Contents
What is celiac disease?
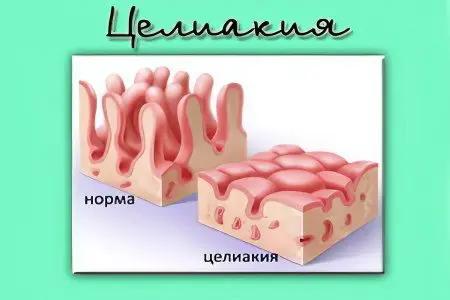
Celiac disease is a disease accompanied by intolerance to foods containing gluten. A pathological reaction to this substance gives the human intestine. The disease is congenital and is inherited. However, the full picture of its development is still not entirely clear.
Once in the intestines, gluten cannot be completely broken down, as a result, the formation of toxins. They negatively affect the walls of the body, damaging them. This process in childhood is accompanied by profuse vomiting, foamy stools, and bloating. If a child has gluten intolerance, then this can be understood immediately after the introduction of complementary foods, since a pathological reaction will occur after the food reaches the intestines.
Adults with celiac disease can be treated throughout their lives for flatulence, for stool disorders, not suspecting the true cause of persistent dyspeptic disorders.
There are some interesting facts about gluten intolerance:
People have been suffering from this pathology for many centuries, it has appeared since the moment when a person began to sow wheat, rye and other cereals for food;
Most often, the female population suffers from the disease, while there are racial differences. So, in Japan, China and Africa, celiac disease is practically not diagnosed. Scientists believe that the whole point is both in the nutritional habits of the population of these countries, and in their genetic status;
Some regions of Russia have not yet recognized celiac disease as a disease, so such a diagnosis cannot be found there;
Some foreign scientists are of the opinion that gluten intolerance significantly affects the risk of developing cancer of the digestive system, so they refer to the disease as a precancerous condition;
The risk that a child of parents who are carriers of this disease is 1:10.
Causes of celiac disease
Scientists have put forward theories that explain the development of the disease in humans:
Immunological. This theory is based on the fact that people with gluten intolerance have certain antibodies to it in their blood. In addition, autoimmune antibodies to the cellular structures of the intestine are detected. Intraepithelial lymphocytes, the number of which is increased, perceive gluten that has entered the body as something foreign. As a result, they begin to damage the intestines.
Enzymatic. This theory is based on the absence of an enzyme in the small intestine that can break down incoming gluten. This assumption has the right to exist, however, there is no evidence for it. After all, if a person adheres to dietary nutrition, the enzymes in the intestines are fully restored.
Viral. Studies have shown that the vast majority of sick people have an increased rate of antibodies to one of the types of adenovirus. However, as a result of an adenovirus infection, the disease cannot develop, since it is congenital. The thing is that gluten and adenovirus have a similar antigenic state.
Pathoreceptor. This theory is based on the fact that the inner surface of the intestines of sick people has certain disorders. They are associated with a violation of the protein composition in the small intestine, as a result of which it is not able to absorb gluten.
It is worth noting that most scientists consider the immunological theory the most likely. Nevertheless, it is not worth rejecting the remaining assumptions; it is more expedient to combine them. As a result, the following picture is formed: due to the lack of a special enzyme, the body is not able to break down gluten, as it accumulates, intestinal poisoning with toxins occurs. He, in turn, gives a reaction by activating certain receptors. In this “fight” damage occurs to the intestine, its ability to digest and absorb is disturbed. As for adenoviruses, they are considered a possible provocateur of an immune reaction to gluten that has entered the intestine.
Symptoms of celiac disease

The educational literature describes only three possible manifestations of the disease. However, there are many more symptoms, they are simply perceived as other pathologies of the digestive system. As a result, the correct diagnosis is extremely rare, and people are treated for other diseases. And the therapy is completely ineffective.
However, do not forget about the existing cases of a negative result of a biopsy of the intestine to detect celiac disease. In this case, the entire clinical picture and blood tests indicate the presence of the disease.
In addition, the early introduction of gluten-rich foods into the diet has a negative effect. For example, semolina porridge, which all grandmothers simply adore, can provoke the early development of the disease. In addition, the severity of the course of the pathology will also worsen.
Symptoms of celiac disease in children
Vividly the disease will be manifested by three signs:
Increased bowel movements. The chair can be five times a day or more, it is plentiful, has a mushy texture. There is a sheen on the surface of the stool due to fat. The smell is sharp and unpleasant, the color varies, foam may be present. Washing off feces is problematic.
The child’s belly bulges forward, which sometimes makes the doctor suspect rickets.
In the first two years, there will be a noticeable lag in weight. After two years of age, the child’s lag in growth is more pronounced. At the same time, it is worth paying attention to the fact that insufficient weight gain will begin to appear after the baby is introduced to complementary foods. Prior to that, his weight was normal.
If these symptoms are pronounced, then there are other signs.
They begin to appear as a result of a lack of many nutrients in the child’s body:
The child can be passive, or, on the contrary, aggressive. He gets tired faster, often irritated.
The skin is flaky, the hair is in poor condition. Atopic dermatitis is often observed.
The child has frequent fractures uncharacteristic for childhood. Normally, they rarely happen, since the bones of the baby are elastic.
Posture disorders.
The appearance of the child is painful, unhappy.
Muscle tone is reduced.
Often there are pathologies from the oral cavity. The baby recurs stomatitis, the gums bleed, caries develops, the enamel is in poor condition, it can crumble.
There are signs of anemia.
The baby may look like a spider, he has thin limbs and a belly protruding forward.
As the child grows older, there is a disorder in the reproductive system. In girls, menstruation does not occur on time, and in boys, sexual dysfunction develops.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease in Adults
Pathology can be latent and atypical. The latter form develops after the patient reaches 30 and even 40 years.
In general, the manifestations of the disease are as follows:
Neurological disorders manifested in depressive disorders and migraines.
Skin diseases such as: dermatitis.
Stomatitis, glossitis, thinning of enamel.
Nephropathy.
Infertility.
A biochemical blood test shows a decrease in cholesterol levels, an increase in transaminases, phosphatases and albumin.
Arthritis. In addition, the joints may hurt for an unknown reason.
If a person suffers from a latent form of the disease, then it will not manifest itself in any way. Rarely, minor digestive disorders, as well as dermatitis, can be observed. It is possible to detect pathology only by chance.
Gluten intolerance complications

The latent form of the disease poses a certain danger if you do not know about it for a long time:
Cancer diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diabetes
Pericarditis
Autoimmune form of hepatitis or thyroiditis
Scleroderma, myasthenia, etc.
Diagnosis of celiac disease
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient will need to go through three stages of research:
Blood analysis. It is necessary to determine the amount of antigliadin antibodies, to detect the presence or absence of antibodies to endomysium, reticulin and tissue transglutaminase.
If the result is positive, then a biopsy of the small intestine is necessary. The study will provide information about the condition of the villi of the mucous membrane, whether there is an inflammatory reaction and whether there are lymphocytes with altered receptors. It is the biopsy that is the most important stage of the study.
The patient is prescribed a gluten-free diet for a period of 6 months. If his health improves, then the diagnosis is confirmed definitively.
After 12 months, the patient again donates blood for an immunological study. After another 12 months, a biopsy is necessary, the condition of the intestine should be excellent.
Differential diagnostics
Before sending a person for a biopsy procedure (it is performed under general anesthesia), it is necessary to determine whether digestive disorders are the result of allergies, immunodeficiency, infection, etc.
It is important to know that with celiac disease there will be no mucus and blood in the feces, and a gluten-free diet will give a positive result.
Treatment of celiac disease
If a person really suffers from a disease, then he will have to adhere to a gluten-free diet for the rest of his life. To do this, it will be necessary to exclude pasta and bread, pearl barley, semolina and oatmeal, inexpensive sausages and sausages, cutlets, confectionery and sauces from the menu. In addition, it is important to give up beer, cocoa, coffee, cheese, yogurt, cottage cheese, canned food, ketchup and mayonnaise.
Allowed for use:

Fish and meat;
Eggs and natural milk, as well as products based on it;
Fruits and vegetables;
Buckwheat, millet and corn;
Beans;
Marmalade and chocolate.
Children under 12 months old will need to eat mixtures based on soy or casein hydrolyzate. When the need arises for the introduction of complementary foods, it will be possible to use gluten-free cereals.
Once the diagnosis is established, symptomatic therapy may be required:
To restore microflora: Enterofuril (as an antiseptic), Linex, Bifiform, Aktimel (as probiotics), Hilak forte (as a prebiotic).
To normalize the digestive process – Pancreatin or Creon.
To eliminate bloating – Plantex or Espumizan.
To eliminate diarrhea – Imodium or Smecta.
To normalize the water and electrolyte balance – Calcium Gluconate and Panangin.
To gain muscle mass, a complete correction of nutrition with an increase in the calorie content of dishes is necessary.
If signs of vitamin deficiency are observed, the patient will need to drink a multivitamin complex. In especially severe cases, nicotinic acid and vitamins – K, A, D, E, B are administered intravenously.
Glucocorticosteroids are prescribed for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
If protein deficiency is detected, albumin and amino acids will be required.
In addition, it is necessary to eliminate concomitant pathologies, if any.
Celiac disease is not a sentence
If the diagnosis is indeed confirmed, then often patients are given disability. However, when a person adheres to a diet, his quality of life practically does not suffer, and the prognosis is quite favorable. Already after 14 days, problems with the gastrointestinal tract disappear, and after 60 days, the water-electrolyte, mineral, vitamin and protein balance of the body is normalized.
After 12 months, children are completely catching up with their peers in the physical development. However, if the diet is broken, this will lead to the return of all negative phenomena, and the risk of developing oncology also increases.









