Contents
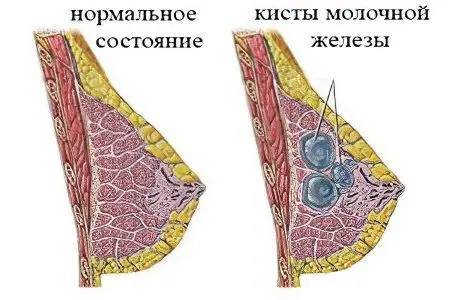
breast cyst – this is a common, single or multiple pathology of the breast cavity with liquid-like contents formed in the ducts. Usually, the disease is asymptomatic for a long time, and only after a while, pain and burning sensations appear in the mammary gland. These symptoms are worse before and during menstruation. The breast cyst is accompanied by inflammation and suppuration of the cystic cavity. The disease itself rarely degenerates into cancer, and, nevertheless, has an overestimated risk of developing a neoplasm. Often accompanied by dyshormonal pathologies occurring in the genital area. Large cysts change the shape of the breast.
Physiologically, a cyst is a cavity bounded by a connective capsule and filled with a non-inflammatory fluid. This pathology is a consequence of fibrocystic mastopathy.
The cavity is formed due to an increase in one duct of the gland, accumulation of secretions and the gradual formation of a fibrous capsule. Neoplasms are round, oval or irregular in shape. The size varies from a few millimeters and in difficult cases up to five centimeters. An ordinary cyst has smooth and absolutely even inner walls. With regards to an atypical cyst, on its walls it has growths inside the cavity.
Cysts can be either single, in more complex cases – multiple. In polycystosis, numerous cysts of different sizes unite, forming multi-chamber clusters. altered cystic tissue is able to occupy half or more of the tissues of the gland.
The cavity of the cyst may consist of benign cells, but may also contain malignant cells.
A fatty cyst that is not associated with secretory tissue can develop in the chest area. It is formed as a result of blockage of the skin sebaceous gland and its overflow with a secret. This disease is not a cause for concern.
The development of cysts in the mammary gland is affected by hormonal balance. With excessive production of estrogens and a skewed hormonal balance, as well as when taking hormonal contraceptives, a disorder of sexual hormonal regulation may develop, which leads to the formation of a cyst.
The development of cysts is provoked by: pathology of the thyroid gland, mastitis, ovarian dysfunction, inflammation of the genital organs.
Signs and symptoms of a breast cyst
Small cysts, very rarely disturb the patient. They are most often detected by chance, after undergoing a mammogram. Enlarged cystic formations cause pain, a thickening of the mammary glands is felt, this manifests itself a few days before menstruation.
Large cysts filled with secretion are manifested by constant pain, pulling sensations, burning, uneven seals.
Breast cyst, clinically manifested regardless of the menstrual cycle. Huge, gigantic cysts are determined by the visible deformation of the mammary gland, redness and even cyanosis of the skin.
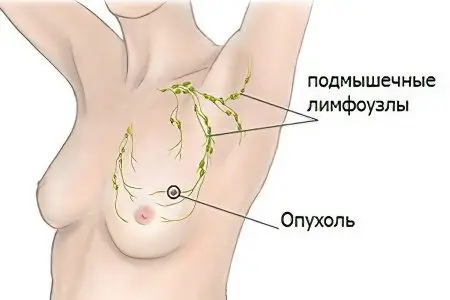
Any inflammation in the cyst is characterized by fever, redness of the skin, a small or even large increase in axillary lymph nodes.
Typical symptoms:
Perceptible pain in the chest.
Burning and pulling sensations.
Skin discoloration.
Breast deformity.
Fever.
Causes of breast cysts
Hormonal failure in the body of a woman is not uncommon. At this point, the ovaries secrete above the prescribed amount of estrogens, the main female sex hormones. This leads to the growth of tissues under the influence of estrogen, the epithelium of the ducts of the mammary gland, and edema of its tissues. Such processes clog some ducts and form cysts.
In practice, a cyst is the main element of fibrocystic mastopathy. If the disease is diffuse in nature, i.e. equally distributed in the mammary glands, then many small cysts appear. Nodular mastopathy is characterized by large nodes.
The female hormonal system is neurohumoral and is controlled by the central nervous system. With any impact, the system can cause a failure in its operation. The neurohumoral system is most sensitive to all kinds of psycho-emotional stress. First of all, the development of cysts is affected by:
Long intellectual loads.
Constant emotional stress.
Frequent worries and stress.
Susceptibility to problems.
Abortion deals the biggest blow to the endocrine system. They can be the cause of failures in the body of a woman. Frequent abortions disrupt the functioning of the ovaries, provoke the release of a large amount of estrogens, and the maturation of cysts.
An increase in estrogen can provoke overweight, especially obesity. Since adipose tissue cells contribute to the production of estrogen, in overweight women, the chances of hormone-dependent diseases increase.
Improper nutrition is another main reason for the development of hormonal disorders. Poor nutrition causes metabolic disorders, which will sooner or later affect the neuroendocrine system. Other endocrine glands and their work is also reflected in the state and activity of the mammary gland.
Any thermal procedures and ultraviolet rays stimulate the production of estrogens.
The reasons for the formation of cysts in the mammary glands can be any injury. The risk of neoplasms also increases after surgery. Since the breast tissue is very thin, it reacts to any physical impact. The use of oral contraceptives is a predisposing and frequent factor in the development of cysts.
Answers to popular questions
Why is a breast cyst dangerous? Neoplasm of the mammary gland is not dangerous for a woman’s life. Of course, it can reduce the quality of life with certain symptoms, but it is rarely a pathology that degenerates into a cancerous tumor. Despite this, its nodular forms are able to stimulate a malignant tumor. Quite often, a breast cyst, given the risk factors for mastopathy, and all the danger of a malignant process, represents the background for cancerous development. According to statistics, every third woman has a cyst in the mammary gland, and many do not even know about it. Faced with the disease, the fair sex begin to panic, in fear that cancer may develop. You don’t need to do this, you just need to start treatment in a timely manner. With the timely detection of the disease, it is necessary to have time to eliminate the cause and conduct complex therapy. (read also: stages, symptoms, signs and treatment of breast cancer)
Does a breast cyst resolve on its own? It is quite a rare occurrence when an independent resorption of a breast cyst occurs, therefore, the disease should not be started. Even small cysts do not resolve on their own, but are treated with a conservative method. If the cyst has a size of 1,5 centimeters, then a puncture is prescribed to take the contents and introduce ozone or air into the cavity. With this size of the cyst, it is necessary to smooth its walls. Any self-treatment (with herbs and compresses), in the hope that the cyst will resolve itself, is unacceptable. Only a doctor prescribes treatment, carefully observing the dynamics of the cysts. Self-treatment without establishing a diagnosis is also unacceptable. Experimenting with your health, in the expectation that the seal will resolve, is unacceptable.
Is it possible to massage the mammary gland? Breast massage is prohibited. The fact is that her tissues are very delicate, and an attempt to squeeze the liquid out of the nipple with the help of an intense massage will lead to her injury. Therefore, the gland is not only forbidden to intensively massage, but it is better not to touch it at all. Any injuries and bruises of the chest should be avoided, including underwear with sharp bones. It is necessary to protect not only breast tissue, but also its skin. As you age, you should lubricate your breasts with olive oil to prevent excessive dryness. Breast massage can be performed 2-3 days after childbirth. It is extremely necessary at this time, since the breast is filled with milk, and its stagnation can lead to the formation of lactational mastitis.
The cyst can resolve itself, it does not need to be treated? Indeed, cystic formations can dissolve, but this happens extremely infrequently. Cases of self-elimination are so rare that when a cyst is found, doctors almost always recommend their removal. If the size of the formation is more than 15 mm, then the patient is assigned a puncture and sampling of its contents for further research. This is done to clarify the diagnosis and prevent a possible relapse.
Is it possible to sunbathe or go to the sauna with a breast cyst or after its treatment? Sunburn is harmful to any, even a healthy woman – this is known for certain. Therefore, doctors do not recommend visiting a solarium, sunbathing without a bra, and spending time in the sun from 11 am to 16 pm. In addition, any overheating of the body can become an impetus for the formation of a cyst or its rebirth, and not only in the chest. Therefore, visiting saunas and baths is also not recommended.
What conservative or alternative treatment can be carried out? Any treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor. This is done after a comprehensive examination or after an operation.
No self-treatment can be carried out with a breast cyst. This prohibition is quite understandable, since it is based on the principle of maintaining a woman’s health. Do not use herbs or compresses unless there is a medical control of the dynamics of the development of the cyst. Moreover, it is impossible to self-medicate until an accurate diagnosis is established. Do not forget about the increased oncological tension. Even today, a benign tumor can become malignant in a few days. Sometimes it is self-treatment that accelerates this dangerous process and leads to sad consequences.
Types of breast cysts
Neoplasms, breast cysts are determined by several types:
Cysts are oval, rounded.
Irregular cysts.
Small or large cysts.
Single or multiple. Polycystic is determined not only by the fusion of cysts, but also by the formation of multi-chamber clusters.
Unilocular or multilocular cysts.
Cysts with or without inflammation.
Typical, having smooth inner walls or atypical, having growths on the walls.
There is atypical, fibrous, ductal, solitary, multi-chamber, cysts of the mammary glands.
Atypical breast cyst – this is the accumulation of fluid, with the expansion of the duct of the gland, in the resulting cavity. Such a cyst has a fibrous capsule, round, oval in shape of different sizes. An atypical cyst is a benign cyst with growths protruding into the cavity.
The main causes of an atypical cyst:
Long-existing cysts.
Often recurrent breast cysts.
Inflammatory processes occurring in the cyst.
The presence of papillomatous (benign) growths.
The presence of papillomatous formations in the cyst cavity.
Fibrous cyst of the breast occupies a central place in oncology and is a background disease in the development of breast cancer.
Fibrous cyst is: Reclus disease, cystic mastopathy, Schimmelbusch disease, cystic disease, chronic cystic mastitis. At the moment, these terms are not used in medicine. The following forms are distinguished: non-proliferative and proliferative.
Fibrous cyst of the breast is determined by characteristic symptoms:
Before menstruation, the pain in the mammary glands increases.
One feels the presence in the chest, grape-shaped nodular seals.
Fluid comes out of the nipples.
The pathogenesis of fibrous mastopathy is not fully understood. There are certain factors that provoke its development:
Such cysts develop in the tissue during menopause, due to hormonal failure.
With weakened immunity and disruption of the work of individual organs.
Solitary cyst of the breast – this is a benign dysplasia, which does not pose a particular danger. But this does not mean that you should not pay attention to it and not engage in treatment. It is necessary to contact a mammologist in a timely manner and start treatment, adjust the hormonal background and the defense system.
A solitary cyst is a formation, rounded in shape and elastic in consistency. It is a swelling filled with liquid of various colors. The longer the cyst, the denser its capsule. A solitary cyst is a large cavity that is located in one breast.
The reasons for the development of this form of cyst:
Наследственность.
neuroendocrine disorders.
abortion.
Age, after 35 years.
Great weight.
Late childbirth.
Stress, nervous strain.
Complete rejection of breastfeeding.
Early puberty.
Mastitis.
Breast trauma.
A solitary cyst manifests itself with chest pains, which increase in the second phase of menstruation. The pains are dragging, pressing and aching. There is a burning sensation and itching in the chest area. Such pains are accompanied by compressed nerves of the mammary gland and surrounding tissues. Pain can radiate to the shoulder blade, neck or shoulder. As soon as menstruation ends, the pain stops.
Another characteristic symptom is determined by palpation, which any woman can determine, especially if the solitary cyst is large.
Ductal cyst of the breast develops at any age, but is most often diagnosed after 48 years. This disease has 1% of all breast neoplasms.
The worst thing is that the ductal cyst is a full-fledged precancerous condition, despite the fact that reliable data have not been identified.
A ductal cyst is an intraductal papilloma, cystoadenopapiloma is a small growth inside the mammary gland. Pathology belongs to the group of benign diseases.
Causes of a ductal cyst:
Hormonal disorders.
Ovarian dysfunction.
abortion.
Inflammation of the appendages of the uterus and ovaries.
Overweight.
Diabetes.
Endocrine diseases.
Stress.
Clinically, this pathology is manifested by discharge from the nipples of a clear, brown, bloody or greenish liquid. A ductal cyst can be palpated if it is present in the area of the lactiferous ducts.
The ductal cyst of the mammary gland is palpated in the form of a dense formation, pain is not felt during palpation. The disease is detected most often by chance, during a routine examination.
Multilocular breast cyst – a very unpleasant diagnosis. First, one cyst develops, then new ones arise, next to each other, after which they merge. This is how a multi-chamber cyst is formed. The disease is detected by ultrasound.
The main factor in the development of pathology is an unhealthy lifestyle, but there are other factors:
Abuse of alcoholic beverages.
The use of nicotine and drugs.
Incorrect food.
Metabolic disease.
Frequent medication.
Stress, experiences.
Hormonal failures.
Infectious diseases.
A multi-chamber cyst of the mammary glands is a dangerous disease that can turn into a malignant tumor.
Diagnosis of a cyst

In order to diagnose an existing medium-sized cyst of the mammary gland, a standard palpation is sometimes enough for a doctor. If the formation is smaller, then an ultrasound or mammogram will be required.
These two diagnostic methods differ from each other not only in the course of execution, but also in the results that the doctor receives. So, ultrasound allows you to clarify whether there are cystic growths inside the mammary gland, you can also distinguish between a cyst and fibroadenoma. Based on the results of mammography, one can draw a conclusion about their size, shape and exact number.
In addition, the patient may be recommended to undergo an MRI, however, it is performed only in severe cases. After all, there are still disputes between physicists regarding the safety of this procedure for the human body. Although everywhere this method is positioned as absolutely harmless.
In this regard, before you go for diagnostics using a tomograph, you should make sure that it is really needed. If the doctor is not fundamental in this matter, then it is better to stop at mammography or ultrasound. This will definitely save the body from unnecessary stress.
A biopsy is performed when there are papillomas inside the formation. A biopsy is performed under ultrasound guidance. This method is necessary in order to be able to conduct a histological examination in the future. According to its results, a cancerous tumor can be suspected (if the substance taken for research is brown or brown, and also if a large number of epithelial cells are found).
Breast cyst treatment
First of all, a woman should contact a mammologist to undergo an examination and determine an effective method of treatment. For the treatment of small cysts, adequate conservative treatment is selected. To do this, it is necessary that the size of the cyst does not exceed 0,5 mm. In this case, removal of the neoplasm is not required. First of all, the doctor directs all his actions to normalize the hormonal balance. To do this, you need to be examined by a gynecologist, immunologist and endocrinologist.
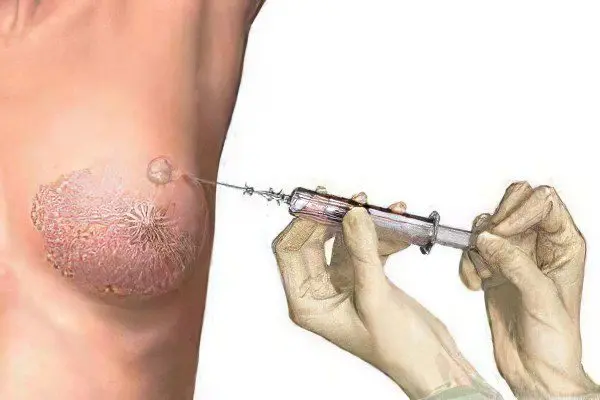
In order for the cyst to resolve, modern drugs are prescribed, or a puncture of the cyst. The doctor makes a puncture, pumps out the liquid and injects a solution to destroy the capsule. This method is suitable for the treatment of single-chamber cysts. If the cyst has atypical features, then an operation is prescribed, and the tissue extracted during the surgical intervention is sent for histological examination.
Another method of treating cysts is aspiration. This is a procedure during which a thin cannula is inserted into the cavity of the cyst, and cystic fluid is pumped out through it. If there are no bloody impurities in this fluid, then treatment is not required. If there are streaks or even traces of blood, then additional studies are required.
The cyst can be treated with hormone replacement therapy. For the treatment of cysts, many doctors resort to a course of taking drugs that are aimed at normalizing the hormonal background. This method of treatment also strengthens the immune system. Such treatment can cure the disease and eliminate the recurrence of the cyst.
If, according to the results of observation, it becomes clear that the cyst is growing, it is drained. To do this, using a thin needle, the cyst is pierced, the contents are aspirated, and either air or ozone is injected into the resulting cavity. This conservative and low-traumatic method of therapy is available for implementation only if single-chamber cysts are found that have not undergone malignancy, inside which there are no papillomas. In addition, you will need to undergo repeated mammological examinations every 6 months, as well as regular follow-up with a mammologist. This will allow timely detection of a possible relapse. The success of the operation depends on how completely the contents of the cyst are removed, whether there are cells in it that can grow, and ultrasound does not detect fluid, then the possibility of recurrence is reduced to 20%. However, when the fluid is retained and gradually accumulates, it will require a second procedure.
It is worth refusing to perform an operation in a clinic where a woman is offered to enter not ozone or air, but ethyl alcohol. This is an unsafe method of treatment, which very often causes tissue necrosis. Therefore, it is so important to clarify all the points of the upcoming operation. Even air in this case will be preferable to the introduction than alcohol.
If a simple cyst is found, then most often it does not require an operation, however, if a parietal formation is detected, a puncture is necessary. This will make it possible to exclude the oncological process. When cancer cells are absent, the woman is offered to undergo a vacuum biopsy. With its help, the growth is removed within half an hour, for which only local anesthesia is used. When cancer cells are still detected, more complex treatment in an oncology clinic is required.
If, after aspiration of the cyst and the introduction of ozone, relapses still occur, but there are no cancer cells, then such a formation must also be removed using vacuum aspiration.
How safe are these operations? There is no need to worry about the fact that the breast will be removed if a cyst has been found in it. As a rule, even large cysts are removed while preserving the mammary gland.
Surgeons strive to make incisions as small as possible, since every doctor wants to deliver a woman a minimum of aesthetic discomfort in the future. Therefore, most often such operations do not leave behind any visible traces.
The risk of malignant formation varies from 1 to 4%. That is why it is so important to start treatment in a timely manner.
Sectoral resection leaves behind scars. This can further adversely affect breastfeeding due to the destruction of the ducts. To avoid congestion, women who are planning to give birth should, as far as possible, avoid intervention.
Laparoscopy (removal of a breast cyst)
Doctors sometimes face a situation where the pathology associated with a breast cyst cannot be cured by conventional methods and laparoscopy is indispensable.
Usually, the cyst becomes the cause of a hormonal imbalance and is detected on ultrasound or mammography. If the disease is detected at an early stage, then it is treated only with medicines. If the doctor suspects the transition of an ordinary cyst into an oncological tumor, then it is important to remove it in a timely manner.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. Incisions are made on the chest wall in order to gain access to the cyst. A special instrument designed for the operation is inserted into one incision, and a laparoscope with a built-in video camera is inserted into the other incision. An image is displayed on the monitor thanks to this camera. Thus, experienced surgeons, with a special tool, manipulate the cyst, draw fluid accumulations out of it and inject absorbable fluid.
Laparoscopy is an innovative technique. It is used in various branches of medicine, which allows you to cope with even the most difficult situations. Thanks to the information displayed on the monitor, what is happening inside, the doctor can implement complex manipulations in the most inaccessible places.
Laparoscopy is a complex operation and requires some preparation. First of all, urine, blood, biochemical tests, blood clotting tests, ECG are prescribed. Before laparoscopy, the patient should refrain from eating for 8 hours.
Advantage of laparoscopy:
Minimal injury.
There are small, almost imperceptible cuts.
Postoperative wounds heal quickly.
The minimum number of complications after laparoscopy.
This method of treatment and removal of breast cysts is rare and yet may be accompanied by complications associated with anesthesia, accidental injuries, injuries of blood vessels, infectious complications, the formation of adhesions, hematomas, seromas, and the formation of a postoperative hernia.









