Contents
Osteoporosis – This is a disease of bone tissue, increased fragility of bones due to a lack of calcium. For a patient with osteoporosis, even minor injuries can result in a fracture. The occurrence of osteoporosis, as a rule, occurs due to metabolic disorders.
Suppose a person stumbled, unsuccessfully opened a heavy door, or dropped a heavy book on the floor. For a patient with osteoporosis, any situation that seems simple can end very badly – a fracture. Women are more susceptible to this disease, especially during the period of hormonal failure, with menopause, men suffer from this disease much less frequently.
Most often it occurs in women who have experienced the onset of menopause and are in the menopause period. It is they who are in the “risk group” who should be especially attentive to their health and take into account all manifestations of the disease.
A very interesting video in which you will learn the true essence of osteoporosis and how to protect yourself from fractures?
Degrees of osteoporosis
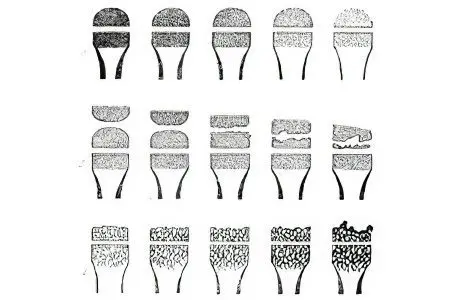
Determine the severity of osteoporosis, such as:
the primary degree, which is revealed in a decrease in bone density. X-ray diagnostics reveals significant transparency of the X-ray shadow and striated silhouettes of the vertebrae. This degree of illness is determined exclusively during medical research;
osteoporosis of the secondary degree, or moderate – an obvious decrease in bone density. In this case, the vertebral bodies acquire a specific biconcave shape, a wedge-shaped deformation of one of the vertebrae is formed. This degree of illness is manifested in the strongest painful sensations;
pronounced osteoporosis, or tertiary degree – there is a sharp transparency of the vertebrae during x-ray examination. Otherwise, it is called glazing and the presence of a wedge-shaped deformity at the same time in several vertebrae. At this stage, osteoporosis is already evident.
Osteoporosis of the hip joint
This form of this disease is known as osteoporosis of the hip joint. According to its genesis, it is no different from osteoporosis of other bones, except for localization in the area of the same name. The most vulnerable place in this manifestation of the disease is the neck of the femur. A fracture of the presented area in older people quite often ends in death or the inability to move in the usual normal mode.
In the vast majority, only endoprosthetics makes it possible to fully restore the functioning of the hip joint.
Osteoporosis of the presented type can have the following three types of localization:
local – at the same time, there is a decrease in the degree of density of bone tissues and the tip of the femur at the initial stage of such ailments as specific necrosis of the tip of the femur and Perthes’ disease;
regional – it is formed exclusively with arthrosis of the hip joint;
common – gets its development in connection with circulatory dysfunction in the lower extremities.
Osteoporosis of the hip joint can be formed as a result of systemic osteoporosis, which is much more typical for this disease.
With the presented form of the disease, bone tissues lose the ability to maintain optimal physiological loads. The total defeat of the hip and knee joints in this case is provoked by the fact that it is mainly on them that the most significant load “falls” in the process of movement.
Osteoporosis of the hip joint begins to develop for a whole list of reasons:
prolonged loss of motor functions of the lower extremities during the long-term treatment of fractures, dislocations and other injuries. This causes atrophy of motor functions, which is almost impossible to bring to a normal state;
a significant load on one limb in the event that the work of the second was removed or disrupted. This option also negatively affects the functioning of a certain limb, as a result of which it loses muscle memory;
complication of blood circulation in some specific conditions. We are talking about burns, frostbite, phlegmon (inflammatory or purulent decomposition of tissues) and others, which also become catalysts for muscle and tissue atrophy;
transient osteoporosis should be considered a special form of osteoporosis of the hip joints in women. It is formed in females in the later stages of pregnancy and in men aged 30 to 40 years.
It is possible to detect this form of the disease on an x-ray or on palpation (in some cases). Timely detection is very important, because this will make it possible to start adequate treatment as early as possible.
Regardless of the causes of the manifestation of the presented disease, the mandatory components of the treatment process should be considered, first of all, physiotherapy exercises. It is it that makes it possible to bring metabolic processes in bone tissues “in shape”, to regulate the degree of joint mobility and muscle activity. Such recovery takes a very long time, and the older the person, the more complications it passes.
A strict, well-balanced nutrition schedule and frequent exposure to passive and active sun are very important. The second makes it possible to make the production of vitamin D faster, and, accordingly, strengthen bone tissue. It is also allowed to take medications, but only as prescribed by a specialist. These can be both drugs containing calcium and vitamin D3 (or its other metabolites), and bisphosphonates. It is undesirable to take any hormonal preparations for those women who have reached the age of over 70 years. However, sometimes this is the only way to bring the structure of bone tissue back to normal.
Diagnosis of osteoporosis
A sufficient number of methods have been developed by which the diagnosis of osteoporosis is carried out. Radiography makes it possible to detect depletion of bone tissue only when their loss has reached more than 30%. Therefore, it makes sense to resort to this method only in the secondary degree of the disease.
A more modern method, which is almost always carried out in osteoporosis, is the analysis of the height of the spine and the calculation of their relationship. Densitometry should be considered the optimal method. This is what makes it possible to accurately indicate the degree of bone density, the ratio of calcium in the human body, as well as the number of muscle and fat deposits.
This method should be considered the safest, because only it does not use the so-called isotope methods of irradiation, which are clearly harmful to humans. It is based on the determination of skeletal density and reveals the mineral and other active components of bone tissue. Its advantage is the speed of obtaining results and perfect painlessness.
Also, one should not underestimate the standard blood and urine tests, which make it possible to realistically assess the state of the phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
This helps with information such as:
General analysis of calcium is one of the fundamental specific components of bone tissue, the most important trace element that takes part in the creation of the skeleton, the functioning of the heart muscle, nervous and muscular activity, as well as blood clotting and all other processes. Variations in the form and stage of osteoporosis are manifested in various shifts in the degree of calcium concentration. The optimal indicators of calcium: are as follows: from 2,2 to 2,65 mmol per liter.
Inorganic phosphorus is a component of the mineral substance of bone tissue, which is present in the human body as salts (calcium and magnesium phosphates) and takes part in the process of bone tissue formation and cell-type energy metabolism. 85% of all phosphorus is located in the bones. Modifications in terms of the ratio of phosphorus in the blood can be noted in all kinds of changes in bone tissue, it is not only about osteoporosis. The optimal indicators of phosphorus should be considered from 0,85 to 1,45 micromoles per liter.
The substance parathyroid hormone, which is produced by the parathyroid glands and is responsible for the exchange of calcium and phosphorus type in the body. Identification of the concentration of parathyroid hormone can provide the most important information base for identifying various forms of osteoporosis. The optimal parameters of parathyroid hormone are from 9,5 to 75,0 pg per ml. This is between 0,7 and 5,6 pmol per litre.
Deoxypyridonolin, which is referred to as DPID, is a designation for the degree of destruction of bone tissue. It can be found in urine. Urinary expression increases with postmenopausal osteoporosis, osteomalacia, thyrotoxicosis, initial hyperparathyroidism.
Optimal PIID values vary by gender:
for males, this is from 2,3 to 5,4 nmol;
for a woman, from 3,0 to 7,4 nmol.
Osteocalcin is the main specific protein of bone tissue, which takes an active part in the process of bone repair and the development of a new tissue of this type. Excessively high levels of osteocalcin are present at the initial stage of hyperparathyroidism, in those who are sick with hyperthyroidism and acromegaly. With osteoporosis of the postmenopausal type, it is within the optimal range or increased. In osteomyelia and renal osteodystrophy, the ratio of osteocalcin decreases. The presented examination is necessary to detect osteoporosis and control treatment, with an increase in the ratio of calcium in human blood.
The optimal indicators of osteocalcin are as follows:
men – from 12,0 to 52,1 ng per ml;
women in the premenopausal period – from 6,5 to 42,3 ng per ml;
women in the postmenopausal period – from 5,4 to 59,1 ng per ml
Thus, in the process of diagnosing osteoporosis in women, it is important to pay attention to any fluctuations in the data and to carry out all available studies. This will make it possible to make an accurate, timely diagnosis and, as a result, receive optimal treatment that will help in the shortest possible time.
How to treat osteoporosis?

Osteoporosis is treated with medication, people with endocrine disorders are prescribed drugs that will help restore hormonal levels. Elderly people are prescribed nutritional supplements rich in calcium and vitamin D. Women in menopause are prescribed hormone replacement therapy, as well as bisphosphonates.
Also, patients can sometimes be prescribed physiotherapy exercises, massage, all this in small dosages – due to the fragility of the bones. They can, if necessary, write out the wearing of special supporting corsets.
It is not possible to fully treat osteoporosis, but it is possible to learn to live with it and stop the further development of the disease. To do this, there is a need for walking, jogging, dancing. All this can provide the bones with the healthy “stress” they need and make them stronger. Such exercises will give you the opportunity to strengthen muscles and modify coordination and balance.
Another way to treat osteoporosis, which is recommended for all women, should be considered a “healthy” diet with an individually selected ratio of calcium and vitamin D. It is best to refer to a balanced diet, which is based on the postulates of the food pyramid.
It is especially necessary in this case to make sure that the patient receives the required amount of not only calcium, but also vitamin D. This can occur both in the process of eating food and when using nutritional supplements.
A detailed and visual video on how to properly treat osteoporosis?









