Contents
What is psoriasis?
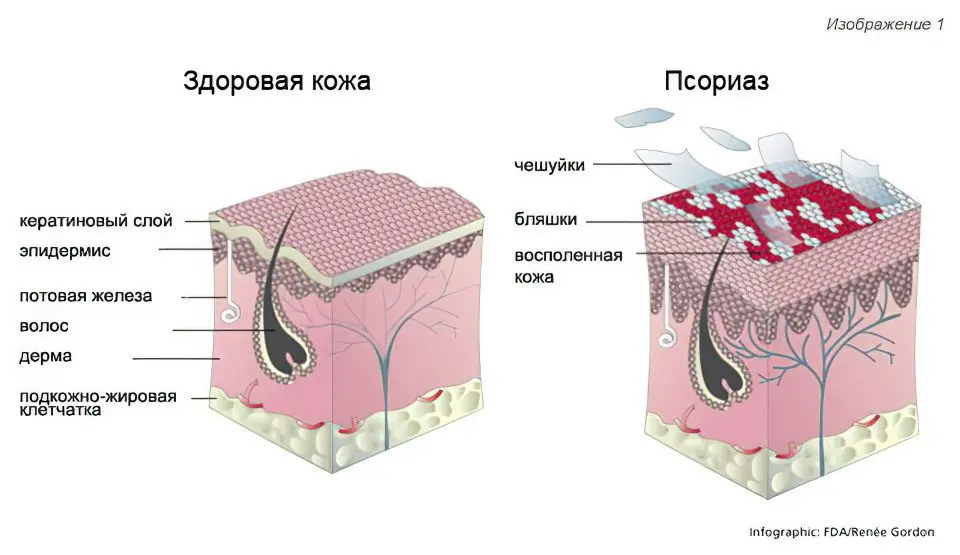
Psoriasis is a skin disease characterized by the presence of a monomorphic rash in the form of pink-red nodules with a loose, silvery-white scaly surface. The disease proceeds for years, there is an alternation of periods of relapses and remissions.
It usually causes dry, red patches that are raised above the surface of the skin, but some people with psoriasis have no visible skin lesions. These spots, called psoriatic plaques, in most cases first form on places that are subjected to pressure and friction – the buttocks, the surface of the knee and elbow folds.
However, they can also be located and occur on other areas of the skin, including the palmar surface of the hands, the scalp, the genital external organs, and the plantar surface of the feet. Psoriasis is a chronic disease characterized, as a rule, by an undulating course. The patient can have both periods of improvement and remission (caused by methods of therapeutic exposure or unexpected), as well as periods of exacerbations or relapses (most often provoked by adverse external factors – stress, alcohol consumption).
Stages of psoriasis
One of the most important elements in the clinical picture and course of psoriasis is its division into stages. If this is less important for acute diseases, then in the case of chronic pathology, a clear staging is essential. Indeed, in this way it is very easy to assess the course of the disease, determine its sensitivity to a particular method of treatment and choose further tactics for managing patients with psoriasis.
There are such stages of psoriatic skin lesions:
Progressive stage of psoriasis;
Stationary stage of psoriasis;
Regressive stage of psoriasis;
Progressive stage of psoriasis
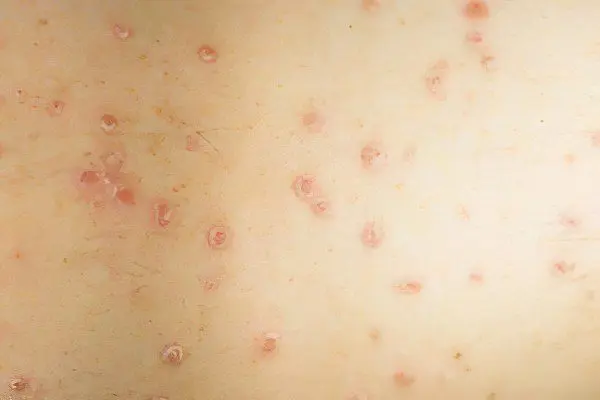
She says that the disease begins its next exacerbation. After all, psoriasis is characterized by wave-like development. Clinically, the progression of the process can be recognized on the basis of such signs:
The appearance of new, characteristic of psoriasis, papules in typical areas of the skin of the extensor surfaces of the limbs or trunk;
The fusion of papular elements with each other with the formation of peculiar conglomerates (plaques) of a whitish color against the background of reddened skin;
Formation on the surface of newly formed psoriatic elements of variegated peeling in the form of multiple small scales;
The edges of the scaly plaques are free from scales in the form of a small hyperemic rim. This symptom is one of the main evidence of the progression of psoriasis. After all, redness is one of the signs of ongoing inflammation. At the same time, the scales do not have time to cover new inflamed areas;
Koebner phenomenon. It is such a feature of plaque-free skin areas in patients with psoriasis, in which any damage to it does not turn into healing scars, but into typical psoriatic plaques.
Stationary stage of psoriasis
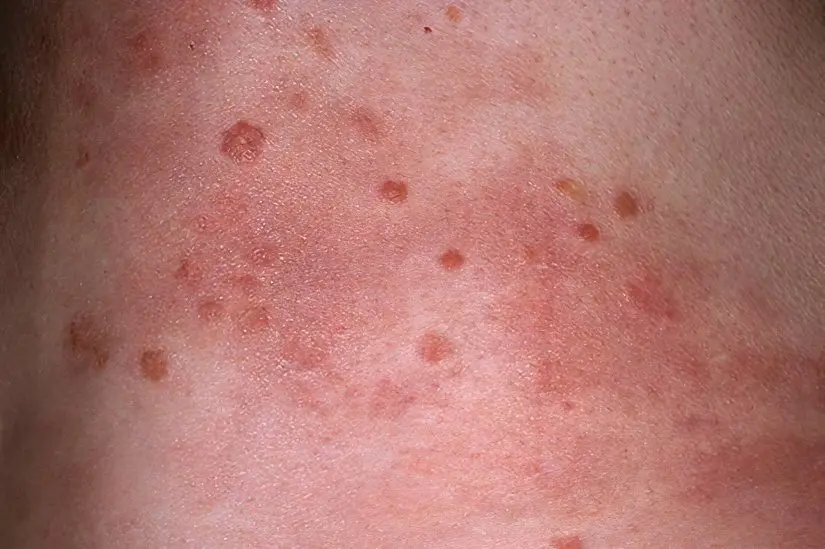
It is an indicator of a decrease in inflammatory changes in the skin. These data indicate the effectiveness of the treatment and the need to change it to less aggressive methods. Clinical features of the stationary phase of psoriasis are:
Stopping the appearance of new red papules;
Stopping the growth of existing plaques;
Scales begin to cover the entire psoriatic skin plaque;
There is no rim of redness around the flaky elements;
The Koebner phenomenon is not observed.
Regressive stage of psoriasis
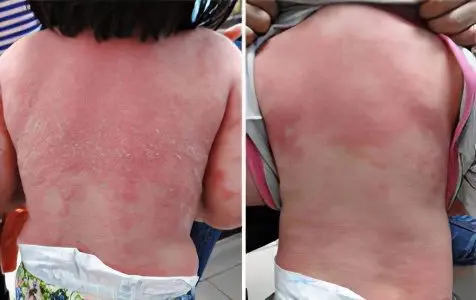
It is perhaps the most pleasant moment in the treatment of psoriasis, both for the patients themselves and for the attending physicians. She says that the exacerbation of the disease is practically defeated and the main task for the near future will be to prevent its next exacerbations. Signs of the regressing stage of psoriasis are:
Pseudo-atrophic rim of Voronov. Represents light small folds and radial lines of the skin around psoriatic plaques;
Gradual reduction of peeling, up to its complete disappearance;
The formation of whitish hypopigmented or dark hyperpigmented spots in place of the plaques.
The basis of the staging of psoriasis is the activity of the inflammatory process. The pattern of clinical manifestations is that the more pronounced redness of the skin, the more active it is.
Symptoms of psoriasis
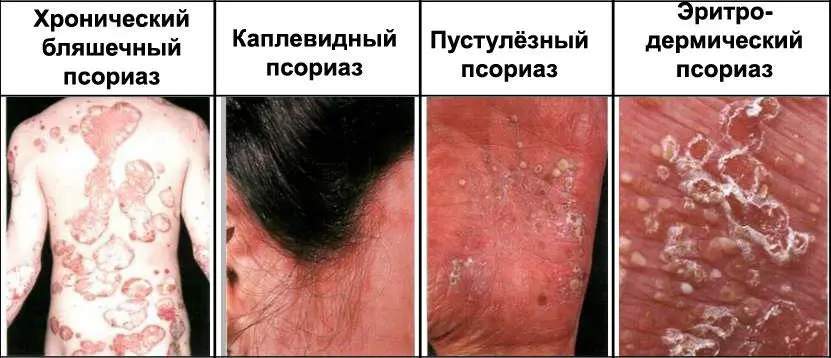
The classic symptoms of psoriasis include bulging areas of the skin that are red in color and covered with a silvery hue of a flaky crust. They usually form on the elbows and knees. Several types of psoriasis are known. Their symptoms can come in different combinations and have differences in intensity. The most common symptoms of psoriasis are:
Bright red psoriatic plaques, often covered with flaky crusts of a silvery hue. They can occur everywhere, but, as a rule, their places of localization are the elbows, feet, lower back, knees, hands. Approximately 90% of people with psoriasis have a similar symptom.
Bleeding areas of small size, located in places where scaly skin completely peels off or breaks off.
Violation of the condition of the nails is a very common symptom, especially in the case of severe forms of the disease. Small dimples appear on the nails, the end of the nail separates from the nail bed, the toenails or in some cases on the hands become yellowish discolored.
Itching, especially in spontaneous flare-ups or plaques, such as under the buttocks or breasts.
Other symptoms of psoriasis can include:
Similar plaques located in the same places on both sides of the body.
Flashes in which a large number of droplet-like plaques appear.
Joint pain, hypersensitivity, swelling.
The course of this disease can be divided into several stages. The first stage begins with an exacerbation, when there is a constant increase in the number of fresh rashes. The second stage is the stationary stage, in which the pattern of rashes is preserved, they do not become smaller or larger.
Regression is the third stage, characterized by the absence of rashes. A person affected by psoriasis feels suffering not only from external manifestations – red papules and crumbling scales. Patients are forced to experience discomfort from itching, which appears periodically.
The general condition of the body with psoriasis remains unchanged, the disease does not affect the usual way of life, does not require to be in any specific conditions. But still, this is a serious, aesthetically unattractive skin disease, and if the process of its development is not controlled, it will entail a lot of inconveniences and restrictions, such as, for example, the inability to wear short sleeves or sunbathe on the beach.
Causes of psoriasis
Psoriasis cannot be contracted through a handshake or through household items and personal hygiene items. The disease appears between the ages of 18 and 25. It appears in large spots on the skin, located anywhere on the human body.
A fairly common cause of exacerbation, development or occurrence of the disease is stress. Psoriasis can be triggered by emotional shock of varying degrees. To date, the exact causes of psoriasis are unknown.
Possible causes of psoriasis include disruption of the endocrine system, changes in immunity, severe shocks and hereditary predisposition, although this area has not been fully explored.
The only thing that can be identified exactly is the mechanism of the appearance of a psoriatic rash. It is based on an immune imbalance. It is a malfunction in the normal functioning of the immune system, in which the cells and antibodies of the body begin to show aggression against their own tissues. And since the skin is one of the mirror images of the general state of health, it is most often affected by any autoimmune reactions.
The following factors can lead to the emergence of such a strong immune imbalance in the body:
genetic predisposition. The risk of developing psoriasis is much higher in the immediate family, especially the first line;
Severe stress or constant neuropsychic overstrain;
Diseases of the endocrine system;
Metabolic disorders, vitamins and microelements. Especially in this regard, it is worth dwelling on the deficiency of silicon in the body;
intestinal parasites;
Viral infections.
There is no need to separately dwell on all the listed reasons, since there is more than enough information of this kind in various sources. It is worth pointing out those new elements that have been established by scientists in relation to the etiology of psoriasis.
Parasitic diseases
A special role among these pathogens belongs to roundworms, giardia, whipworms, bovine and porcine tapeworms. Their role in the development of the problem is explained by the fact that during long-term existence in the intestine there is a constant release of toxic products of their vital activity into the blood. They have high allergenic abilities, which lead to immune imbalance. The result is psoriasis.
Silicon deficiency in the body
It turned out that this microelement plays a very important role in the body, in particular in the structure of the skin, blood vessels and connective tissue. Poverty of the soil and malabsorption from the intestines can lead to its deficiency. Again, the main role here belongs to intestinal parasites, the growth of which takes almost all the silicon that comes from the external environment.
Diagnostics
Psoriasis is diagnosed by a dermatologist or therapist by external signs. The disease is easily recognizable by the characteristic location of lesions on the body. Usually, a clinical examination is sufficient, the diagnosis is always unmistakable, since a patient with psoriasis has skin changes that are typical only for psoriasis. If the picture of the disease is unclear, especially at an early age, then additional studies may be required, namely a skin biopsy.
In this case, a small piece of skin is taken and the pathologist, examining the tissue sample, gives a conclusion. A blood test for psoriasis is not taken, because the blood retains its physical properties. The exception is severe psoriasis, which spreads over the entire surface of the body, contributing to dehydration of the body and disruption of the water-salt balance of the blood.
If the patient has pain or swelling of the joints, he is prescribed an examination for psoriatic arthritis. Any specialist in diseases of the skeletal system, after an X-ray and a blood test, will prescribe the correct treatment, it is desirable that this be a timely measure.
Is psoriasis transmitted?
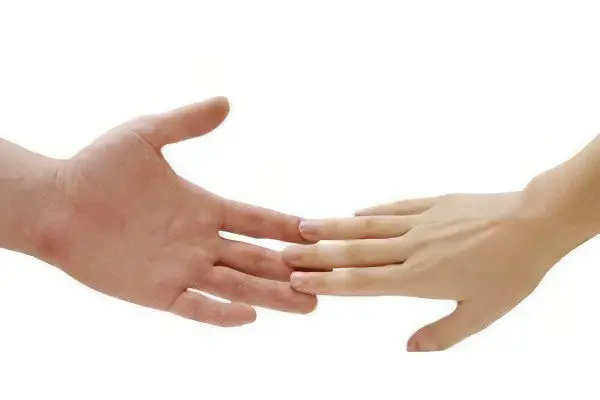

The question of the possibility of transmission of psoriasis from sick people to healthy people does not lose its relevance. This is due to the fact that patients with common forms of psoriasis look very noticeable against the background of the general mass. Not everyone understands that this disease is strictly individual and should not cause concern for others. This raises many different types of questions:
Is contact psoriasis contagious? Numerous studies have established that psoriasis is not transmitted by direct contact under any circumstances.
Is psoriasis sexually transmitted? Sexual relations with patients with psoriasis are absolutely safe, since this disease is a purely individual feature of a sick organism.
Is psoriasis transmitted to children during pregnancy? Pregnancy and childbirth are not directly related to the transmission of the disease from mother to child.
Is psoriasis hereditary? Genetic predisposition refers to one of the reasons for the development of psoriasis. The risk is higher, the closer relatives are sick with psoriasis.
How to treat psoriasis?
Treatment of the disease should be carried out by a qualified doctor and take place individually for each patient. Treatment depends on the age of the patient, general health, profession (influence of professional factors), gender and personal characteristics of the patient. The nature of the course of the disease, its stage is established, provoking factors are eliminated (drinking alcohol, drug intolerance, allergic diseases).
Attention is drawn to the general condition of the patient (psychological and physical). Normalization of the environment, rest, a short stay in the hospital, or a change in work routine can make a difference in the course of the disease. If signs of psoriasis are found, it is recommended to seek medical help immediately. It is the doctor who prescribes various drugs and other therapeutic methods of exposure.
One of the newest and most effective methods of treating psoriasis are genetically engineered biological drugs (GEBP), the second common name is biology.
The principle of action of these drugs is to act on various molecules that cause inflammation and contribute to the formation of plaques, damage to nails, joints. The first GEBPs acted on the tumor necrosis factor, reduced the manifestations of psoriasis, but at the same time weakened the anti-infectious (especially anti-tuberculosis) and antitumor immunity of the body. Modern drugs block IL-17, which is responsible for the appearance of psoriatic plaques. The impact on interleukin IL-17a is point and affects the normal functioning of the body’s immune system slightly. These drugs are well tolerated by patients.
How to apply genetically engineered biological preparations? GIBPs were developed quite recently, less than two decades have passed since their appearance. Unfortunately, psoriasis cannot be completely cured, however, with the help of long-term continuous use of GEBA, it can be brought into long-term remission. This is exactly the option when a person with psoriasis can lead a normal life without the presence of manifestations of the disease.
Treatment begins with several frequent injections (induction of therapy), then only maintenance injections are required once in a certain period of time.
Often, an obstacle to the treatment of psoriasis with GEBAs is their high price. But now there are drugs available at a cost for self-purchase.
Therapeutic therapy can be represented in the form of the following table:
Systemic therapy (indicated in severe or no effect of local treatment) | Local treatment (indicated in all cases of psoriasis alone or in combination with other methods) | Instrumental methods (Appointed differentiated and individually) |
|
|
|
Prevention of psoriasis
First, you need to know if you have psoriasis – self-treatment is more than dangerous, you can only aggravate the disease. Secondly, you should constantly monitor the condition of the skin, try to avoid scratching itchy areas, and refrain from drinking alcohol.
The patient’s diet should be balanced, it is necessary to exclude refined foods, spicy foods, sweets. Be sure to protect yourself from colds, because a weakened immune system negatively affects the course of the disease. Alas, there is no universal remedy for the treatment of psoriasis, the offered ointments, creams, tablets must be purchased only by prescription from the attending physician, but, as a rule, their choice is limited.
You can use ointments containing corticosteroids as a quick help to relieve itching and redness, they act superficially. But ointments, which include tar, and salicylic acid have anti-inflammatory, exfoliating and resolving properties. Vitamin D-based products are characterized by excellent qualities, their actions are aimed at slowing down the process of cell division, and even stopping it.
Treatment of psoriasis is carried out individually with each patient. The doctor is faced with the difficult task of choosing an effective treatment that is suitable for a particular person. For a patient with psoriasis, it is recommended to see the same specialist so that he can choose from different existing treatment options. It is important to understand and remember that it is impossible to cure psoriasis, but it is possible to control the course of the disease.









