Contents
What is foot fungus?
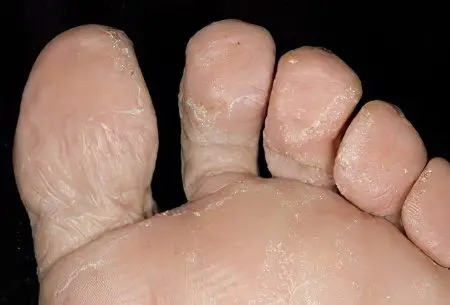
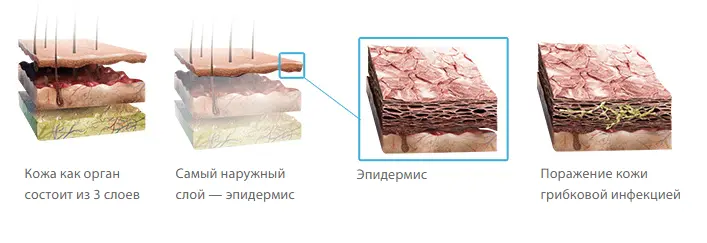
Foot fungus is a mycotic lesion of the skin of the interdigital spaces with the possibility of including the toenails (onychomycosis) in the pathological process and further spreading to other parts of the human body. This disease is caused by infection of the skin of the legs with microscopic fungi – dermatophyte, yeast and mold. Any fungal skin lesions can be combined into a group of diseases called “dermatomycosis”. See also: Causes and symptoms of dermatomyositis.
According to statistics, fungal diseases of the feet in Russia alone affect 20% of the total population of the country. Almost 500 species of mycotic organisms that exist in nature represent a potential danger to humans. All of them, under certain conditions, are able to parasitize on the human body and inside it, contributing to the development of local and systemic fungal pathologies.
Fungal infection of the feet causes a change in the structure of the skin, and later on the nails. The severity of symptoms will depend on the type of fungus that led to the disease. Often the pathology is accompanied by peeling, layering of skin scales, severe itching. Perhaps the accession of inflammation.
Foot fungus symptoms
Symptoms of foot fungus will depend on the type of pathogen and the degree of involvement in the pathological process of the skin and nails.
Symptoms of a foot fungus with a lesion with trichophyton red:
Manifests the disease by lesions of the interdigital folds. Moreover, the initial place of localization of rubrophytia is the closest folds of the feet – between the third and fourth fingers. After that, the soles, lateral and dorsal surfaces of the feet are sequentially involved in the pathological process, the infection can pass to the palms and nails;
The skin becomes dry, thickens. The formation of furrows is characteristic. As the disease progresses, the stratum corneum thickens to coarse calluses, the cracks become deeper, painful sensations join;
Peeling of the skin is floury or lamellar;
Most of the patients complain of itching that disturbs them;
An erased clinical picture is possible with exudative variants of rubrophytosis, including intertriginous (flowing like diaper rash), dyshidrotic (with the appearance of blisters) and mixed interginous-dyshidrotic lesions. The cracks between the fingers are hardly noticeable, the peeling is superficial, itching is mild. In this form, the disease can exist for a long time, so a person often does not seek medical help;
Sometimes there is leukonychia – the appearance of white stripes and spots on the nails;
In addition to feet, large skin folds, for example, buttocks, inguinal, under the mammary glands, can be affected by the fungus;
The fungus of the feet occurs with multiple lesions of the nail plates.

Trichophyton red rarely affects children, which scientists attribute to the high rate of regeneration of the skin and nail plates. In adolescence, the disease is diagnosed in 17% of cases, and young men suffer more often.
Symptoms of foot fungus in case of damage by trichophyton interdigital:
Most often, the third and fourth interdigital folds suffer, as well as the sole of the foot, its lateral surface, fingers and arch;
The inflammatory process is pronounced, has a similarity with the foot fungus described above, but never proceeds hidden;
Peeling is often accompanied by exudative phenomena;
Perhaps the development of allergic reactions with rashes on the trunk, face and limbs;
The defeat of the nails is single, it is observed more often on the first and fifth toes.
Symptoms of foot fungus, depending on the clinical form of the disease:
With the erased form of the fungus, peeling is small, often it occurs only in one interdigital fold. Cracks are small, imperceptible, superficial. The patient does not feel discomfort, does not go to the doctor;
With a squamous form, the lateral surface of the feet and the folds between the fingers peel off. Inflammation is not observed, sometimes hyperemia of the skin is possible, which is accompanied by itching. On the soles, the skin is lichenified, due to the thickening of the stratum corneum, the effect of its lacquer shine is created. In the area of natural skin furrows, lamellar peeling is observed, and the skin pattern is noticeably enhanced. However, the patient does not experience any concern about the condition of the skin of the legs, except perhaps for an aesthetic defect;
With the hyperkeratotic form of the foot fungus, dry and flat papules with cyanotic plaques form on its arches. In the center of these rashes, scaly layers are formed that have a grayish-white tint, and along their periphery there are borders with exfoliating epidermis. On closer inspection, bubbles can be visualized. Existing rashes tend to merge with the formation of large foci and the gradual capture of the entire sole. The clinical picture may resemble psoriasis. See also: Psoriasis – stages, causes, symptoms. The skin is dry, moderate itching may occur, sometimes patients complain of sore feet;
In the intertriginous form of the disease, the clinical manifestations are similar to those of diaper rash. The folds between the third and fourth, as well as between the fourth and fifth fingers, are most often affected. The skin in these places turns red, swells, maceration develops. Erosions can be deep and quite painful. The rounded borders of the affected area, their sharp severity, and the presence of whitish epithelium along the periphery allow differentiating a fungal lesion from diaper rash. Itching, soreness and burning are common subjective symptoms of this form of the disease;
With the dyshidrotic form of the foot fungus, a lot of blisters appear on the skin, which have a thickening on top. Most often they are localized on the arch of the foot. It is possible to capture large areas of the sole, interdigital folds. When the blisters open, pinkish-red erosions form on the skin, which continue to get wet. As inflammation increases, hyperemia and edema increase, which makes the dyshidrotic form of foot fungus similar to acute eczema. See also: Causes and symptoms of eczema on the leg.

Foot fungus is a chronic disease that is prone to frequent relapses. A monotonous course of a dry type is typical for elderly patients. Exacerbations predominantly occur in young and adulthood. Often the fungus is defined as a long-term process, and infection occurs even in early youth.
Symptoms of a foot fungus caused by fungi of the genus Candida:
The skin is hyperemic and edematous;
The lesion is surrounded by a rim of exfoliated epidermis;
On the periphery there are vesicles with serous contents and small pustules.
Causes of foot fungus

Foot fungus is an infectious disease. More often than others, fungal infections of the feet are caused by fungi belonging to the group of dermatophytosis. These are mold fungi-ascomycetes, 30 species of which are capable of provoking a disease – rubrophytosis or rubromycosis. They account for more than 70% of cases of foot fungus.
Approximately 10% of the world’s population suffers from athlete’s foot, which is provoked by the fungus Trichophyton mentagrophytes. It is possible that the skin of the feet is affected by mold and yeast-like fungi, but this happens much less often – in about 1,5% of cases.
Possible causes of foot fungus include:
Most healthy people (up to 28%) become infected with foot fungus while visiting public places. It can be not only saunas, swimming pools, baths, but also sports clubs, fitness centers;
Perhaps intrafamilial infection with a fungus of the foot in the presence of a sick relative who evades treatment. Most often, these are relatives of the elderly and older. The use of shared towels, slippers, personal hygiene products, baths, showers, foot mats – all this increases the risk of intrafamilial infection;
Decreased immunity leads to an increase in the number of patients with mycosis among the elderly. Moreover, men are most often ill, and their foot fungus is combined with onychomycosis. See also: Onychomycosis – causes and prevention;
Provoking factors may be environmental degradation and neglect of hygiene rules;
Uncontrolled intake of antibacterial drugs, immunosuppressants, cytostatics, glucocorticoids – all this leads to an increased risk of mycotic infection;
Occupational risk factors. There is a high possibility of infection among the attendants – these are employees of saunas, baths, showers, pools. The risk group also includes athletes, miners, metallurgists, military personnel;
Lifestyle in general;
Existing somatic pathologies;
Vascular disease;
Excess body weight;
foot pathology;
Diabetes mellitus, and the risk occurs with a symptom of diabetic foot;
Injury to the skin of the feet also increases the risk of introducing the fungus. Among the possible injuries: calluses, corns, hallux valgus, osteoarthritis.
Why is foot fungus dangerous?

If the treatment of foot fungus is absent for a long time, then it is dangerous for the development of serious consequences.
First of all, as a result of the impact of mycotic organisms and the influence of their metabolic products (pigments, toxins, enzymes, antibiotics), polyvalent sensitization develops. As a result, the number of allergic manifestations from the skin, blood vessels and mucous membranes increases. Complications from such allergic reactions are greatly enhanced and become more frequent. Formed drug resistance and intolerance to antibacterial drugs, especially the penicillin series.
Existing hay fever become more pronounced, the same applies to vasculitis. Mycogenic sensitization can aggravate the course of various forms of dermatitis (atopic and seborrheic), as well as other skin pathologies: hemoderma, psoriasis, dermatoses.
In addition, pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate through the cracks and erosion formed on the skin. Patients with foot fungus are three times more likely to suffer from pyoderma and erysipelas, accompanied by lymphostasis and elephantiasis. An additional danger of such bacterial complications lies in the fact that they are extremely difficult to treat with antibacterial drugs. This is due to acquired resistance resulting from prolonged exposure of bacteria to antibiotic substances produced by fungi.
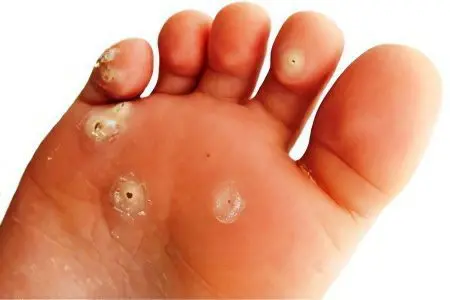
Another danger posed by untreated foot fungus is an increased risk of developing plantar warts. They very often form in places where calluses and hyperkeratosis are present. This is due to a drop in local immunity, which is unable to control the growth and development of papillomaviruses.
Treatment of foot fungus
For the treatment of foot fungus, the following drugs are used:
Griseofulvin
The main effect that allows you to get rid of foot fungus is a fungistatic effect. That is, as a result of the use of this drug, mycotic organisms cease to multiply.
Possible contraindications:
Pathology of the liver;
Pathology of the kidneys;
Oncological processes in the body;
The period of bearing a child and breastfeeding;
Leukocyte deficiency.
Terbinafine
Other drug names: Lamisil, Binafin, Termikon, Terbinoks.
It has a pronounced antifungal activity. The drug has a detrimental effect on all groups of mycotic organisms, including fungi of the genus Candida.
Possible contraindications:
Severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys;
Hematological diseases;
Malignant tumors;
Angiopathy of the vessels of the legs, obliterating endarteritis;
The period of lactation and gestation.
Fluconazole
Other drug names: Diflazon, Medoflucon, Mikosist, Diflucan, Flucoral, Mikomax, Flucostat, Flucoric, Flumed, Flumicon, Flusenil, Florcan.
It has high activity against fungi of the genus Candida.
Possible contraindications:
Age up to 4 years;
Joint reception with astemizole and terfenadine;
Severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver;
The period of gestation.
Sertaconazole
Other drug names: Sertamicol, Zilain.
It has a wide antimycotic activity against yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida and against gram-positive streptococci and staphylococci. Able to have a fungistatic and fungicidal effect.
Possible contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
During lactation, it is forbidden to apply the cream to the mammary glands.
Itraconazole
Other drug names: Irunin, Canazol, Canditral, Orgunal, Sporanox.
Allows you to fight dermatophytes, yeasts and molds. Some strains of fungi show resistance to the main active ingredient.
Possible contraindications:
Heart failure;
Breastfeeding period;
The period of bearing a child;
Pathology of the liver and kidneys;
Peripheral neuropathy;
Severe pulmonary pathologies;
Elderly and children’s age.
Econazole
Other drug names: Ifenek, Ekalin, Gino-Pevaril, Ecodax.
It has a wide antimycotic spectrum of action, is able to have bactericidal and fungicidal effects. Active against molds and yeast fungi, as well as against dermatophytes. Recommended for use in cases of fungal resistance to other drugs.
Possible contraindications:
Age up to 18 years;
Individual hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Childbearing period.
Natamycin
Other drug names: Pimafucin, Pimafucort.
It has activity against all groups of mycotic organisms that can provoke foot fungus.
Possible contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Clotrimazole
Other drug names: Vikaderm, Candid B, Antifungin, Imidil, Lotrimin, Candibene, Yenamazol, Kandil, Kanizol, Kanesten, Clomazole, Lotrimin, Clofan, Faktodin, Funginal, Fungizide, Fungitsip.
A broad-spectrum drug that is the basis for many antimycotic drugs. Only local application is possible.
Contraindications: First trimester of pregnancy.
Naftifine Hydrochloride
Other drug names: Fethymin, Exoderil.
The drug is effective against all groups of mycotic organisms that cause fungal infections of the feet. In addition, it has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Possible contraindications:
Childhood;
The period of bearing a child;
Breastfeeding period.
Prevention and care of feet with fungal infection

Prevention of the disease is reduced to the following actions:
It is necessary to maintain the state of the immune system at the proper level. To do this, it is worth abandoning malnutrition, from prolonged and uncontrolled intake of antibacterial drugs. Prevention and timely treatment of chronic infections, hypovitaminosis, avoidance of stress and overwork – all this will positively affect the body’s defenses;
It is necessary to get rid of diseases that can lead to foot fungus. Among such diseases are flat feet, leg skin injuries, including improper pedicure, and corns. It is important to avoid excessive sweating of the legs, since a humid environment is the most favorable for the development of pathogenic flora;
Avoid contact with fungi. When visiting any public places, you need to use only personal belongings, it is forbidden to wear any other people’s shoes and socks, to dry yourself with non-own towels or to wash with a common washcloth;
When there is a sick fungus in the house, it is necessary to insist on his mandatory treatment and make sure that he follows the rules for foot care;
All people require timely and high-quality foot hygiene;
If signs of the disease are detected, you should seek advice from a dermatologist or mycologist as soon as possible.
When identifying a foot fungus, you must adhere to the following care rules that will allow you not to infect other people:
Slippers must be closed. You can not walk barefoot even around the house. The infection can be transmitted through microscopic skin flakes that are easily separated from diseased feet and remain on the floor;
Shoes must be treated up to 2 times a day with antimycotic agents, for example, Gibitan, acetic acid in a 40% solution or formaldehyde in a 25% solution. It will not be possible to rid the shoes of the fungus by exposing it to sunlight or heating on the battery;
Wash your clothes separately from things belonging to healthy family members;
Feet should be washed daily and antifungal drugs prescribed by the doctor should be used;
After taking a bath, it must be rinsed with hot water and additionally treated with a disinfectant;
Important daily wet cleaning in the apartment and ventilation of the room;
Socks should be changed as often as possible, feet should be dry;
When the course of treatment is completed, you should get rid of all socks, shoes and personal hygiene products that the sick person previously used.