Contents
Most people use the term “jaundice” to understand hepatitis, or Botkin’s disease. In fact, this word is used to denote a number of pathological changes that can affect not only the liver, but also other organs. However, the appearance of jaundice is always associated with a violation of bilirubin metabolism, which can occur for various reasons.
What is jaundice?
Jaundice is a series of symptoms that manifest as yellow discoloration of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes, which is associated with excessive accumulation of bilirubin in the body. Normally, this substance is released during the breakdown of red blood cells, which occurs in the spleen. Then bilirubin moves to the liver and, after participating in metabolic processes, leaves the body.
If any stage is violated, bilirubin accumulates in the blood, which leads to staining of the sclera and mucous membranes in yellow. Why is this happening? During the breakdown of hemoglobin, a yellow pigment is produced in the body. In the normal state, it leaves the body in the process of defecation. With the development of jaundice, which is accompanied by liver failure and obstruction of the biliary tract, quite a lot of bilirubin remains in the blood. At the same time, a small amount of this substance is excreted through the skin or kidneys.
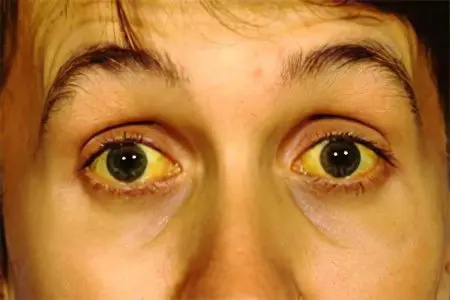
This disease is one of the most common. Jaundice is especially common in countries with a warm climate and unfavorable sanitary conditions. For example, in Central Asia, almost every child manages to get sick with this disease. In Eastern European countries, the prevalence of the viral form of the disease is 250 people per 100000 population per year.
Jaundice is what hepatitis?
Most often, jaundice is popularly called hepatitis A, or Botkin’s disease. This is a viral pathology, which is accompanied by general intoxication of the body and disruption of the liver. In addition, there are viral hepatitis B and C, as well as autoimmune, mononucleosis, toxic, bacterial, medicinal forms of the disease.
The incubation period for the development of jaundice can last for several months. Depending on the duration, the disease can be acute, protracted or chronic.
Symptoms of jaundice
Common signs of the disease in adults include the following:
yellowness of the skin;
an increase in the size of the liver and spleen;
an increase in the content of red blood cells in the blood;
the appearance of a venous network in the abdomen.
In adulthood, jaundice can manifest itself as severe itching of the skin, changes in the color of urine and feces. Due to the high concentration of bilirubin in the body, the feces acquire a grayish tint, and the urine becomes very dark. A person loses his appetite and often experiences severe pain in the right hypochondrium, which may be spasmodic or pulling in nature.
Causes of jaundice
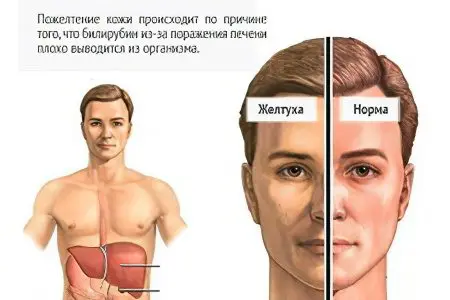
There are quite a few factors that can trigger the appearance of jaundice in an adult:
formations in the liver of a benign or malignant nature;
congenital pathologies of the structure of the biliary tract;
infection with parasitic microorganisms;
pathology of the liver and gallbladder;
postoperative complications;
the use of certain groups of drugs.
If we talk about the threat of infection with viral hepatitis A, then the following categories of the population are at risk:
people whose close relatives are infected with the virus;
people who have had sexual contact with an infected person;
people who are going to visit a country with a high prevalence of this virus;
people who use drugs.
Types of jaundice
Symptoms and methods of treatment of jaundice directly depend on the type and stage of the disease. There are many forms of this pathology, which differ depending on the cause of occurrence.
Conjugative jaundice
This form of jaundice does not act as an independent disease – it is associated with a violation of the conversion of indirect bilirubin, which leads to a sharp increase in its content in the body. This phenomenon is more typical for newborn children, since their metabolic processes are still imperfect. However, sometimes this form of jaundice is diagnosed in adults. It usually develops as a result of exposure to the liver of negative factors – for example, the use of drugs. Also, conjugational jaundice can be the result of congenital pathologies, among which it is worth highlighting the Gilbert-Meulengracht syndrome.
Hemolytic jaundice
The pathological destruction of red blood cells, the accumulation of excess amounts of bilirubin and the difficulty in removing it from the body lead to the development of this form of disorder. This condition can be provoked by various disorders and pathologies – anemia, lymphocytic leukemia, tropical malaria, lymphosarcoma. Also, hemolytic jaundice can be the result of the toxic effect of drugs on the body.
Physiological jaundice
This type of jaundice is typical for newborns and is associated with the child’s adaptation to new conditions of existence. Most often, the physiological form of the disease develops due to the immaturity of the enzyme system. In addition, it may be associated with impaired bilirubin metabolism. In most cases, jaundice occurs in premature and debilitated babies. This condition is characterized by yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as high drowsiness of the baby.
neonatal jaundice
This type of jaundice also occurs immediately after birth and is associated with the accumulation of a high amount of bilirubin in the blood. This violation is very common and may be due to enzymatic immaturity of hepatocytes, increased production of bilirubin and insufficient serum ability to bind this substance. In some cases, the pathology needs immediate treatment. Indirect bilirubin is a neurotoxic poison, and sometimes it can lead to damage to the cerebral cortex and subcortical nuclei.
Parenchymal jaundice
This type of disease is considered very common. It is associated with a violation of the structure and functioning of hepatocytes – liver cells. The main diseases that provoke the appearance of parenchymal jaundice are acute viral hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver. As a result, the size of the liver increases in the patient, the skin first becomes yellow, and then acquires a reddish tint. At the same time, telangiectasias appear on the body, which are spider veins.
Hepatic jaundice
This disease is a consequence of a malfunction of the liver cells, which can be triggered by an increase in the volume of direct bilirubin in the blood. Viral hepatitis, drug-induced liver damage, cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, malignant tumors in the liver can lead to the development of hepatic jaundice. Most often, this form of the disease is accompanied by icteric staining of the skin, loss of appetite, nausea, pain in the right hypochondrium, discoloration of urine and feces. The choice of tactics of therapy is carried out depending on the cause that provoked the development of hepatic jaundice.
Diagnosis of jaundice
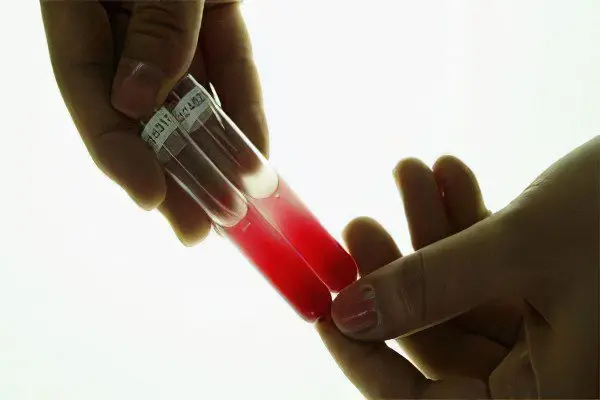
If symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Thanks to the means of modern medicine, this violation can be quickly eliminated.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the specialist will prescribe the following studies:
General and biochemical blood test.
Tests to determine the content of bilirubin in the blood.
Liver studies.
Liver biopsy – allows you to determine the nature of the disease and assess the severity of organ damage.
Treatment of jaundice
Treatment methods for pathology directly depend on its form and stage of development. For therapy to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to establish the cause of the development of the disease. In any case, to eliminate the symptoms of jaundice, conservative treatment can be used to help cope with the underlying disease, and surgical intervention is usually required in advanced cases and consists of liver transplantation.
Conservative therapy includes the following components:
The use of drugs – antihistamines, steroids.
Plasmapheresis
Phototherapy.
Compliance with a diet.
The goal of treatment is to get rid of the virus, prevent cirrhosis of the liver, and reduce the risk of infecting others. If a person develops a chronic form of autoimmune hepatitis, treatment with corticosteroids is indicated.
If therapy is not started on time, the pathological process can develop so strongly that doctors fail to achieve a period of remission. In this case, dangerous complications appear, the elimination of which is impossible without liver transplantation.
Sometimes a person develops obstructive jaundice, which is associated with a violation of the outflow of bile. If it is benign and appears as a result of the formation of stones in the bile duct, endoscopic papillosphincterotomy is used – this procedure helps to remove about 90% of the stones in the bile duct. If obstructive jaundice is associated with malignant tumors, the patient is shown radical treatment. Typically, such patients undergo palliative surgery, which is aimed at reducing the level of cholestasis.
With the development of viral hepatitis A, patients recover without treatment. In this case, antiviral drugs are not prescribed, and the drugs used in modern medicine are not aimed at fighting the virus, but at reducing the concentration and cleansing the body of harmful substances that have arisen as a result of impaired liver function.
In this case, patients can be given detoxification solutions, glucose, and vitamins. It also shows the use of hepatoprotectors – drugs that are designed to protect liver cells.
In difficult cases, the principles of treatment remain the same, but much more attention is paid to symptomatic therapy. As a rule, liver function is fully restored over time.
To speed up the healing process and restore the normal exchange of red blood cells, you must adhere to a special diet. A person must necessarily consume foods containing proteins, iron, B vitamins. This category includes fish and poultry meat, eggs, dairy products. It is also worth including dried apricots and grain bread in the diet.
To restore the processes of hematopoiesis, folic acid is needed. Its sources are green vegetables, liver, yeast, cabbage, legumes. Fiber is no less important during this period, and therefore oatmeal should be present in the diet. In addition, it is worth eating raw and boiled vegetables – cucumbers, tomatoes, carrots, cabbage, zucchini. It is equally important to consume enough fruits and juices.
Regardless of the type of jaundice, a person needs to stop drinking alcohol, fatty and spicy foods – they all put an additional burden on a weakened liver. With the development of this disease, it is recommended to eat small portions.
Jaundice in adults is a fairly common group of disorders that can be associated with various diseases. In any case, the appearance of yellowness of the skin and pain in the right hypochondrium should be the reason for an immediate visit to the doctor. Only timely treatment will help to cope with the disease in a short time and avoid negative health consequences.









