Contents
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system are among the most dangerous, because. restrict human movement. Most often, the disease affects the junction of bones – the joints.
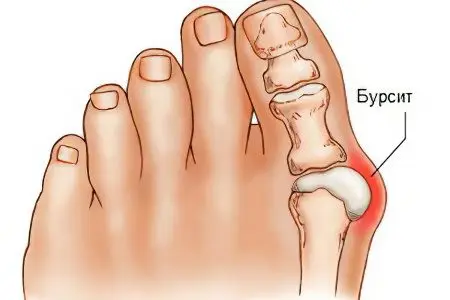
What is bursitis?
Bursitis – this is an inflammatory disease of synovial bags, accompanied by increased formation and accumulation of exudate in their cavities. The causes of this disease are bruise, abrasion, small wounds and secondary infection of the synovial bag with pyogenic microbes.
It is more common in the shoulder, elbow, or knee in men younger than 35, especially athletes. The hip, wrist, or ankle may also be affected. Usually this is an occupational disease, but it also occurs in people who are overweight or wear ill-fitting shoes.
The swelling may be about 10 cm in diameter. It appears because the volume of the articular sac increases abnormally. Exceeding the normal size occurs, for example, due to blood. Rupture of blood vessels and hemorrhage occur as a result of a strong blow. Gradually, the blood elements decompose, and the blood turns into a yellowish liquid. There is an exudative effusion. The resulting sac pulls back the skin if the joint is shallow.
So exudate begins to accumulate in the cavity – a special liquid characteristic of foci of inflammation. Then the adjacent tissues are squeezed, and the transudate is “squeezed out” into the intercellular space. There is swelling, pressure on the nerve endings causes pain.
Edema may develop in a bursa that is so deep that there is no visible change. This applies, for example, to popliteal bursitis. In such “deep” cases, X-rays are indispensable. Sometimes radiography is accompanied by contrast – bursography. A special coloring substance is injected into the bursa with a needle.
Exudate from the bursa, according to macroscopic features, can be of the following types:
serous;
serous-fibrinous;
purulent;
purulent hemorrhagic.
Some experts distinguish other varieties. The most severe form is accompanied by suppuration. Pus is a collection of white blood cells that have died in the fight against inflammation. They turn into purulent bodies. Hemorrhagic exudate has a reddish tint, because it is saturated with red blood cells from destroyed vessels.
According to the cytological picture, i.e. cellular composition, this fluid has such forms as:
neutrophilic in acute conditions;
lymphocytic in the chronic course of the disease;
eosinophilic in allergic inflammation;
mononuclear in chronic form;
mixed
Neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, and monocytes are types of white blood cells. At different stages of the disease, their proportion, i.e. leukocyte formula, in the cellular composition changes. The predominance of these defender cells is associated with the presence of special receptors in them, the ability to synthesize toxic substances that accelerate the death of the pathogen. The mechanism of exudation is triggered by the penetration of a pathogenic agent, it contributes to the process of phagocytosis.
Bursitis is characterized by the deposition of salts in the walls of the articular sac – calcification. Calcium salts should not be contained in them in undissolved form. This leads to dysfunction. To restore balance, magnesium’s ability to dissolve abnormal deposits is usually used.
The bursa is a pocket located at the point of greatest friction against bony prominences. To mitigate this, the bag of connective tissue is filled with synovial fluid of a viscous consistency. It is a kind of shock absorber of movements, a hydraulic cushion. There are more than 100 such “devices” in the human body, respectively, and the risk of developing bursitis with the appearance of provoking factors is very high.
Causes of bursitis
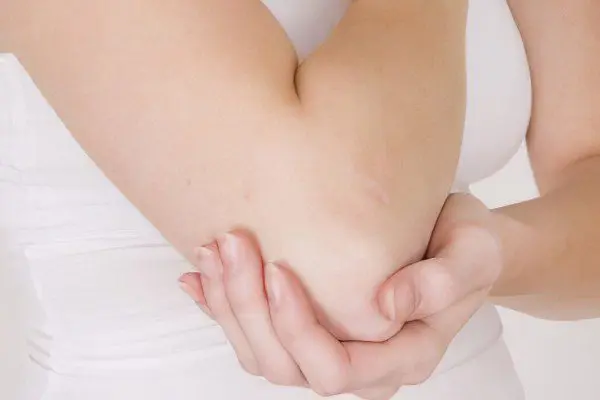

Cause of bursitis usually serves as an injury, bruise or abrasion, that is, infection through the blood or damage to the diseased area. It is also possible to get pus from erysipelas, this happens with osteomyelitis, bedsores, boils, carbuncles. This disease is more likely in people involved in traumatic sports: cyclists, football players, jumpers. The infection enters through abrasions or severe bruises. The chronic manifestation of this disease occurs due to the constant irritation of the focus of inflammation.
There are other reasons too:
mechanical strain of the joint due to its “curvature” (for example, hallux valgus, flat feet), damage or when lifting weights, wearing too narrow shoes and high heels, with excess weight;
various diseases accompanied by inflammation, for example, arthritis (gout and scleroderma including), furunculosis with and without carbuncle, erysipelas, osteomyelitis, SARS, influenza, tonsillitis, brucellosis, drives, bronchitis, sinusitis, otitis media, abscess;
metabolic disorders, for example, with bedsores;
calcification of tendons and nearby areas;
injuries to the bursa, patella, or adjacent tendons;
damage or pathological change in the skin in the joint area, leading to the penetration of infection into the bursa. This can happen when careless cutting of corns and corns;
allergies cause an overabundance of antibodies. In the acute phase of the immune response, basophils secrete various inflammatory mediators;
poisoning (toxins, getting into the blood, poison the tissues);
autoimmune diseases. The immune system begins to produce antibodies against healthy tissues.
Excessive stress on the joints is a common thing. They are typical for women who love to walk in high heels, men who drag weights, and all overweight people. If bursitis develops as a complication of another disease, treatment is carried out in a complex manner. In arthritis, inflammation spreads to the periarticular sac from the joint, and in osteomyelitis, from the bone marrow.
Any inflammation goes through 3 stages:
Alteration – damage to cells (including pathogens);
Exudation – the release of fluid;
Proliferation is the restoration of integrity.
The second stage is fraught with “infection” of other organs. The causative agents of the inflammatory process quickly spread throughout the body with the blood.
Bursitis symptoms
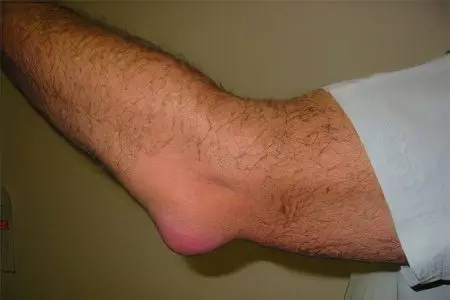
The main symptom of bursitis is the appearance of swelling in the area of the injured part of the body.
The symptoms of bursitis include the definition of a rounded limited patient swelling, elastic consistency, fluctuating, at the site of the anatomical location of the bag. Such a swelling can be about eight or ten centimeters in diameter.
There are symptoms of bursitis, such as:
accumulation in the bursa of excess fluid – exudate
pain syndrome – aching, shooting, strong, throbbing pains that radiate to the limb. They intensify at night. This happens because at night there are much fewer stimuli that can distract the patient. When a person is immobile for a long time, swelling increases, and pain too.
joint contracture. Limited movement appears due to the resulting pain, swelling and deposition of lime salts in the walls of the bag.
edema – accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space as a result of hyperosmia
redness of the skin – hyperemia. It occurs due to the tension of the skin, its thinning, the rush of blood to the inflamed area.
increase in local or general body temperature up to 40
general malaise, weakness
nausea
enlargement of surrounding lymph nodes
If the disease is phlegmatic, then the body temperature will be from thirty-nine to forty degrees. With bursitis, swelling of some skin tissues occurs, while the person will feel increased pain, and the body temperature will rise up to forty degrees.
Chronic bursitis is characterized by a rounded limited swelling of a soft consistency, it occurs at the location of the bag. The skin over the swelling is mobile, not changed, the function of the limb is not impaired.
Chronic bursitis can turn into hygroma, this is due to the occurrence of a large amount of fluid in the edema cavity.
Types of bursitis
Experts use several bases to classify the types of this disease. According to the nature of the course of the disease, acute and chronic bursitis are distinguished. The acute form develops in a couple of days, the chronic form can occur with periodic exacerbations. These forms differ in the nature of pain.
Types of bursitis by causes:
infectious or septic;
aseptic, including traumatic.
The infection penetrates from the outside or from the inside: directly through broken skin, blood (hematogenous infection with pyogenic microbes) or lymph (lymphogenic). By the nature of the pathogen, nonspecific and specific bursitis are distinguished.
The latter are caused by the following pathogens:
gonococci;
Brucellases;
staphylococci;
streptococci;
pneumococci;
tuberculosis or Escherichia coli.
The type of pathogen determines what the exudate will be like, how the disease will proceed.
Types of bursitis depending on the location of the lesion:
brachial;
elbow;
hip;
knee: sub-(infrapatellar), patella (prepatellar) or Baker’s cyst on the inside – hygroma;
ankle;
calcaneal or Achilles bursitis;
wrist.
Synovial bags are located in various places. In accordance with their position, the types of bursitis are also differentiated:
subcutaneous develops in the subcutaneous tissue on the convex surface of the joint;
subfascial;
dry;
axillary.
Varieties of inflammation of the bursa according to the nature of the exudate:
serous;
purulent;
hemorrhagic.
The type of disease is usually determined by the type of infection, sport or profession. Bursitis caused by straining the legs from prolonged kneeling is referred to as water knee, roofer’s knee, parquet floorer’s knee, tiler’s knee, or maid’s/housewife’s knee. There is also a “footballer’s knee” caused by frequent injuries. Occupational diseases of the hands are called “watchmaker’s elbow”, “jeweler’s/engraver’s elbow”, “miner’s elbow”, tennis players’ bursitis, etc. There is also a “loader’s shoulder”. The form and number of relapses of bursitis depend on the profession of the patient and working conditions.
Diagnosis of bursitis

Different types of bursitis have slightly different symptoms. The chronic form may be virtually asymptomatic. At different stages of the disease, the swelling changes its size and density. Signs of bursitis appear in stages.
In the acute form in the morning, the patient may find a painful swelling. The skin in this place is reddened, hot to the touch, mobile. Over time, it will become increasingly difficult to act with a limb. When pus appears in the focus of inflammation, fever will begin. If a focal change in the organ of the musculoskeletal system is a complication of another disease, then its manifestations will progress.
Regional lymph nodes near the affected joint increase when inflammatory products enter them. This is an immune system response. Lymphadenitis may begin. With shoulder bursitis, the lymph nodes are enlarged on the neck and in the armpits, with hip and knee bursitis – in the groin.
The reason for going to the clinic is usually pain and limitation of body movements. Methods for diagnosing bursitis:
conversation;
inspection;
radiography;
Ultrasound;
CT scan;
Magnetic resonance imaging;
puncture with laboratory tests of the extracted fluid;
arthrography – endoscopy of the knee;
Complete blood count to detect signs of an inflammatory process;
angiography of blood vessels to determine the boundaries of inflammation.
Diagnosis of some types of bursitis is complicated by the fact that their symptoms are similar to other inflammatory diseases. An example is arthritis – inflammation of the joint and synovitis – its membranes. In addition, these pathologies can occur simultaneously. In this case, it is quite difficult to identify the root cause.
Depending on the test results, the orthopedist prescribes treatment. But most often, only visual methods and palpation are enough to make a diagnosis.
Simple tests help diagnose bursitis:
The doctor asks the patient to try to put his hand behind his head as when combing his hair.
The patient should squat a little.
If soreness and limited movements are detected, then the likelihood of the disease increases. The farther from the surface of the body the inflamed bag is located, the more difficult it is for a specialist to make a diagnosis. But no matter how deep the focus is hidden, when pressed, the patient will definitely feel pain.
The general symptoms of inflammation of the synovial bags differ little from the signs of other similar diseases. It is all the more important to be examined by a specialist in order to differentiate this disease in time and begin treatment.
Complications of bursitis
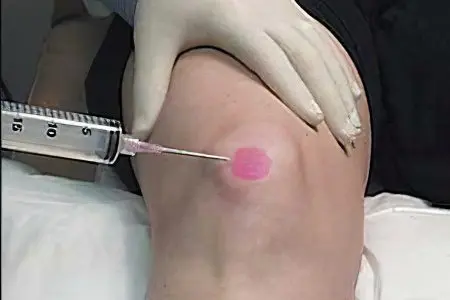
cicatricial adhesions – seals that cause immobility of the limb – contracture
calcification
infection of other organs, such as tendon bursitis and tendon rupture, abscess, osteomyelitis, subcutaneous and intermuscular phlegmon, arthritis, including purulent (when pus breaks into the joint) and coxarthritis
fistula – fistula with pus formation
necrosis of the bursa wall
sepsis
The adhesive process sometimes proceeds pathologically. The healing of the walls of the mucous bags of the joints damaged by bursitis proceeds abnormally, extra “threads” are formed – adhesions. They create unnecessary connections that prevent normal organ movements.
The unfortunate thing is that such growths often occur imperceptibly. It is not always possible to see them even with the help of ultrasound. Over time, pain appears, adhesive disease progresses. If this process is provoked by hip bursitis, abnormal scarring can also capture the woman’s genitals, causing infertility.
Inflammation easily spreads from the joint capsule to the tendons. Their fibers are closely intertwined with the outer fibrous sheath of the bursa. So the muscles can more effectively perform the motor function, activate the process of movement of the articular surfaces.
Purulent bursitis is the most severe. Suppuration spreads to nearby soft tissues and bones. Melts the connective tissue of the phlegmon. It differs from an abscess in that it does not have clear boundaries. These are unfavorable outcomes of necrosis. Sometimes there is a spontaneous opening of abscesses. Fistulas appear.
Fixing dressings can increase the pressure inside the bursa so much that pus gets into other tissues, blood. It contains a large amount of proteolytic enzymes that melt proteins. So necrotic destruction of cells begins in other parts of the body.
Lymphoid tissue is almost always involved in inflammatory processes. The immune system must respond to the penetration of the infection. During the next examination, the orthopedist palpates those lymph nodes to which lymph flows from the affected area. Soreness indicates the progression of the pathological condition.
Necrosis of the inner lining of the bursa will lead to the cessation of synovial fluid secretion.
Synovial fluid performs very important functions for the health of the joint:
nourishes,
moisturizes,
helps glide.
Complicated bursitis exacerbates pain. All parts of the joint, except for the hyaline cartilage, are perfectly innervated. At the same time, developing pathologies increase the number of foci of inflammation. Strengthening of the inflammatory process of pressure on numerous nerve endings exacerbates the pain syndrome.
If left untreated, the patient may become disabled or die. Self-medication is dangerous and can lead to tragic consequences. As surgeon D.S. Tews: “It’s better to overestimate the severity of your symptoms than to seek medical help too late.”
Treatment of bursitis
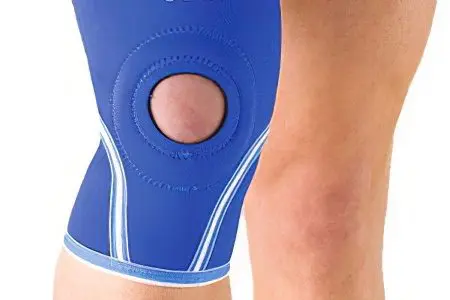
Conservative treatment of acute bursitis
In acute bursitis, the most important thing for the patient is peace and immobility. If bursitis occurs on the joints of the shoulder or elbow, then the joint must be fixed with a plaster splint. If a person feels severe pain, give him aspirin or some pain medication, sometimes the pain will go away on its own. In some cases, in order for the exudate to dissolve better, heat is used or Vishnevsky’s ointment is applied.
Modern methods allow patients to undergo a therapeutic course on an outpatient basis. Mandatory rest, diet. Specific measures depend on the causes of the disease. Usually they include suppression of the inflammatory process with intravenous antibiotics, anesthesia, strengthening the immune system.
In addition to drug treatment, massage and physiotherapy are prescribed:
ultraviolet irradiation;
shock wave therapy;
induction therapy;
paraffin or ozokerite applications;
electrophoresis with various drugs.
Physiotherapeutic procedures should activate metabolic processes, prevent stagnation. They help relieve swelling, reduce muscle tension in the affected area. Strong absorbing effect of physiotherapy. Specific procedures are prescribed depending on the stage of the disease and the patient’s well-being.
The movement of the diseased limb is limited with elastic bandages and a special fixator: a bandage, splint, etc. Massage is carried out with an ice pack through the clothes. These measures help reduce pain. The diseased joint is raised to prevent the development of edema.
After removing the inflammation, physical activity is increased gradually. A leg or arm is developed using special exercises. The complex of physiotherapy exercises is selected individually. With a favorable course of the disease, it is possible to suppress it in a week, otherwise – in 3 months. After treatment, it is important not to forget about preventive measures.
Surgical treatment of chronic post-traumatic bursitis
In chronic bursitis, surgical intervention is also possible, since the patient will complain of calcium deposits – provided that they are quite large, create long-term discomfort or interfere with movement.
With calcium deposits, they are removed with a needle or by surgical intervention. Sometimes, with complete immobility of the joint, it is developed under anesthesia.
The bursa can be opened, cleaned, adhesions and calcium deposits cut out, and the cavity treated with antiseptics. With purulent bursitis, extirpation of the periarticular bag is sometimes required. Only part of it, for example, the mucous membrane, is surgically removed. Modern methods allow minimizing the recovery period. With a favorable outcome, the operated can return home in a couple of hours. The last resort is bursectomy, which is the complete removal of the bursa. A special type of surgical intervention – osteotomy, is accompanied by the movement of bones, and even their fixation in the correct position with special metal rods.
In the media there are recommendations for aspiration of exudate at home. Doing so is deadly! This procedure is carried out only by a specialist, under sterile conditions. “Well-wishers”, giving such advice, forget how quickly pathogenic microbes can spread. Sepsis causes death within a few days.
Prevention of bursitis
disinfection of scratches, abrasions, minor wounds, abrasions with antiseptics;
timely suppression of inflammation;
overload avoidance;
correction of deformed joints;
diet food.
sports taking into account the individual health index.
Immediately treating wounds with disinfecting compounds, you can significantly reduce the risk of an infectious disease. If there is a focus of inflammation, there is a high probability that it will spread further with lymph and blood. By timely suppression of the disease, many complications can be avoided.
People who are prescribed to wear special models of shoes, use special insoles or inlays, should not neglect the recommendations of specialists.
There are the following types of orthopedic products for various activities:
orthoses for adjustable fixation of the hip and knee joints;
bandage and sports orthosis on the knee joint and cup;
compression and anti-varicose knitwear with devices to facilitate its donning/removal;
hip bandage;
bandage for fixation of the Achilles tendon;
bandage and sports orthosis on the ankle joint;
abductor bandage for the first toe with non-fixed hallux valgus;
under- and heel pad;
pad, lining and forefoot pad;
supinator;
insoles and half-insoles;
interdigital insert;
bursoprotector;
interdigital corrector;
metatarsal and support-corrective linings;
interdigital septum and insert;
protective cap and toe ring;
pilot-fixator;
protective insert against corns;
interdigital separator;
elastic band and forefoot cuff;
metatarsal pad;
protector to protect the joint of the big toe and little toe;
pad under the heel and toes;
anti-corn ring;
protective socks;
corrector and padding between the toes;
metatarsal roller;
orthosis for the big toe.
Here are listed not only products useful for professional athletes, but also means for correcting deformed joints. Orthopedic treatment is always a complex and time-consuming process. In severe cases, surgery is required.
Those whose profession is associated with constant stress on the joints should, if possible, take care of them. Put soft pillows under your knees or elbows, wear special protective bandages, take breaks with a little warm-up. Before heavy loads, be sure to “warm up” the joints with a special set of exercises. Before performing any exercise, stretching is necessary: light – moderate – full. Walking, jogging, dumbbell work and swimming are recommended.
There are frequent cases when, having discovered puffiness, the patient does nothing, continues to live on the principle of “it will pass by itself.” The swelling goes down. But usually this is only an indicator of the onset of the chronic stage of the disease. Neglecting treatment, you can provoke the spread of infection throughout the body.









