Contents
Endometrial polyps are single or multiple formations of a benign nature and localized in the uterine cavity. Endometrial polyps are hyperplastic in nature, that is, the inner lining of the uterus grows. The shape of the outgrowths can be very diverse: mushroom-shaped, and round, and on a thin stalk, and on a wide base. In addition, uterine polyps vary in color, ranging from barely pink to deep burgundy. Their maximum size is 3 cm, although more often they are very small. Often, polyps of the cervical canal are found in parallel with endometrial polyps. In gynecological practice, it is customary to remove these formations, since they are considered precancerous. Although the frequency of their malignancy is low and does not exceed 2%.
As for statistics, most often women who have crossed the line of 35 years suffer from endometrial polyposis. Although endometrial hyperplasia is not excluded at a younger age. The incidence of pathology varies from 6 to 20%.
Symptoms of endometrial polyps
Regardless of the structure of the uterine polyp, it gives rather meager symptoms. Therefore, it is possible to identify it only during an ultrasound examination, especially if it is small in size.
However, a polyp in some cases makes itself felt with the following symptoms:
The menstrual cycle is disrupted. Discharge during menstruation becomes profuse (menorrhagia), which most often occurs in young women. In the intervals between cycles, smearing meager discharge may appear. As for women who have entered the postmenopausal period, they have single uterine bleeding, which they most often do not associate with polyps;
Frequent, and even more so, heavy blood loss becomes a factor influencing the formation of anemia, which is accompanied by dizziness, weakness and pallor of the skin;
In the lower abdomen, there may be pain that has a cramping character. They tend to intensify during intimacy and after it. Also, women often complain of pain in the lumbar region;
Between periods, profuse leucorrhoea may appear, which most often signal fairly large polyps;
After intimacy, a woman may experience slight bleeding;
Formations can interfere with the process of conception and lead to infertility;
If the polyp was not removed before the moment of conception, then its presence in the uterus can provoke a miscarriage or premature birth.
Causes of endometrial polyps

Regarding what causes the formation of endometrial polyps, several hypotheses have been put forward, including:
Disruptions in the hormonal sphere. First of all, the formation of polyps is affected by an increased content of estrogen in the blood, since it is they that contribute to the accelerated growth of the endometrium. The activity of the process is also affected by the level of another hormone – progesterone. The lower it is, the faster polyps grow;
Growth of blood vessels penetrating the uterus. Most often this happens when they are blocked. As the vasculature grows, the surrounding epithelial cells multiply;
Cervicitis and endometriosis, causing inflammatory reactions in the uterus. Strengthening local immunity provokes an increase in the number of leukocytes that are trying to cope with the infection and in parallel cause the formation of polyps;
Violation of blood circulation in the capillaries due to diabetes mellitus or hypertension. Increased cell division occurs against the background of oxygen starvation;
Traumatic medical procedures. For example, it can be abortions or curettage;
Diseases of the endocrine system. The growth of the endometrium is explained by the connection of all the glands of the body with each other;
Significantly overweight. Against the background of excess weight, metabolic disorders almost always occur, which provokes excessive formation of estrogens and the formation of polyps;
Hereditary predisposition. If a woman had endometrial polyps, then it is likely that her daughter will have them;
Lack of physical activity. It is hypodynamia that leads to stagnation of blood in the pelvis, which negatively affects the production of hormones and the activity of endometrial cells;
Taking certain medicines, in particular, Tamoxifen, which is used to treat oncology;
Intrauterine device (when worn for a long time);
Births in which there was no complete delivery of the placenta. The remaining clots and fibrin are replaced by connective tissue, from which a polyp is formed.
Types of endometrial polyps
Depending on what structure the polyp has and what cells it consists of, they are isolated:
Fibrous formations, which are formed from connective tissue, have a dense structure and are most often found in women of mature age (over 40 years old);
Glandular fibrous formations, which are formed simultaneously from glandular cells and from connective tissue;
Glandular formations, which are formed from the corresponding cells and are more often found in young women, before the menopause period (they may resemble a cyst in structure and be filled with fluid);
Adenomatous formations, which consist of atypical cells and have a high risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor;
Placental formations, which are formed from the particles of the placenta remaining in the uterine cavity, more often than other polyps lead to infection and are manifested by prolonged and heavy bleeding.
Fibrous endometrial polyp
Fibrous formations are able to grow only from the connective tissue, they are penetrated by rare blood vessels, which causes their denser structure. They may contain single glands. Most often they are diagnosed in women who have crossed the line of 40 years. These outgrowths are formed against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
Such polyps are found less frequently than others. Usually they do not exceed 10 mm, although fibrous growths of a larger size are extremely rarely found. In addition, they are most often single. The clinical manifestations of such polyps do not have any special differences. Beli can disturb a woman only when the formation is large, or against the background of the formation of necrosis.
Glandular fibrous endometrial polyp
The formation, which has a glandular-fibrous structure, is represented by overgrown areas of the mucous membrane of the uterus and glandular epithelium. This is a benign polyp that grows into the uterine cavity. Most often it is found in adulthood, as well as in older women.
This species differs from other polyps in the presence of not only connective tissue, but also glands, but there are few of them in the formation structure.
Iron polyp endometrium
Glandular formation is represented by stromal cells, as well as endometrial glands. The stroma in the polyp is represented by a connective tissue with a loose structure. It is quite densely permeated with blood vessels. As for the glands, they are arranged in a chaotic manner and vary in length and width. Sometimes a cyst can be found in the thickness of such a formation.
Most often, such polyps form in women in the reproductive phase. It is believed that the main reason for their occurrence is hormonal imbalance. Therefore, when a glandular polyp is found in a woman, it is advisable to check her for other hormone-dependent diseases. In size, such polyps do not exceed 15 mm. After the glandular polyp is removed, no additional treatment is required.
As for the clinical manifestations, they largely depend on what the polyp is formed from. If it was formed from the unchanged endometrium, then the symptoms are most often completely absent, or scanty discharge between menstruation is observed. When the formation reaches a large size, the volume of menstrual blood increases.
The more intensively the glands grow inside the polyp, the higher the risk of its degeneration into the adenomatous type. Although the likelihood of such a transformation is small, nevertheless, the risk exists, so treatment should be timely.
Adenomatous endometrial polyp
This type of pathology is a glandular formation in which atypical cells are found. It is it that has a high risk of malignancy, that is, it threatens to develop into endometrial cancer. This necessitates the urgent removal of the polyp and more careful monitoring of the sick woman.
Such outgrowths can be diagnosed at any age, but they are most often found in older women.
What is the danger of an endometrial polyp?
Pathological formation in the uterine cavity is dangerous for its complications, including:
Impossibility of conception at reproductive age;
Failures of the menstrual cycle, during which a significant amount of blood is lost, which leads to the development of anemia;
Degeneration into a malignant tumor, which causes endometrial cancer;
Refusal of sexual activity, which is associated with severe pain in large polyps.
Diagnostics

During a preventive gynecological examination, formations localized on the cervix can be detected. They look great on mirrors. At the same time, endometrial polyps are difficult to palpate, and visualization is generally not available.
In order to detect polyps in the uterine cavity, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. In this case, the doctor will note the expansion of the organ, the thickening of the endometrium and the growth of the mucous membrane.
However, for a number of reasons, ultrasound is not always an informative method:
Those polyps that have a glandular nature can be poorly visualized, since they are similar in structure to the natural layer of the uterus – the endometrium;
It is impossible to differentiate polypous formation from fibroids or from adenomyosis;
It is difficult to clarify the structure of the polyp, which means that it is impossible to confirm or disprove the presence of atypical cells.
A hysteroscopy is required to make a diagnosis. This is a standard procedure for suspected endometrial polyposis, it increases the reliability of the diagnosis up to 97%. Another method of diagnosing the disease is metrography-radiography. A contrast agent is injected into the uterine cavity, which allows you to see the existing seals under the influence of x-rays.
If surgical removal of polyps is planned, then it is advisable to identify hidden genital infections. A smear is taken for bacteriological, microscopic and oncocytological examination.
Hysteroscopy for endometrial polyps
In order to carry out hysteroscopy, it will be necessary to insert a device with a video camera through the cervical canal. It is he who allows you to visually inspect all the available formations. This will give the doctor a complete picture of what is happening in the uterine cavity: it will allow you to determine the number of formations, their size, and assess the state of the endometrium.
In addition, during this procedure, one growth is removed to determine its nature. This will allow a histological examination. Diagnostic curettage can also be used for tissue sampling.
Answers to popular questions
Do I need to remove an endometrial polyp? The vast majority of doctors are inclined to believe that any formations found in the uterus should be subjected to resection. The same rule applies to polyps. Therefore, they must be eliminated from the body, if there are no serious contraindications to this. In this case, hormone therapy is an alternative method.
Is it possible to get pregnant with an endometrial polyp? It is possible to conceive a child in the presence of polyposis overgrowth of the endometrium, however, in some cases, this pathology can cause infertility. Multiple formations act as a mechanical obstacle to the fertilization of the egg and the fixation of the embryo. In addition, the ability to conceive is influenced by the size of polyps, their malignant degeneration. Also, the overlap of the cervical canal with polyps leads to infertility.
Is it possible to get pregnant after scraping the endometrium? Curettage of the endometrium is a rather traumatic procedure, which is similar in technique to surgical abortion. For its implementation, the doctor uses a special curette, with the help of which, after anesthesia, the uterine cavity is cleaned. If the norms of the procedure were violated and the hysteroscope was not used, then this could threaten the woman with such complications as infertility. Therefore, they try to use this method as rarely as possible. If the operation is performed by a competent specialist and the technique of its implementation is not violated, then it is possible to get pregnant after the procedure.
Delayed menstruation after removal of the endometrial polyp – is this normal? The approximate period for the restoration of the menstrual cycle after the polyp has been removed is 30 days. It depends on the age of the patient, the number of removed formations. The larger the tissue area that had to be treated, the longer the delay may be. After the restoration of the normal menstrual cycle, pain and spotting in between should stop.
Is it possible to have sex with an endometrial polyp? Most often, education is not an obstacle to entering into an intimate relationship.
However, sexual relations in the presence of polyps can be complicated:
The risk of sexually transmitted infections increases, as the defenses of the uterine mucosa are reduced.
The pleasure of intimacy is reduced, as polyps can provoke a decrease in the secretion of natural lubrication.
The chance of getting pregnant is reduced.
After intercourse and during it, a woman may experience pain, especially with the impressive size of the formations.
The risk of bleeding increases, since there are blood vessels inside the polyps, and they are not as strong as in the whole body of a woman.
Is it possible to go to the bath with endometrial polyps? You should refuse to visit the bathhouse, since with such a diagnosis all thermal procedures are contraindicated.
I was diagnosed with a small endometrial polyp during pregnancy. How does a polyp affect the fetus? Is it possible to get rid of it before the baby is born? The formation of a small size does not affect the fetus in any way. Until the moment when the child is born, any treatment should be abandoned.
Do virgins have endometrial polyps? Polyps may well be diagnosed in girls who have not had sexual relations. Moreover, during puberty, a serious hormonal change occurs in the body, which causes an increase in the level of estrogen in the blood. It is the excess content of this hormone that can lead to the fact that the endometrium begins to grow, and a polyp appears.
Treatment of the endometrial polyp
In some cases, removal of the polyp with the help of surgical intervention is not possible. As a result, medical treatment may be attempted. Sometimes it is possible to reduce the formation in size, and sometimes even make it self-destruct. Doctors always try to get rid of the formation in a non-surgical way if the patient is young, because it can be diagnosed in a girl as early as 11 years old.
For treatment, various drugs are used, which in each case are selected individually:
For women under the age of 35, shows the use of oral contraceptives with a combination of estrogen and progestogen. They are taken according to a certain scheme, which is necessarily discussed with the doctor. You should tune in to a long course of treatment. As a rule, it is at least six months;
Women who have crossed the milestone of 35 years, most often use gestagens, which can also be prescribed only by a doctor. The course of taking these funds is also six months, the scheme is negotiated with the doctor individually;
During the menopause, as well as women over 40 years of age are shown taking such drugs that can protect the uterus from the negative effects of estrogens. The course can be up to six months, the minimum period for taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists is 3 months;
If a woman is having heavy periods, then it is advisable for her to wash herself using antiseptic solutions. This will eliminate the possibility of infection.
Removal of an endometrial polyp
The most modern method of removing such formations today is hysteroscopy and subsequent curettage of the cervical canal. In addition, it is possible to resect endometrial polyps with a laser and carry out diagnostic curettage separately.
To determine the optimal method of treatment, the doctor needs to focus on the following criteria:
When multiple polyps are found in a patient, they must be eliminated without fail;
Hormone therapy after removal of the polyp will be required if a glandular fibrous polyp has been diagnosed;
If an adenomatous formation is detected, and the woman’s age is over 40 years old, then the uterus is removed without fail.
After the possibility of the operation is determined, the choice of technique is made.
Hysteroscopy
The modern method of removing endometrial polyps – hysteroscopy – can threaten the patient’s health with minimal complications. To do this, the patient needs to contact the clinic, where there is equipment for such a procedure, and there are also experienced gynecologists.
This technique is the most sparing, as the doctor can fully control his every movement. The uterine cavity and the formations present in it are visualized. For an optimal picture, surgery should be scheduled immediately after the end of menstruation. Before the intervention, you must refrain from eating and drinking 6 hours before the start.
Most often, hysteroscopy requires the introduction of general anesthesia. The uterine cavity is examined with a hysteroscope, and then the polyps are removed. Subsequently, the biological material is transferred to the laboratory, where the necessary histological studies are carried out.
If formations are found on the stem, then they are unscrewed, and the polyp bed is cauterized using electrocoagulation or the cryogenic method. Sometimes a laser is used for these purposes. It is able to destroy pathogenic cells, which will reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease. The procedure is short in time and takes no more than half an hour.
Diagnostic curettage
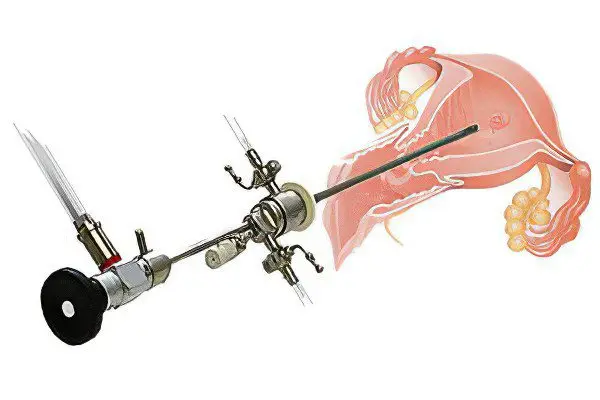
Since the risk of polyp recurrence is high and is at least 30%, it is necessary to carefully coagulate its bed. Therefore, if a woman is offered a conventional diagnostic curettage, and there is no hysteroscopic equipment, then this increases the likelihood of tissue injury. This technique is used less and less, as the doctor does not see what he is doing in the process of curettage. A similar operation is practiced in hospitals with outdated equipment.
Modern medicine has recognized this procedure as absolutely useless, since there is no possibility of cauterization of the polyp bed. Diagnostic curettage should be carried out only after hysteroscopy, in order to determine the presence or absence of atypical cells.
It can only be carried out on an emergency basis if the polyps cause bleeding that cannot be stopped in other ways. That is, the purpose of curettage in this case is hemostasis, and not ridding the patient of education.
Laser removal of polyps
This modern technique is less traumatic and is applicable in women planning to become pregnant. After it is carried out, there are no scars and scars on the uterus, the reproductive function is fully preserved. In this case, the woman does not need to go to the hospital. A few hours after the intervention, she will be able to go home.
The depth of penetration of the laser is completely controlled by the doctor, which contributes to the rapid restoration of tissues, the absence of bleeding, and the instant sealing of blood vessels. In addition, already six months after the intervention, a woman can plan a pregnancy.
Recovery after deletion
When the formation has been removed from the uterus using hysteroscopy, the risk of complications is minimized. But, despite the safety of the procedure, it is important to determine what is the reason for the appearance of growth. This will determine the tactics of further treatment and will serve as an excellent prevention of relapse.
After the operation has been performed, the woman will need to take a muscle relaxant such as No-shpa. The course of admission is 3 days, three tablets per day. This is necessary in order to avoid complications after an operation called “hematometra” (accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity).
Do not refuse the prescribed preventive anti-inflammatory therapy. Its necessity is due to the fact that growths are often the result of an inflammatory process, which must be eliminated.
When the results of the histological examination of the tissues taken during scraping are ready, they must be discussed with the doctor observing the woman. Most often, tests are ready after 10 days.
If it was found that the growth of the endometrium occurred due to a hormonal disorder in the woman’s body, and they themselves had a glandular or fibro-glandular structure, then hormonal correction is necessary. For this purpose, gestagens can be prescribed.
The following recommendations will help to avoid a recurrence of the disease:
Timely treatment of any infectious processes of the genitourinary system;
Permanent sexual partner;
Leading an active lifestyle;
Exclusion of traumatization of the mucous membranes of the uterus;
Regular preventive check-ups with a doctor.
All these measures will reduce the risk of re-growth of the endometrium, which means that they will save the woman from the need for a new surgical intervention, even the most modern one.
As for the prognosis, it is most often favorable, no more than 1,5% of uterine polyps are subject to degeneration.









