Contents
The sciatic nerve is the largest and thickest nerve in the human body, resulting from the fusion of the lumbar and sacral nerve roots. It is responsible for the movement and sensation of the thigh, lower leg, ankle, foot and toes. Pinching or inflammation of the sciatic nerve causes discomfort and pain in the lower extremities and lower back. However, pinching of the sciatic nerve can occur without back pain, which occurs mainly in women.
What is a pinched sciatic nerve?
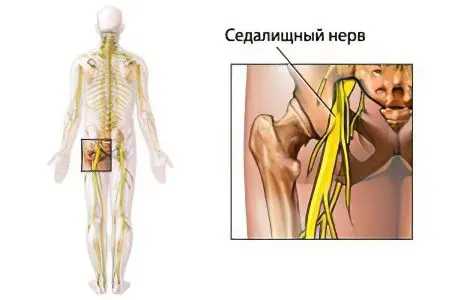
Pinching of the sciatic nerve is an inflammation of one of the longest nerves in the body, which manifests itself in the region of the lumbosacral spine with severe pain. In medicine, this phenomenon is also known as sciatica.
The sciatic nerve is considered one of the most powerful in the human body. The iliac-sacral joint, which is formed by the roots of the spinal nerves, is the region of its origin. Further, the sciatic nerve passes through the entire thigh, branching out with nerve endings in all the tissues surrounding it. In the popliteal fossa, it is divided into parts ending in the tibial and peroneal nerves. They connect the central nervous system and tissues of the lower leg and foot. Such a vast area of distribution of the sciatic nerve causes the clinical picture of its pinching. Pain covers the lower back, back of the thigh.
Pinched sciatic nerve is a syndrome or manifestation of symptoms of other diseases. Therefore, inflammation can be caused by problems in the work of other organs and systems of the body, but in most cases, pathologies are associated with the spine.
Symptoms of pinched sciatic nerve
Pain sensations. A symptom that accompanies a pinched sciatic nerve is always pain of varying intensity. Depending on the cause that caused the pinching, the pain can manifest itself as a slight tingling sensation, or a very strong burning sensation or dull heaviness. In some cases, the pain can reach such strength that the patient cannot move. Remarkably, the pain is predominantly felt only on one side of the body. If acute pain is felt, for example, in the right leg, then only weakness or numbness can be felt in the left. In a calm state, the pain is usually not too intense. But as soon as a person stands up, sits down, bends over or changes position, the pain intensifies. Often its intensity increases at night. Sometimes pain may be preceded by a decrease in the mobility of a limb (foot or knee joint), its weakness and slight tingling. If the sciatic nerve is inflamed, the patient may develop lower back pain. It is usually milder than leg pain, but also causes significant discomfort.
Gait disturbance. This symptom is also known as intermittent claudication. It occurs due to paroxysmal pain. When the sciatic nerve is pinched, the discomfort increases with movement. To weaken them, a person instinctively changes his gait, which is why a slight lameness is observed. The patient tilts the body in the opposite direction from the one in which the pain is felt. During movement, he chooses a healthy leg as a reference, while bending the patient a little. From the outside, it looks like a person has an injury, which leads to intermittent claudication.
Violation of sensitivity. A change in the reaction of nerve endings is observed in that part of the body where the sciatic nerve is infringed. Sensitivity in this area can be both increased and weakened.
Burning, numbness, tingling. To a greater extent, such sensations are characteristic of the buttocks, back of the thigh, lower leg, and foot. The toes are often numb. Sensations, as well as in violation of sensitivity, the occurrence of pain, are localized in this case in one direction.
Decreased mobility. During the diagnosis of a pinched sciatic nerve, there are difficulties with mobility in the knee joint or in the foot area. Changes in the position of the leg are accompanied by pain. Patients cannot perform flexion-extension movements in the knee joint, twist the foot.
Weakening of the musculoskeletal system. Patients with pinched sciatic nerve complain of lack of strength. It becomes difficult for them to perform actions that require muscle tension on the affected side.
Increased body temperature. Thus, the body sometimes reacts to an attack of pain when pinched. This dangerous symptom indicates that it is necessary to contact specialists as soon as possible. Edema may occur on the back, accompanied by reddening of the skin. Patients with pinching also suffer from dysfunction of the pelvic organs. This manifests itself in the form of pain during urination, incontinence, problems with potency in men.
It should be remembered that sometimes the symptoms of a pinched sciatic nerve are similar to the manifestations of other, more dangerous diseases. You should definitely seek medical help if pain in the leg or lower back is accompanied by even a slight increase in body temperature, swelling, redness of the skin, severe pain that does not go away for a long time, or burning when urinating.
Causes of pinched sciatic nerve
One of the most common causes of such an unpleasant syndrome as a pinched sciatic nerve is osteochondrosis. In this case, the piriformis muscle and the sacrospinous ligament change and compress the nerve (piriformis syndrome). Displacement of the spinal disc, hernia, all kinds of damage to the muscles and organs of the pelvis, as well as tumors can also provoke pinching.
osteochondrosis
This disease is the most common cause of pinched sciatic nerve or sciatica. During its development, the cartilage of the spine is damaged. This process implies a violation of their structure, as a result of which the intervertebral discs cease to perform their functions in the human body. In their normal state, they give flexibility and elasticity to the spine. The destruction of cartilage leads to problems directly with the vertebrae.
Osteochondrosis is caused by various causes, which are conventionally divided into endogenous and exogenous. The first group includes factors associated with the characteristics of the body: age, intrauterine development of the spine, genetic predisposition. As an exogenous cause, uneven distribution of the load on the spine is distinguished. It can be caused by carrying heavy weights, stooping, keeping one position for a long time, infections, weakened back muscles. Not only incorrect posture causes osteochondrosis. Often, even athletes with well-developed muscles and a trained body are faced with cartilage damage that causes problems with intervertebral discs. Metabolic disorders, lack of vitamins and minerals – all this also contributes to the development of the disease.
The destruction of the intervertebral discs leads to a reduction in the distance between them, and contributes to the clamping of the nerves. As a result, the patient experiences pain in the neck and spine. Their localization depends on the place of occurrence of problems with cartilaginous tissue. Thus, osteochondrosis causes pinching of the sciatic nerve. In addition to pain, nausea may occur, turning into vomiting, tinnitus.
It will be possible to get rid of inflammation of the sciatic nerve by eliminating the manifestations of osteochondrosis. As part of his treatment, they resort to the use of conservative and manual therapy, folk methods, massage, and therapeutic exercises.
Spondylolisthesis
In medicine, this phenomenon refers to the displacement of the vertebrae. It is most often caused by microtrauma of the spine, congenital pathologies, muscle weakness or ligamentous apparatus. There are several types of spondylolisthesis, depending on the factors provoking it. So, dysplastic is usually associated with congenital pathologies. Isthmic spondylolisthesis affects athletes, such as gymnasts. Elderly patients are faced with such a type of this disease as degenerative. It develops as a result of age-related changes occurring in the vertebrae. Mechanical damage to bone and muscle tissue leads to traumatic spondylolisthesis.
In many cases, the disease is diagnosed only during an X-ray examination. Prior to this, the patient may not experience discomfort or other problems caused by the displacement of the vertebrae at all. But at some point, they can lead to pinched nerves, including the sciatic nerve, and cause severe pain. In women, the factor contributing to the manifestation of the disease is pregnancy. The occurrence of pinching during displacement of the vertebrae is associated with weight lifting, overwork. Pain in spondylolisthesis is felt in the back, legs.
The disease is dangerous with serious complications: narrowing of the spinal canal and spasm of the artery, impaired functioning of the lower extremities. Spondylolisthesis can be managed with conservative methods. If they are ineffective, they resort to surgical intervention.
Spinal stenosis
It manifests itself in the form of a decrease in the lumen of the central spinal canal. The process is chronic and is caused by a number of factors, including ischemia, increased epidural pressure and aseptic inflammation. Their formation, in turn, leads to compression of the neurovascular structures in the spinal canal. Its volume depends on the position of the human body. When squatting, the lumbar lordosis is straightened, as a result of which an increase in the lumen of the intervertebral foramen is observed. As a result, blood vessels that were previously compressed are released, blood flow and nerve nutrition are restored.
In some cases, spinal canal stenosis is a consequence of osteochondrosis, developing in the later stages of this disease. The instability of the vertebral elements leads to the formation of osteophytes. These are growths on the bone tissue that help stabilize the musculoskeletal system. The formation of osteophytes and becomes the cause of stenosis of the spinal canal.
The pathological processes caused by this disease manifest themselves in the form of pinching of the sciatic nerve. Among his symptoms are also pain in the lower back and legs, weakness of the lower extremities, impaired sensitivity and functions of the pelvic organs. For the treatment of spinal canal stenosis, antalgic, vascular, anti-inflammatory drugs are used as part of conservative therapy. Most patients require surgical intervention.
piriformis syndrome
The sciatic nerve in this case is compressed between the piriformis muscle, which is located just behind it, and the sacrospinous ligament. This reason is more typical for women than for men. Pinching of the sciatic nerve is accompanied by pulling and aching pains in the sacral and hip joints, as well as in the buttocks. Some patients complain of numbness or burning in the legs, intermittent claudication may develop. It manifests itself in the form of periodic pain, disturbing only during movement. The skin of the extremities becomes pale. The patient has to stop frequently in the process of walking to rest or change pace.
Piriformis syndrome is diagnosed by palpation. Treatment includes the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, superficial thermal procedures. The most important thing is to provide rest to the sore muscle. After the discomfort subsides, you can perform special gymnastics, conduct wellness and relaxation massage sessions. All these remedies will allow you to get rid of the piriformis syndrome, which means eliminating the pinched sciatic nerve.
Herniated disc
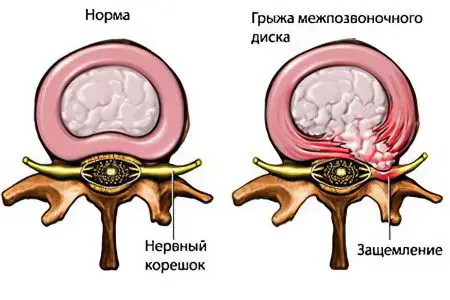
The intervertebral disc acts as a kind of shock absorber in the body, protecting the vertebrae from excessive stress. Its hernia involves the displacement of the intervertebral disc, which leaves the zone of its natural localization, breaking the fibrous ring. The cause of this process may be trauma or degenerative changes. It all starts with a minor deformity known as a disc protrusion. In the future, it develops into a hernia. A nerve root emerges from the intervertebral foramen, which is subjected to compression or infringement. The result is neuralgia of the sciatic nerve.
Symptoms of a hernia suggest the occurrence of local pain at the site of the affected intervertebral disc. It can spread over the buttock and thigh. The lower limbs become numb, they feel tingling. You may even lose sensation in your legs. As additional symptoms, by which a hernia of the intervertebral disc of the back is determined, there is a violation of the functions of the pelvic organs.
Surgical intervention is required if conservative treatment, which involves the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve pain, does not give positive results. In addition to the operation, it helps to relieve pain in case of a herniated disc and, at the same time, to get rid of the pinched sciatic nerve, therapeutic exercises, massage, therapy with multifunctional electrodes.
Dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint
In manual therapy, this term refers to problems with a joint of a mechanical nature. Pain in dysfunction in this case occurs in the sacrum, spread from the buttocks along the back of the thigh to the knee. The most severe discomfort is felt in the morning after waking up and gradually decreases in the evening. Particularly severe pain disturbs patients while walking. Irritation of the fifth lumbar nerve root, which runs in the region of the sacroiliac joint, leads to pinching of the sciatic nerve. With dysfunction, tension occurs in the iliopsoas muscle, as a result of which discomfort may occur in the lower abdomen.
Dysfunction is diagnosed on the basis of various tests: mobility, flexion, pressure. In this case, injections of local anesthetics and corticosteroids help to stop acute pain. In the future, resort to manual therapy, physiotherapy, gymnastics.
Radiculitis of the lumbosacral spine
It is often a consequence of osteochondrosis and is a radicular pain syndrome. As a common cause leading to its development, there are problems with the sacro-lumbar region, which is experiencing heavy loads. In the course of osteochondrosis, deforming spondylarthrosis, intervertebral hernias and other degenerative-dystrophic processes, the spine is damaged, which causes such a pain syndrome. With cerebrospinal meningitis, influenza, syphilis, brucellosis, tuberculosis, rheumatism, similar back problems also occur.
Radiculitis of the lumbosacral spine manifests itself in the form of sciatica or as a pinched sciatic nerve. Eliminate the pain syndrome and its causes should be complex, only then it is possible to get rid of discomfort for a long time. Treatment is carried out in 2 stages. On the first of them, the pain syndrome is eliminated, and on the second, the deep causes of the disease are eliminated. For this, chondoprotectors are prescribed, vitamins are taken, and special exercises for the back are performed. Well helps with sciatica massage. The use of folk methods is also possible, but only in combination with traditional methods of treatment.
Other diseases
Tumors, fibromyalgia, abscesses, blood clots, all kinds of infections – all this can also cause pinching of the sciatic nerve, but it is much less common.
Treatment of a pinched sciatic nerve

Diagnosis of pinching of the sciatic nerve is carried out on the basis of X-ray examination, magnetic resonance imaging and biochemical blood analysis. According to the results of the examination, the doctor confirms the presence of inflammation.
Since a pinched sciatic nerve is considered a pain syndrome caused by other serious diseases, it can only be eliminated by coping with the causes. Therefore, therapy must be comprehensive.
First of all, the pain is relieved. For this, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, including various gels. They act more slowly, but have a warming and relaxing effect, allowing freedom of movement. They have a warming and irritating effect. After applying them to the diseased area, blood circulation increases in it, which allows you to expand blood vessels and improve tissue nutrition.
Exercises for pinched sciatic nerve
You can proceed to therapeutic exercises only after the pain syndrome has passed. Perform the exercises for the first time with a specialist. Movement should not cause pain. If you experience discomfort, you should stop the session.
Yoga, gymnastics in the pool can act as physiotherapy exercises. But first of all, you should start with traditional exercises. You need to perform them in comfortable and designed for sports clothes and shoes. Do not make jerky movements. They should be smooth, gradual, to prevent possible pain. Exercises are performed 6-7 times. Gradually, the number of repetitions should be increased to 10-12 times.
From a standing position, it is recommended to perform the following exercises: walk, raising your knees high; tilt the body in different directions; holding on to the back of a chair or other support, raise your leg as high as possible;
In the supine position, bend the lower leg at the knee, and straighten the upper leg and perform forward and backward movements;
Lie on your back and perform circular movements with your foot, then pull your fingers well forward;
Standing on all fours, swing your legs alternately back and forth. In this case, the movements should be very smooth, without jerks;
Lying on your side, bend your legs and pull them towards your chest. After performing the movement, return the limbs to their original position;
Lie on your back, bend your leg at the knee, lift and straighten at a right angle. After doing the movement several times, lower it to its original position;
Standing on all fours, straighten your leg and try to draw an imaginary circle in the air with it.
[Video] 2 Effective Exercises to Unblock a Pinched Nerve in Your Leg:









