent arthritis?
Purulent arthritis – inflammation in the joint cavity, which is caused by pyogenic microbial agents. Purulent arthritis is dangerous because it causes the development of other more serious and serious diseases: arthrosis, contractures. In some cases, it can lead to the development of a number of infections, for example, an abscess, phlegmon, sepsis. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent these complications.
In most cases, the causative agent of the disease is staphylococcus aureus. Due to the activity of this bacterium, purulent arthritis develops in 80% of cases. Gonococci, streptococci, meningococci, pneumococci are also the causative agents of this disease.
However, they become the cause of its development much less often: only in 20% of cases. Purulent arthritis affects both adults and children, in whom it is extremely difficult to determine the causative agents of the disease.
Causes of purulent arthritis
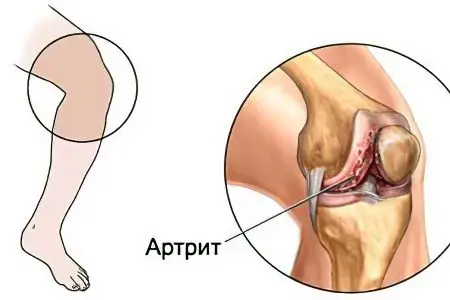
Purulent arthritis develops as a result of infection in the joint cavity. This can happen in several ways. Contact spread involves the introduction of infection through a non-penetrating wound in the joint area, abrasions and suppuration. Osteomyelitis of the bone, abscess, phlegmon of the surrounding tissues can also contribute to the entry of arthritis pathogens into the body.
In addition, there are such ways of infection as lymphogenous and hematogenous. Favorable conditions for the pathogens of purulent arthritis to enter the body in this case are created by abscess, sepsis, osteomyelitis and phlegmon. Some diseases that are accompanied by bacteremia, such as erysipelas, pneumonia, gonorrhea, typhoid fever, also cause arthritis.
Symptoms of purulent arthritis
The development of purulent arthritis in most cases is acute. The first symptoms appear unexpectedly. Usually, the joint is red, swollen, and feels hot to the touch. The patient experiences acute pain, which quickly increases and soon makes even simple movements impossible. After a few days, there is swelling of reactive tissues located above and below the joint.
Among the main symptoms, the general signs of intoxication of the body are pronounced: fever, high temperature, chills, nausea and severe headaches. Patients with purulent arthritis experience weakness and malaise, their pulse quickens. On examination, swelling and a characteristic shade of the skin below the joint area are clearly visible. As a rule, the acute development of purulent arthritis is preceded by an infectious disease, a serious injury or a purulent process.
Types of purulent arthritis
Purulent arthritis, depending on the causes that caused it, is of two types:
non-traumatic nature – its treatment is carried out by surgeons;
traumatic nature – in this case, arthritis is caused by infections that have entered the bloodstream due to injury or an open wound. With arthritis of this type, you should contact a traumatologist.
There is another classification of purulent arthritis.
In accordance with it, they can also be of two types:
primary – the cause of such arthritis is infection directly in the joint tissue. This can occur as a result of an open fracture, dislocation, penetrating injury. The causative agent of purulent arthritis often enters the joint cavity during surgery and during puncture;
secondary – the infection is introduced through the surrounding tissues and lymph.
Diagnostics
To determine purulent arthritis allows palpation and external examination. The joint has a forced position, practically does not move, its functions are impaired. On palpation, the patient experiences severe pain. The results of a biochemical blood test show the presence of acute inflammatory processes. This is expressed in an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and the leukocytosis formula shifts to the left. As part of the diagnosis, a puncture of the joint fluid and instrumental studies are also performed.
If there is a suspicion of purulent arthritis, an x-ray is mandatory. This research method may not be very informative in the early stages of the disease. However, the possibility of developing an inflammatory process cannot be ruled out. Its symptoms may appear later.
Treatment of purulent arthritis
Treatment of patients with purulent arthritis involves urgent hospitalization. The main method of combating inflammation is medication. The most effective drugs in this case are antibiotics. They are used in the initial stages of the development of purulent arthritis. As part of conservative treatment, in this case, a plaster is applied to the affected joint, a puncture is performed, and then antibiotics are administered. These measures are appropriate in case of synovitis without pus. Synovitis is an inflammatory process in the synovial membrane, in which the joint cavity is filled with fluid.
If a significant amount of pus accumulates in the joint cavity during arthritis, an arthrotomy is required. This is a surgical intervention during which the joint is opened or exposed, which is necessary for further drainage. As a result of such surgical intervention, purulent formations and dead tissues are removed from the joint cavity.
Purulent arthritis may be accompanied by the development of sepsis, that is, a general infection that is caused by the penetration of pathogens into the blood. To stop the inflammatory process, it is required to remove the source of infection surgically. In this case, a resection of the joint is performed. During the operation, the damaged articular ends of the bones, cartilage and synovial membrane are excised. Between the ends, which are artificially given a natural shape, fabrics are laid to prevent fusion. Resection allows you to stop the inflammatory process and maintain joint mobility. After the operation, a plaster is applied for some time. After its removal, it is necessary to carry out therapeutic exercises in order to fully restore the mobility of the joint and its function.










Плегмонаны операциядан кейін қалай емдейміз түсіндіресізбе?