What is a hemothorax?
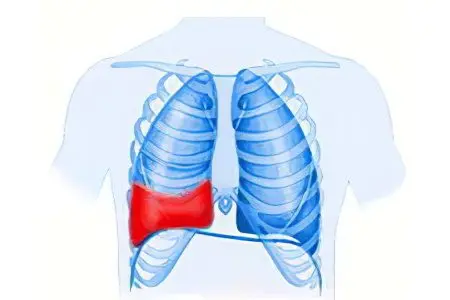
Hemotorax – this is an accumulation of blood in the slit-like space, which is located between the visceral and parental layers of the pleura of the lung. This area is also called the pleural region, which normally contains a small amount of serous fluid. The Big Encyclopedic Dictionary characterizes hemothorax (derived from the Greek thorax – chest + haima – blood) as an accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity due to internal bleeding.
When the pleural region is filled with blood due to a number of reasons, the lung is compressed, and organs such as the thymus gland, trachea, aortic arch and its branches, the upper vena cava with main tributaries are shifted in the opposite direction.
Doctors distinguish hemothorax from the place of accumulation of blood and its amount:
large or total hemothorax, when incoming blood fills the pleural region completely;
apical – blood accumulates in the region of the apex of the lung;
small – the level of filling with blood does not reach the angle of the scapula;
interlobar – blood is in the interlobar cracks;
supradiaphragmatic – blood is located in the pleural region adjacent to the diaphragm;
limited or encysted – the blood is in the pleural region, limited by adhesions;
paracostal – blood is located in the area next to the ribs;
paramediastinal – blood is in the area adjacent to the organs of the mediastinum;
clotted – the accumulated blood has undergone clotting.
The severity of hemothorax and the overall clinical picture is determined depending on the volume of blood entering the pleural region, the total amount of blood loss, the degree of compression of the intrathoracic organs and the presence or absence of infection.
Most often, the cause of hemothorax is a chest injury, with a violation of the integrity of the vessels, but there are other factors that cause the accumulation of blood.
Causes of hemothorax
Experts identify several reasons leading to the development of a pathological condition, namely:
The occurrence of accumulation of blood due to a closed or open chest injury. Most often they occur due to road accidents, gunshot or stab wounds, rib fractures, falls from a height or other torcal injuries (according to statistics, in 70% of cases, injuries are right-sided). Blood in the pleural region accumulates due to damage to various organs of the chest (diaphragm, heart, lungs) or abdominal cavities (liver, spleen), as well as intercostal vessels, aortic branches or internal mammary artery.
Less common, but still occurring grounds for the occurrence of hemothorax, can be a variety of serious diseases. Tuberculosis and cancer of the lung or pleura, aortic aneurysm (expansion and then rupture of its section due to a number of reasons), benign and malignant neoplasms in the chest wall or in the organs of the mediastinum, hemorrhagic diathesis, pulmonary infarction, bleeding disorders (coagulopathy) – all these diseases can become pathological causes that can lead to the development of hemothorax.
Hemothorax can occur as a result of surgery, performed operations on the lungs and pleura, drainage of the pleural region, as a result of taking diagnostic or therapeutic pleural punctures (thoracocentesis), installing a catheter on the central veins. These are the so-called iatrogenic causes of hemothorax.
In general, the causes of hemothorax can be divided into three main groups: traumatic, pathological, and iatrogenic.
Symptoms of hemothorax

Depending on the strength of the bleeding, the amount of blood poured out, the displacement of the environmental organs and the compression of the lung, the symptoms will be more or less pronounced:
If the hemothorax is small and the blood has not reached the level of the scapula, then the victim may complain of pain in the chest, which intensifies during coughing, as well as mild shortness of breath.
With a large or medium-sized hemothorax, the symptoms manifest themselves quite clearly. A person complains even with calm breathing and a slight cough of sharp, severe pain in the chest region with irradiation to the shoulder and back, general weakness occurs, pressure drops, shallow breathing increases. Without treatment, respiratory and cardiovascular disorders continue to worsen, even with little physical exertion, the victim experiences severe pain, cannot be in a horizontal position and is forced to take a sitting or semi-sitting position.
Severe hemothorax is characterized by symptoms such as: tachycardia, dizziness, fainting, cold sweat, severe chest pain, anemia, pallor of the skin.
If hemothorax is accompanied by a fracture of the ribs, then subcutaneous emphysema, soft tissue hematomas often occur, and hemoptysis appears when the lung ruptures.
If the outflowing blood has clotted, a person feels severe shortness of breath and unbearable pain in the chest, the lung tissue is subjected to sclerotic processes, and the respiratory function is impaired.
With an infected hemothorax, fever with severe chills, lethargy, general intoxication of the body appears.
Regardless of the severity of the hemothorax, there will always be a violation of breathing and pain in the chest region. To diagnose the severity and clarify the diagnosis, an x-ray or computed tomography is performed, which is a more reliable way to detect accumulated blood. In addition, it is possible to additionally identify the cause that caused hemothorax, for example, to detect a tumor. If necessary, doctors take a puncture of the accumulated blood, this allows you to detect bacteria or fungi, as well as the type of cells.
Treatment of hemothorax

Modern methods of treatment allow not only to quickly identify, but also to eliminate hemothorax. Naturally, the choice of treatment methods will depend on the type of hemorrhage, the severity of symptoms, and the causes of hemothorax.
Small hemothorax can be eliminated by conservative methods: symptomatic treatment, immunocorrection, antibiotics, and antiplatelet therapy are prescribed. Bleeding is promptly stopped. If a small amount of fluid has accumulated, then the human body is able to cope with this condition on its own within about 2 weeks. But at the same time, the patient must be under constant monitoring in order to exclude the possibility of re-bleeding or the occurrence of a bacterial infection.
If blood aspiration is required, then thoracocentesis or drainage of the affected area is performed. Antibiotics, antiseptics and proteolytic enzymes are introduced inside. Surgical intervention is carried out with clotted hemothorax, in cases where the expansion of the lung is impossible and vital organs are affected. If large vessels are damaged, then the operation is performed on an emergency basis by a thoracic surgeon.
The success of treatment depends on the type of injury or the nature of the disease that caused the hemothorax. Timely seeking medical help gives more chances for the successful elimination of accumulated blood and for an uncomplicated course of the disease. Prevention of hemothorax consists in preventing injuries and seeing a doctor if there is a risk of its occurrence due to various diseases.









