Contents
Cancer in children It is an oncological disease that manifests itself in childhood. According to statistics, this form of the disease occurs in 15 out of 1000 children.
Classification of cancer in children
Most often in childhood they are faced with cancer of the hematopoietic organs. We are talking about leukemia, malignant lymphomas, lymphogranulomatosis. The probability of this is about 70%. These tumors are called hemoblastoses.
More rarely, formations are formed in the central nervous system, bone and soft tissues. The most rare should be considered “adult” types of cancer – from 2 to 4% (tumors of the skin, genital organs).
Thus, the treatment depends entirely on what type of cancer manifested in the child. Therefore, it is necessary to consider each of them separately.
Causes of Cancer in Children

The cause of all oncological diseases should be considered a genetic breakdown in any of the cells. It is she who provokes uncontrolled growth, as well as the reproduction of tumor cells. It is also characteristic that, if in older people it is possible to determine a number of risk factors that are able to provoke such mutations, then in the case of children, minor genetic anomalies that were transmitted from parents become a catalyst for cancer.
Many people have similar anomalies, but not all of them provoke the development of malignant tumors. Risk indicators that affect the child himself (radiation, smoking, negative environmental background) do not really matter.
It should be borne in mind that almost all diseases of a genetic nature, namely Down syndrome or Klinefelter syndrome, as well as Fanconi anemia, are associated with an increased risk of cancer.
Cancer symptoms in children
leukosis
In children, leukemia manifests itself in:
significant fatigue and weakness in the muscles;
pallor of the skin;
loss of appetite and body index;
increased body temperature;
excessively active degree of bleeding;
painful sensations in the area of bone tissues and joints;
a change in the size of the abdomen, which is the result of the fact that some organs become larger;
changes in the size of the lymph nodes in the cervical, inguinal and axillary region;
the formation of shortness of breath;
frequent urge to vomit;
dysfunction of vision and balance while walking;
hemorrhage or redness on the skin.
Leukemia is characterized by the fact that all the signs do not appear simultaneously, but separately. It can begin with all sorts of violations that are formed in a different order. In some children, this may turn out to be a discoloration of the skin and a holistic malaise, in others – walking disorders and problems with visual functions.
Tumors of the brain and spinal cord

Formations that form in the brain appear most often in children aged five to ten years. The degree of danger of this disease is directly dependent on the area of location and the final volumes. Unlike older people, in whom cancer forms in the large hemispheres, in children, the tissues of the cerebellum, as well as the brain stem, are affected.
Signs that indicate the presence of formations in the brain are as follows:
very severe migraine that occurs mainly in the morning and becomes more intense when you cough or when you try to tilt your head. For those who do not yet know how to speak, painful sensations manifest themselves in a state of anxiety or crying. A small child holds his head and actively rubs his face;
vomiting in the morning;
dysfunction of coordination of movements, gait, eyes;
a change in behavior, while the baby refuses to play, closes in on himself and sits as if stunned, without making any attempts to move;
state of apathy;
the formation of hallucinations: visual, vocal.
In addition, in children there is a change in the head in size, convulsions and all kinds of mental disorders can form, for example, personality changes, manic ideas.
If we talk about the formations in the spinal cord, then they are characterized by complaints of unpleasant sensations in the back area, which become more intense in the prone position of the body and less strong in the sitting position.
In children, resistance is detected when bending the body, a change in walking, scoliosis is detected, and the degree of sensitivity in the area affected by cancerous tissues decreases. A positive Babinsky’s sign is also formed (a reflex reaction of the extension of the big toe in case of irritation of the skin), a violation of the functioning of the sphincters, bladder or anus.
Wilms tumor
This formation is also called nephroblastoma and is a malignant tumor of the kidney. This type of cancer is most common in children under the age of three. The disease affects one kidney, more rarely both. Complaints of malaise in most cases are absent. Nephroblastoma is detected randomly at a routine examination. During the implementation of palpation in the early stages, pain is not formed. If we talk about the later stages, then in this case, the asymmetry of the peritoneum is obvious due to the tumor, which compresses the organs located in the neighborhood. The baby’s weight decreases, appetite disappears, temperature, diarrhea come to light.
Neuroblastoma
This type of cancer can only occur in children. In 85-91% of cases, this happens before the age of five. Cancer can be located in the abdominal region, chest, in the cervical and pelvic regions, and often affects bone tissue.
Depending on the location, signs that indicate the presence of neuroblastoma should be identified:
discomfort in the bones, obvious lameness;
weakness, fluctuations in body temperature, pale skin, excessive sweating;
disruption of the intestines and bladder;
swelling in the eyes, face, or neck.
The diagnosis can be made according to the results of a special analysis of blood, urine, puncture and the results of ultrasound.
Retinoblastoma
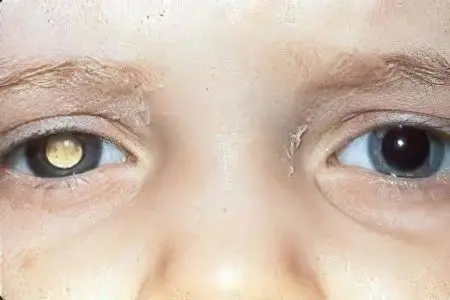
This is a malignant formation that appears near the tissues of the retina. Children under the age of six are affected by this form of cancer. In a third of cases, both the right and left eyes are affected by malignant cells.
In a baby, it begins to blush and hurt, strabismus is formed. At the same time, a specific glow is evident in the eye area, which occurs due to an increase in the tumor behind a certain part of the eye. As a result, it is visible through the pupil. In some patients, this provokes an absolute loss of vision.
To detect retinoblastoma, an eye examination is carried out under anesthesia. Additional diagnostic measures are x-ray examination, ultrasound, computed tomography, as well as a blood test and a puncture of the back.
Rhabdomyosarcoma
This is a malignant formation in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbeither muscle or connective tissue. Formed in children in infancy, preschool and school age. Rhabdomyosarcoma affects part of the head and cervical region, more rarely the urinary organs, upper and lower extremities, and even more rarely the trunk.
Signs of rhabdomyosarcoma:
the formation of a slight swelling of a high degree of pain;
vision dysfunction and changes in the size of the eyeball;
the appearance of hoarseness in the voice and difficulty in swallowing (in the case when the formation is in the cervical region);
urge to vomit, pain in the abdominal cavity and constipation (if the oncology has affected the peritoneum);
the appearance of jaundice may be evidence of the presence of an ailment in the bile ducts.
According to research, about 60% of patients are curable.
Osteosarcoma
The most common oncological disease in extended and humerus bones, as well as hips in adolescents.
The main manifestation of this type of cancer should be considered soreness in the affected bone cover, which becomes more active at night. At the initial stage, the pain may be detected as a shorter one. Obvious swelling comes to light only after two or three weeks.
An accurate diagnosis can be made on the basis of x-rays and computed tomography.
Ewing’s sarcoma
This formation, like osteosarcoma, affects the bones of the arms and legs of the tubular type of the baby. In certain cases, malignant cells affect the area of the shoulder blades, ribs or collarbone. A particularly presented form of the disease is common in children aged 11 to 16 years.
Signs that indicate the presence of a mass are similar to those that appear in osteosarcoma. But in this case, there is a significant increase in body temperature, loss in weight index. In the later stages, sudden soreness and absolute paralysis form.
Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Lymphogranulomatosis is a form of lymphatic tissue cancer. Most often formed in adolescents, that is, after 13-14 years.
In the presented form of oncology, the symptoms are little pronounced or not observed at all. Hodgkin’s lymphoma may have one or more painless lymph nodes that are enlarged and may disappear or reappear. Some children experience itching, active sweating, increased temperature and fatigue rate.
Cancer Diagnosis in Children
The problem of diagnosis arises due to the fact that the child’s well-being may seem positive even at the later stages of the development of the disease. Formations are very often detected randomly as part of a preventive examination.
In most cases, the final diagnosis can only be made after a biopsy. Based on its results, a variant of a malignant formation is determined and the stage of the disease is identified. It is on this that the choice of treatment method depends. When formed in the organs of hematopoiesis, such a biopsy should be considered a puncture of the bone marrow.
Treatment of cancer in children

Pediatric oncologists and oncohematologists deal with the treatment of malignant tumors in children. Such treatment is carried out in special oncology departments of large children’s hospitals and research institutes.
After he was discharged from the hospital, the baby must undergo mandatory observation by a specialist in the children’s department in one of the specialized dispensaries. In order to cure cancer of the hematopoietic type, children’s specialists use only conservative type therapy – chemotherapy and radiation. In the treatment of all other types of cancer in children (which are called “solid tumors”), the method of surgery is used for additional purposes.
The current treatment is carried out according to international programs – treatment protocols that have been worked out separately for each type of ailment. Even the slightest deviation from the protocols leads to a deterioration in the total achieved in the framework of the treatment. The possibility of absolute cure is guaranteed by a high degree of sensitivity of formations in childhood to specific agents.
After the main course of treatment, patients need long-term therapy and rehabilitation, which is aimed solely at maintaining an optimal state of health. At such moments, the entire measure of responsibility for the health of the baby and caring for him is completely on the shoulders of the parents. The results of treatment depend on the thoroughness of the implementation of all the advice of a specialist by 80%.
Thus, it is extremely important to be aware of all the symptoms that can accompany any form of childhood cancer and follow each of the recommendations given by the specialist. This will be the key to recovery.









