Contents
What is a cervical canal polyp?
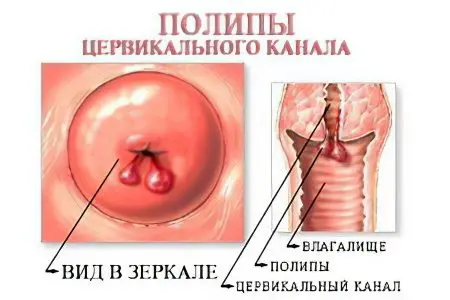
A cervical canal polyp is a benign growth that grows into the lumen of the cervix. Such outgrowths are formed from connective tissue and can be covered with flat multilayered, high cylindrical or immature epithelium of the endocervix. They are attached to the cervical canal with a stem (thin or thick). The place of their localization is the depth of the external cervical os. If the cervical polyp is located on a long stalk, then it can protrude into the vaginal lumen, then the gynecologist is able to visualize it during a standard examination.
All polyps have blood vessels that grow into them as the tumor forms. It is their number that determines the color of education. The fewer of them, the paler the polyp. With a developed vascular network, it can have a rich burgundy color. The more fibrous cells in the structure of the polyp, the denser the outgrowth will be. The size of the tumors varies from very microscopic to very impressive. The larger they are, the brighter the clinical signs of pathology. The maximum size of the cervical polyp is 40 mm, although formations rarely grow to such volumes. The minimum diameter is 2 mm.
It is not uncommon for this disease to be detected during pregnancy – polyps are detected in 22% of women bearing a child. It is worth knowing about the existence of false cervical polyps or pseudopolyps. They are formed within a few weeks after conception, do not have legs. The structure of the cervical pseudopolyp is represented by a transformed endometrium. If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with such an education, then she should be under special control by a gynecologist. When a pseudopolyp does not affect the process of bearing a fetus, it is simply observed. If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy, then the formation is subject to removal, which is carried out during gestation, without waiting for delivery. Polyps can be combined into groups, or they can grow singly.
According to available statistics, this pathology is quite common and is recorded in women at different ages. However, more often cervical polyps occur after 40 years. Among other neoplasms of the cervix, which are benign in nature, polyposis is diagnosed no more often than in 25% of cases. Doctors consider this pathology background. The presence of multiple cervical polyps increases the risk of cervical cancer, and therefore requires regular monitoring by a doctor and timely treatment.
Symptoms of polyps of the cervical canal
The latent course of the pathological process is a fairly common characteristic of polyps. Small formations with a wide stem almost do not betray themselves. They are diagnosed, as a rule, by chance, when a woman goes to the doctor about another disease of the genital area. It is worth noting that with polyposis of the cervical canal, 70% of women have concomitant gynecological diseases.
The fact that there is a polyp in the body can be suspected after its damage, infection, ulceration or inflammation.
In this case, the neoplasm manifests itself as follows:
Bloody discharge, which can often be observed after intimacy or gynecological examination. Also, polyps are sometimes injured by sanitary tampons. This is especially true for tumors on a long stalk that extend beyond the boundaries of the external uterine os into the lumen of the vagina;
If the polyp has undergone necrosis or become inflamed, then in the period between menstruation, a woman may begin to bleed. In all other cases, this is not typical for polyps;
When the formation is infected, a woman will find leucorrhoea that has a mucopurulent character. Large polyposis growths are more often subject to such a process;
Drawing pains also occur with large polyps. They are due to the fact that, due to a large outgrowth, the pharynx of the cervix is not able to close properly;
Abundant mucous discharge appears when the polyp presses on the glands of the cervical canal;
If a large formation is found in a pregnant woman, then this may threaten her with a miscarriage, starting from the early period of gestation. Such risks are due to the fact that the polyp causes reflex irritation of the uterus, which causes it to contract involuntarily.
The structure of the formations affects the symptoms of cervical polyposis.
Depending on the cellular composition of the tumor, a woman is dominated by certain signs:
With fibrosis symptoms are extremely poor. This is due to the structural features of such a polyp. It has no glands, which means it does not secrete mucus. The fibrous stroma is dense and weakly penetrated by blood vessels, which reduces the possibility of injury to the polyp and the risk of bleeding;
glandular polyps produce more mucus, which can increase the amount of intermenstrual flow. But there will not be too many of them, since fibrous formations most often have a small size (up to 10 mm);
Glandular fibrous tumors – These are formations of a mixed type, they give the most pronounced symptoms. A brighter clinical picture of the disease is due to the size, which can reach 25 mm or more. In this case, the woman complains of pain, notes contact bleeding and increased discharge between cycles.
Causes of cervical polyps
Doctors are inclined to believe that the formations localized in the cervical canal are formed under the influence of a number of provoking factors:
Canal injury. Various damages negatively affect the structural state of the epithelium lining the cervical canal. Of particular danger are diagnostic curettage, abortion, aspiration biopsy, hysteroscopy. Often the cervical canal suffers due to an incorrectly installed intrauterine device. In addition, it can be damaged during childbirth, especially if they were accompanied by traumatic obstetric manipulations. After an injury, the epithelium starts the healing process, it is regeneration that causes the growth of polyps. New mucous cells may divide too actively. Moreover, the injury does not have to be extensive at all, sometimes a microscopic wound is enough;
Structural changes in the surface of the cervix. Often the formation of polyps is preceded by such pathologies as true and false erosions, as well as leukoplakia;
Sexual infections. When a woman’s immune defenses are reduced, diseases of the vaginal epithelium such as trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and many others pose a threat to the cervical canal. Rising from the vagina, microorganisms begin to infect the cervical canal, disrupting the natural composition of the mucus located there. Local inflammation occurs, as a result of which the mucous membrane becomes looser and more easily injured. The protective response of the cervical epithelium is an increase in its own area due to cell division. As a result of this process, a polyp or a group of them is formed;
Non-specific infection. The growth of a neoplasm can be stimulated by such pathologies as vulvovaginitis, vaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis, endomyometritis;
Violations of the microflora of the vagina. The longer an imbalance of bacteria is observed in the vagina and the more often fluctuations in the level of acidity occur, the more favorable the environment becomes for the growth of the epithelial layer of the cervical canal;
Disorders of the ovaries. It is with ovarian dysfunction in women that polyps in the cervical canal are most often detected. They are accompanied by such diagnoses as fibroids, endometrial polyposis, endometriosis. Therefore, doctors suggest that excess estrogen is a powerful stimulator of the growth of the epithelium lining the cervical zone;
External factors and endocrine diseases. Not always the cause of hormonal failure is ovarian dysfunction. Cervical polyposis can be caused by obesity, diabetes, overwork and stress;
Physiological processes. Hormonal surges in a woman’s body occur constantly. With the exception of menstruation, they occur during adolescence, during childbearing, and at the time a woman enters menopause.
Unexplained etiology. It is worth noting that polyps are not always formed under the influence of provoking factors. Sometimes the occurrence of such neoplasms cannot be explained by one reason or another. In this case, indicate cervical polyposis of unknown etiology.
Why are polyps of the cervical canal dangerous?
An outgrowth localized in the cervical canal, despite mild symptoms, poses a threat to a woman’s health.
The danger lies in the following:
Polyps can transform into a malignant tumorcausing cervical cancer. Although such changes occur infrequently, nevertheless, the risk of rebirth exists. Therefore, doctors recommend removing such formations, regardless of their size and structure;
The risk of developing uterine bleeding increases. This threat is due to the fact that the polyp has its own blood vessels, and it can reach 30 mm in size. When its wall is damaged, blood loss often occurs. Almost always, it ends on its own, however, regular repetitions lead to anemia. The level of red blood cells and hemoglobin falls, which negatively affects the woman’s well-being;
The presence of a polyp can affect the course of pregnancy extremely negatively, up to spontaneous abortion. Other threats during gestation against the background of cervical polyposis include isthmic-cervical insufficiency, as well as a low location of the placenta;
tumor necrosis if medical care is not provided, which consists in surgical intervention, it can cause the death of nearby tissues, blood poisoning and the death of a woman;
Hematometer – another danger of a cervical polyp. Due to the fact that the tumor has a large size and the ability to move, as well as its inflammation, the cervical canal can be blocked. As a result, menstrual blood will begin to accumulate in the uterine cavity, as its natural outflow will be disturbed. A complication can be suspected by the absence of menstrual bleeding on time, the blood can leak out, but it will have an unpleasant odor and its volume will be much less than it should be. In addition, the woman will experience pain in the lower abdomen, and the uterus will stretch and increase in size. If timely assistance is not provided, an inflammatory process can begin, up to sepsis and death.
In connection with such serious threats to the health and even life of a woman, polyps must be removed as soon as possible after they are discovered.
Diagnosis of polyps of the cervical canal
In order to detect the presence of such formations, sometimes only a standard gynecological examination is enough. During its conduct, the doctor detects thickened and hypertrophied walls of the cervix. Outgrowths protrude from the cervical canal, having a characteristic shape and color.
To confirm the diagnosis, a woman needs to undergo a cervicoscopy. In fact, this is a normal examination of the mucous part of the cervical canal. For a better view, the doctor uses a mirror or expander, as well as binocular optics. The shade of the polyp has an important diagnostic value. So, its cyanotic or purple color indicates the blocking of blood flow in certain vessels and oxygen starvation of the tumor. If the polyp is white, then this is a sign of keratinization. Such a neoplasm acquires greater strength and elasticity.
Cervicoscopy allows you to visualize not only large, but also small polyps. The technique provides information about their structure, possible inflammation, necrosis or ulcerative processes. In addition, a targeted biopsy can be performed during the procedure. The resulting material is then sent for histological examination.
When tumors are found in the cervical canal, it is imperative to conduct an ultrasound examination, which allows you to determine their presence in the uterine cavity. Due to the fact that the treatment of such formations is always operational, a preliminary examination of the smear using the methods of bacterial culture and PCR is necessary. If a woman has infections, they are first eliminated from the body.
Answers to popular questions
Should a cervical polyp be removed? Education found in the cervical canal is subject to mandatory removal. You should not refuse the operation, even if the polyp has a very small size. The need for resection is due to the tense oncological situation in the world.
Can a cervical canal polyp disappear on its own? The formation cannot self-destruct, which is why there are no drug treatment schemes for such tumors.
How long does bleeding last after removal of a cervical canal polyp? If a low-traumatic method of getting rid of the neoplasm was chosen, then spotting may not be observed at all. Sometimes spotting may continue for up to 48 hours. Gradually, they become less and less, and after three days they completely disappear.
What does heavy menstruation mean after removal of a polyp of the cervical canal? When the formation is removed from the body, menstruation should return to normal. Her character can additionally be affected by the age of the woman and the number of removed polyps. Menstruation after surgery should normally become less abundant and less painful. If, on the contrary, their volume has increased or the cycle has broken, then you should consult a doctor for advice.
Removal of polyps of the cervical canal – 5 methods
When a woman decides on the choice of a surgical technique, it is important for her to remember that after any operation she will have to undergo a curettage procedure for the entire cervical canal. Only in this way will it be possible to get rid of pathological cells that can lead to a relapse of the pathology. There are several methods aimed at removing cervical growths.
Diathermocoagulation
This method has been around for quite some time. During the procedure, excision occurs, as well as cauterization of the polyp. For this purpose, the doctor uses an electroknife. A high-frequency current passes through the device. As a result, the polyp cells get burned and die. At the place of its attachment, a wound is formed, which is covered with a crust from above. It is an additional protection against infection and bleeding. However, this method has certain contraindications. The operation is not prescribed to a woman if she is carrying a child, has not given birth before, and also suffers from a bleeding disorder.
Nevertheless, diathermocoagulation has an undoubted advantage, which lies in the ubiquity of the technique, which makes it accessible to every woman.
However, giving preference to such an intervention, it is worth remembering its shortcomings:
After cauterization, a scar will remain at the site of the polyp, which can complicate future childbirth;
The recovery process can take several months;
With incorrect rejection of the formed crust, bleeding may open;
The procedure is quite painful.
However, the procedure is used everywhere, as it is not only affordable, but also makes it possible to get rid of polyps attached to the cervical canal with a wide stem.
Cryodestruction
To implement this intervention, low temperatures are used, which can reach minus 80 °C. The polyp itself is exposed to liquid nitrogen. The affected area is frozen, after which it is cut off. In place of the former polyp, a healthy epithelial tissue of the cervical canal is formed. Cryodestruction is a modern way to get rid of polyposis growths, so it has a number of advantages, including the absence of bleeding and pain. In addition, this method is suitable for women who do not have children, since after the intervention on the cervical canal there will be no scar, which means there will be no complications during childbirth.
The only significant drawback of the procedure can be called a long tissue recovery time. It can take up to two months. Also, a woman who decides to undergo cryodestruction may face the fact that in small towns there is no possibility of carrying out the procedure.
Laser polypectomy
The doctor has the opportunity to use a laser to remove a cervical polyp when it is single and not too large. During the procedure, the doctor monitors its progress with the help of a hysteroscope. A significant disadvantage of this technique is that it cannot be used to remove several formations. In addition, the cost of laser cauterization is quite high, and there is no guarantee that a relapse will not occur in the near future.
However, surgery using a laser beam has its advantages. Firstly, the risk of perforation of the wall of the cervical canal is significantly reduced, since the doctor independently regulates the intensity of the laser exposure and the depth of its penetration into the tissues. Secondly, there will be no bleeding during the procedure, as the blood vessels instantly coagulate. Thirdly, the recovery period is very short, and after a few days the woman will stop any discharge, and menstruation will begin without delay.
Amputation of the cervix
The indication for removal of the cervix, together with the polyps present in it, is a recurrent pathology. In addition, the cervical canal is removed if it is found that the neoplasm has already been malignantly degenerated or has atypical cells. You can perform the procedure in all of the above ways, the doctor gets access to the cervix using a laparoscope. In this case, the cone-shaped part of the neck is removed, as well as the mucous membrane lining the cervical canal. At the same time, the uterus itself does not suffer, and an intact mucous membrane begins to form again in the cervical canal.
Such an operation enables a woman to maintain reproductive function. It is suitable even for nulliparous women with recurrent cervical polyposis.
Hysteroscopic method
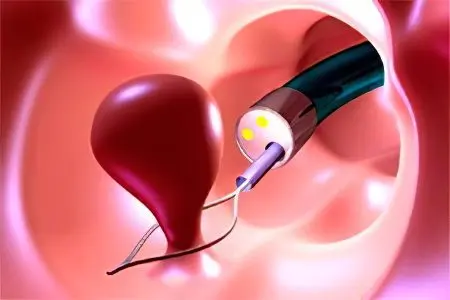
This method of removing cervical formations is the safest, most modern and painless for a woman. To carry out the procedure, a special instrument is required – a hysteroscope. The doctor introduces it into the vaginal cavity, into the desired area of the cervical canal. Having examined each neoplasm with the help of an existing camera, the surgeon removes them using miniature scissors (resectoscope) or a loop for this. She throws herself on the leg of the polyp and unscrews it at the very base. If a resectoscope is used, the polyp is simply cut off. The choice of instrumentation depends on the size of the cervical formation. To minimize the possibility of relapse, the place where the leg was attached is cauterized.
The time that is optimal for performing hysteroscopy is the end of the menstrual cycle. The operation is not carried out later than 10 days from the end of the last menstruation.
Despite the advantages of the procedure, which are its safety, painlessness, and the ability to carry out a thorough curettage, hysteroscopy can not be used in every case. For example, it is not performed if a woman is carrying a child, if she has a pathological narrowing of the cervical canal, infectious, oncological or inflammatory processes.
Recovery after surgery
After the removal of the cervical polyp has been carried out, the treatment does not end there.
A woman must adhere to the recommendations given by the doctor, among them:
It is forbidden to visit baths, saunas, steam rooms for two months, as excessive overheating of the body can cause bleeding;
You should not lift weights, you must abandon physical exertion;
A visit to the doctor should be regular, which is associated with the possibility of recurrence of polyps and the risk of their malignancy;
Sexual life is banned for the next half a month. You should also avoid swimming in open water to minimize the risk of infection;
The use of tampons during menstruation is prohibited. Within two months it is worth using sanitary pads;
Intimate hygiene should be especially thorough, which will also avoid infection and infection of the wound. For washing in the first days after the intervention, you can use antiseptic agents, for example, Miramistin or potassium permanganate solution;
Pregnancy planning should be postponed for the period recommended by the doctor. Most often, the break does not exceed six months, although sometimes it can be somewhat shorter;
Sometimes, in order to avoid infection after the operation (especially after amputation of the cervix), the doctor recommends taking antibacterial drugs for several days;
If any pathological discharge from the vagina is detected or if there is heavy blood loss, a medical examination is necessary.
After the removal of polyps, the woman continues to be registered with the gynecologist, since the formations can recur. For this reason, she should be examined every six months, keeping in mind the asymptomatic course of the disease.
In terms of prognosis, cervical polyps recur in about 30% of cases. There are no specific preventive measures. It is only important to exclude any traumatic situations for the cervix and to get rid of endocrine and gynecological pathologies in a timely manner.
Medication Therapy
As for the effective drug therapy of the cervical polyp, it does not exist. To date, there is not a single remedy that can eliminate such a neoplasm from the body or reduce the severity of the pathological process.
Therefore, if a woman is offered to take medications with a diagnosis of “cervical canal polyp”, then it will be directed only to the treatment of comorbidities that have become provocateurs of tumor growth. It comes down to taking hormones.









