Contents
A benign tumor is a pathological neoplasm with a slow or absent rate of development. Timely treatment gives positive forecasts – in most cases, the patient completely gets rid of the disease, there are practically no relapses. The danger to humans is a tumor that secretly develops in the body. In the absence of symptoms and pathological changes, it is quite difficult to diagnose the disease, which threatens to transform a benign formation into a malignant one.
What is a benign tumor?
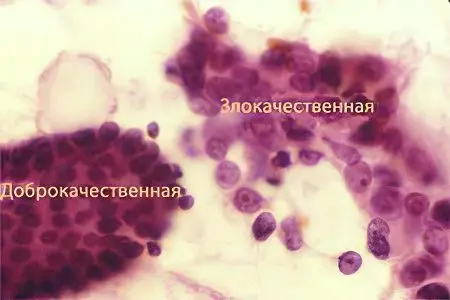
benign tumor is a disease that occurs as a result of a violation of the mechanism of cell division and growth. As a result of this, their structure changes in a certain area, an formation unusual for the normal state of the body appears and, as a result, the manifestation of symptoms.
A feature of a benign tumor is slow growth. Often, the formation retains its original size for several years, after which complete healing occurs or it develops into a malignant one. Another characteristic feature is the lack of influence on the body and the appearance of metastases. The tumor is formed in one area, where it slowly develops. Other organs are not affected. If we compare a benign formation with a malignant one, then in the case of the second, it is not the tumor, but metastases that are of particular danger. They rapidly destroy organs and tissues, leaving almost no chance for a full recovery. With a benign formation, the prognosis is mostly positive and after a course of therapy, as well as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, the disease recedes.
It is possible to determine a benign education by the following signs:
The tumor is mobile, not connected to the surrounding tissues;
When pressed or touched, discomfort or pain is felt;
With internal tumors, there is a deterioration in well-being, fatigue, sleep disturbance;
External tumors of the mucous membranes and skin can bleed.
More often, benign tumors do not manifest themselves, which presents difficulties in diagnosing. It is possible to detect the disease during a preventive examination, pathological changes in the skin.
Causes of benign tumors
In the human body, cells always follow the same path: the cell grows, develops and dies after 42 hours. It is replaced by a new cell, living a similar period. If, as a result of a certain effect on the body, the cell does not die, but continues to grow, then a tumor appears.
It has been scientifically proven that a benign formation is a consequence of a DNA mutation, which can be caused by the following factors:
Work in hazardous production, regular inhalation of hazardous fumes and poisons;
Smoking, drug use, substance abuse;
Drinking alcohol and other drinks unfit for drinking;
Ionizing radiation;
Frequent ultraviolet radiation;
Hormonal disbalance;
Violation of the immune system;
The penetration of viruses;
Injuries, fractures;
Improper nutrition;
Lack of normal daily routine (lack of sleep, work at night).
A study conducted by scientists showed that every person has a predisposition to the formation of a benign tumor. You can prevent it by following a healthy lifestyle. This is especially true for people whose families have previously encountered cancer. Heredity refers to another reason for the occurrence of benign education.
Nervous stresses have an adverse effect on the cells of the body. In combination with a disrupted daily routine, they create an increased risk of gene mutation.
Stages of tumor growth
In total, there are three stages in the development of a benign tumor: initiation, promotion, progression.
Initiation
At this stage, it is almost impossible to detect a mutational gene. Initiation is manifested by a change in the DNA cell under the influence of adverse factors. In this case, two genes are subject to mutation. One of them makes the modified cell immortal, and the second is responsible for its reproduction. If both processes occur, then the tumor becomes malignant. When one gene is changed, the formation remains benign.
Promotion
At the second stage, mutated cells begin active reproduction. Carcinogenesis promoters are responsible for this. The promotion stage can last for several years and practically does not manifest itself. However, the diagnosis of a benign formation at the very beginning of active cell reproduction makes it possible to stop the development of cancer. To do this, therapy is carried out that regulates the action of promoters and stop the further action of the genome. But due to the lack of symptoms, it is problematic to identify the presence of the disease, which leads to its next stage of development.
Progression
The third stage of tumor growth is not final, but the further condition of the patient depends on it. Progression is characterized by a rapid increase in the number of mutational cells that form a tumor. By itself, it does not pose a danger to human life, but can lead to compression of neighboring organs. Also, a benign formation at the progression stage causes a deterioration in well-being, a violation of the functionality of the body, and the appearance of ugly spots on the skin. This facilitates the diagnosis process and forces the patient to consult a specialist. It is not difficult to detect a tumor at the progression stage even without special equipment.
The time during which a benign tumor develops can vary from a few weeks to decades. Often the disease is diagnosed only after death during an autopsy. In this case, the tumor may not be the cause of death of a person.
The progression stage is dangerous because the influence of adverse factors and the lack of treatment leads to the degeneration of the tumor. The mutation of genes continues, cells multiply more actively. Once in the lumen of the blood vessel, they begin to spread throughout the body, settling on the organs. This process is called metastasis. At this stage, specialists diagnose a malignant tumor that threatens the patient’s life.
tumor growth
Tumor growth is also subdivided according to the effect on human organs:
expansive growth. It is characterized by the formation of an external tumor that does not penetrate into the tissues. As it grows, it displaces the organs, becoming covered with a capsule. The tissues surrounding the tumor atrophy and are replaced by connective tissue. The pace of its development is slow, it can last for several years. It is difficult to diagnose such a tumor, patients complain of pain in other organs, undergo long-term treatment without positive results.
infiltrative growth. It is characterized by rapid development, tissue damage. More often, infiltrative growth is characteristic of malignant tumors, but is often found in benign tumors.
appositional growth. It is characterized by the transformation of healthy cells into tumor cells, which leads to the rapid development of the disease. It is extremely rare, affecting more often the organs of the peritoneum.
Types of benign tumors
A benign tumor can grow in any tissue. There are several types of neoplasms.
Fibroma
Fibroma is a tumor composed of fibrous connective tissue. It has a small amount of connective tissue spindle cells, fibers and vessels.
Fibroma occurs most often in women on the genitals. It is manifested by a violation of the menstrual cycle, infertility, severe pain during intercourse, painful and prolonged menstruation. Often there is intermenstrual bleeding, which leads to a deterioration in general well-being, a decrease in hemoglobin levels.
There is also a subcutaneous fibroma, manifested by the formation of flesh-colored. It can be diagnosed by its dense structure.
Lipoma
A lipoma is otherwise called a fatty tumor and is a formation that practically does not differ from normal adipose tissue. When diagnosing, a capsule is noted, which characterizes the disease. Lipoma is more often formed in women during menopause and can reach huge sizes.
Lipoma causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient. It is mobile and painful, causing a long time to be in a lying or sitting position.
Chondroma
Chondroma consists of cartilaginous tissue and has the appearance of hard tubercles. The cause of the development of a benign formation is trauma or tissue damage. Chondroma can appear both in a single instance and in multiple quantities, affecting mainly the limbs. The tumor develops slowly, may not manifest itself. It is possible to identify chondroma when diagnosing the skin.
Neurofibromatosis
Doctors also call neurofibromatosis Recklinghausen’s disease. The disease is the formation of a large number of fibroids and age spots. In this case, inflammation of the nerves joins. Symptoms are pronounced, although diagnosis may be difficult due to the involvement of several tissues in the process of tumor development. Often there are incomplete forms of the disease, manifested by the formation of nodes on the sensory nerves.
Osteoma
Osteoma is a benign formation consisting of bone tissue. It has clear boundaries and rarely develops into a malignant tumor. Osteoma is a congenital disease and is formed as a result of pathological development of the skeleton. A solitary tumor of this type is more common.
Myoma
Myoma is a single or multiple encapsulated formations with a dense base. The disease develops in muscle tissue and affects more often the female reproductive system. The cause of the tumor can be hormonal disorders, abortion, obesity.
Myoma is manifested by a violation of the menstrual cycle, abundant and painful menstruation, infertility. If the disease is not cured before pregnancy, then there is a high probability of miscarriage and fetal death. Myoma is inherited.
Angioma
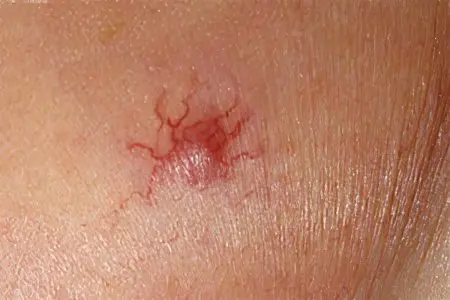
Angioma is a benign tumor that develops from blood vessels. The disease is congenital, spreading mainly on the cheeks, lips, oral mucosa. Angioma is manifested by strongly dilated tortuous vessels that have a flat, swollen shape. They form under the skin, but are perfectly visible on the surface of the integument. Another type of benign tumors – hemangiomas are very common, and are congenital birthmarks with dilated capillaries. Such an education does not always require treatment, it is only necessary to follow the basic rules for caring for moles and systematic observation by a specialist.
But angiomas are not always safe. Under the influence of external factors (ultraviolet, damage), the disease can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Lymphangioma
Lymphangioma is a benign tumor consisting of lymphatic vessels. It is formed during embryonic development and continues to grow in early childhood. More often, lymphangioma stops in development, without posing a threat to life.
Glioma
Glioma is similar in development to angioma, as it can manifest itself as hemorrhage. It is a neuroglial cell with processes.
Neurinoma
Neurinoma is a benign neoplasm that develops on the peripheral nerves and in the roots of the spinal cord. Slightly less common neuroma on the cranial nerves. The tumor looks like a lot of small nodes of different sizes.
Neuroma
Neuroma is a tumor that forms on various elements of the nervous system. The cause of the disease is often amputation and damage to the nerve. There are also congenital neuromas.
The disease manifests itself as pain in the area of the tumor, redness of the skin may occur.
Ganglioneuroma
This type of tumor develops mainly in the abdominal cavity and are dense formations of large sizes. They consist of nerve fibers and practically do not manifest themselves with slow development.
The disease begins to develop in the womb. There are quite a few reasons for this – disturbances in the development of the nervous system, the impact of adverse factors on the mother’s body during gestation, various infectious diseases.
Paraganglioma
Paraganglioma is a tumor composed of chromaffin cells. The disease can develop in any organs and tissues where these cells are present. The tumor is congenital, begins to manifest itself at an early age. The disease is dangerous due to the development of metastases.
The disease is manifested by frequent headache, increased blood pressure, shortness of breath, tachycardia.
Papilloma
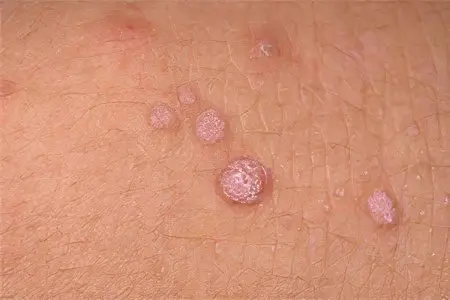
It is a formation in the form of small stems or nipples, in the center of which there is a blood vessel. Papilloma is the most common type of benign tumor and is easily removed. There are no recurrences after surgery.
Papilloma occurs as a result of exposure to the human papilloma virus. More often the disease affects the genitals and mucous membranes. The tumor appears as dense formations that bring discomfort and pain when touched. Warts are also referred to as papillomas, most of them are safe and do not require treatment. Exceptions are formations that bleed and bring pain. The danger is growing and changing color warts.
Adenoma
Adenoma has one characteristic feature – it repeats the shape of the organ on which it is formed. The tumor consists of glands and rarely degenerates into a malignant formation.
Most often, adenoma affects the prostate in men over the age of 45 years. The disease is manifested by painful and frequent urination, decreased sexual activity, early ejaculation, and infertility. Adenoma does not pose a threat to humans, but can significantly impair the quality of life and lead to mental disorders.
cysts
A cyst is a benign formation that does not have clear boundaries. It consists of a soft cavity, often filled with liquid. The cyst develops rapidly, which poses a threat to the patient’s life. If the tumor ruptures, there is a risk of blood poisoning. Cysts rarely develop without symptoms. Appear on the genitals, in the peritoneum, bone tissue, brain.
Appearance of tumors
Benign tumors can have a different structure and structure:
An oval or round knot, similar to the structure of a cauliflower and a mushroom cap;
Tumors associated with body tissues have a stalk (polyps);
Cysts are an elongated formation filled with fluid;
In many cases, tumors penetrate the tissues, due to which their border is not defined.
Treatment of benign tumors

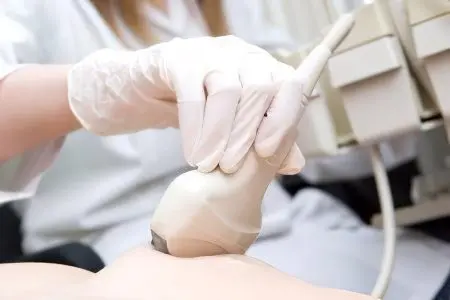
Benign tumors diagnosed at an early stage of development are easily treatable. Several methods are used to detect the disease. Formations can often be seen with ultrasound, palpation. To make an accurate diagnosis, specialists examine the blood and, if necessary, pieces of tissue taken during a biopsy or laparoscopy.
Treatment of benign tumors depends on its type, stage of development and the condition of the patient. This disease cannot be left without the attention of specialists! Even a small neoplasm can lead to sad consequences or long, expensive treatment.
Modern medicine offers several effective methods for the treatment of benign tumors, among which the removal takes the first place. Surgery can prevent further development of the disease and eliminate the accumulation of mutated cells. After removal of the tumor, relapses do not occur, and the patient recovers completely. In rare cases, a second operation may be required if the mutated cells grow.
Removal of the tumor
Removal of benign formations occurs using surgical instruments or a special laser. In order for the treatment to show positive results, the patient is carefully prepared for the operation. To do this, the place of removal of the formation is treated with disinfectants, the patient is given general anesthesia.
Most often, the removal of the tumor occurs by incision of the tissue and exfoliation of the formation. This reduces the size of the suture and prevents infection.
cryocoagulation
A more modern method of treatment is cryocoagulation. It is carried out with the formation of tumors on soft tissues and the skeleton. This technique was first tested in Israel, after which it became widespread throughout the world. Cryocoagulation gives chances for recovery even for patients with bone cancer. The therapy makes it possible to remove the formation without consequences for the tissues and skeleton.
Cryotherapy is effective in the presence of tumors in the following organs:
Shoulder joints;
limbs;
Pelvic bones;
chest;
spine.
Cryotherapy involves the impact on the tumor of extremely low temperatures. For this, liquid nitrogen was previously used, leading to the destruction of damaged tissues and the death of mutated cells. Now scientists from Israel have developed an innovative tool that allows you to remove formations with argon or helium, which have less effect on the body than nitrogen.
The tool creates extremely low temperatures – up to -180 °C. It allows you to control the area of exposure and freeze only damaged cells without affecting healthy organs. The benefits of cryotherapy are obvious:
Minimal impact on the body;
Prevention of relapses;
No contraindications;
Easy preparation for surgery;
Minimal tissue and bone damage.
Cryotherapy successfully replaces radiation and chemotherapy, which have an adverse effect on humans. After the operation, there are no side effects – nausea, fatigue, hair loss.
Replacement therapy
Many benign formations arise as a result of a malfunction in the hormonal system. If the tumor is small and does not tend to develop, then the patient is prescribed replacement therapy. In this case, the patient is under the supervision of a specialist and undergoes regular examinations.
Diet for benign tumors
The effectiveness of treatment depends largely on the observance of the rules of a healthy lifestyle. When diagnosing a tumor, the patient must give up nicotine and alcohol, completely exclude coffee and strong tea from the diet. Specialists also prescribe a diet that will help restore immunity and prevent the development of neoplasms. For this, the patient is recommended lean and low-fat meals, a large number of vegetables and herbs. Dishes can be baked, boiled in water and steamed. Fried, smoked and stewed food with fat is completely excluded.
Prevention of benign tumors
To prevent the formation of benign tumors, it is necessary to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eat right and fully.
The body will begin an independent fight against pathological cells with proper rest, regular sleep and the absence of irritants.
Regular sexual relations with one partner, keeping organs clean, no abortions, and timely treatment of hormonal imbalances will help prevent benign tumors of the female genital area.
Preventive examinations by specialists will help to diagnose the disease in a timely manner.
Many patients underestimate benign formations, neglecting the need to see a doctor. However, only timely treatment can guarantee complete recovery and the absence of negative consequences. It is worth remembering that most malignant tumors are reborn from benign formations that do not pose a threat to life.









