Contents
Oncological diseases are the leading group of pathologies of modern mankind. In world medical practice, there has been progress in the successful treatment of the early stages of the disease. Restraining factors are the complexity of organizing regular large-scale diagnostic examinations at the preclinical stage of cancer, the high rate of pathogenesis of some of its forms. In this regard, educational work is important in order to increase the oncological alertness of the population.
What is cancer?
Cancer is a malignant tumor that grows from the internal tissues of the body. This disease is named that way because in 90% of cases of diseases, malignant outgrowths in patients resemble a cancer claw. In developed countries, 15–20% of all deaths are related to cancer.
Prospects for Cancer Treatment
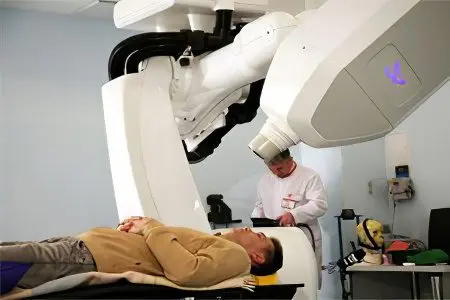
Oncology is a high-tech branch of medicine. The higher the logistics of all stages of the organization of medicine, from diagnosis to rehabilitation, the higher the patient’s chances of recovery. Entire countries are known with a high level of medical care for cancer patients (Germany, Switzerland, Israel, USA). Recently, Russia has also taken certain positive steps by creating high-tech centers.
If we touch on the early or late stage, then in addition to the above, the prospects for recovery in the early stages are significantly higher.
early stage cancer
The optimism with which physicians relate to the treatment of precancerous and early stages of oncology is based on the achievements of science, in the field of their practical use, including:
introduction into everyday practice of highly efficient low-invasive diagnostic complexes CT, MRI, MSCT, PEC-CT, which allow real-time 2D and 3D visualization of single clusters of affected cells (at the precancer stage), document and instantly transmit the results, at any distance for a competent analysis, to leading oncological centers;
medical cooperation, referral of patients, within the framework of the state program, for treatment to leading specialized medical centers, with payment for services from the budget of the Russian Federation or the budget of the territories of the Russian Federation;
better understanding of the mechanism of pathogenesis of the early stages of the oncological process, new methods and methods of treatment based on discoveries in the field of biochemistry, pathophysiology, and clinical medicine.
The above is effective only in relation to the debut of oncological diseases.
last stage of cancer
Patients admitted to medical institutions with advanced forms of pathology are much more difficult to treat effectively.
Reasons for late detection of cancer:
the technology of early detection of oncological diseases in a large population of people has not been worked out, patients who do not have clinical symptoms consider themselves healthy;
high rate of pathogenesis from subclinical course to rapid growth of tumors, and metastasis, in some forms of cancer.
Epidemiology of cancer patients

The highest chance of recovery are those who are diagnosed at the first (early) stage of oncology. The probability of saving life within five years after diagnosis in this group of patients is 95%.
More than a hundred nosological forms of human oncological diseases have been established. The most common malignant tumors are found in organs and tissues with a high rate of apoptosis (programmed death), respectively, the replacement of dead cells with new ones with similar properties.
Oncological diseases with primary localization in the chest girdle:
light;
mammary gland;
thyroid gland.
Oncological diseases with primary localization in the abdominal belt:
stomach;
liver;
kidney;
pancreas.
Oncological diseases with primary localization in the pelvic organs:
prostate;
colon and rectum;
body and cervix;
ovaries;
Bladder;
Oncological diseases with primary localization on the skin and mucous membranes:
melanomas of the skin and mucous membranes.
Oncological diseases of the lymphatic and hematopoietic systems:
leukemia;
lymphomas.
For different age groups, the increased risks of developing oncological diseases are reliably confirmed:
organs of hematopoiesis and lymph formation – up to 30 years;
stomach, thyroid gland, lymphoma, leukemia (men and women), cervix, ovaries, mammary gland (women) – 31-40 years;
lungs, gastrointestinal tract (men, women), mammary gland, female genital organs (women) – 41-50 years;
gastrointestinal tract, lungs – 51-60 years;
lungs, skin, gastrointestinal tract, mammary gland – 61-70 years;
skin, lungs, gastrointestinal tract – over 70 years old.
Cancer causes

What causes cancer, so far no one has proven exactly. Now there are several dozen scientific points of view.
If all of them are combined into one general picture, then three main factors contributing to the development of a malignant tumor are distinguished:
physical factors – these include radiation, ultraviolet;
chemical factors – they include carcinogenic substances;
biological factors are some dangerous viruses.
All of them first lead to the pathology of the DNA structure, the result of which, as a rule, is the activation of the oncogene and the acquisition of eternal life by the cells. As a result, the cells do not die, they begin to multiply at a tremendous speed, forming the very tumor.
These factors are external causes of cancer. But, besides external factors, there are internal reasons. We are talking about hereditary predisposition. In this case, your body either has a reduced ability to repair DNA, or a reduced immunity to oncology. Often the internal and external causes of cancer are so blurred that it is difficult to say about the primacy of their impact.
In the scientific world, the mutation theory of cancer is generally accepted. According to this theory, a cancer cell is the result of point genetic failures of immature body cells under the influence of external or internal factors. Other theories of carcinogenesis are also discussed.
However, none fully reflects the essence of the disease, since:
modern principles of cancer treatment are based on eliminating the consequences of an already developed disease – suppressing the growth of tumor cells with the help of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
there are no principles for understanding the methods of controlling cell mutations.
After the discovery of the universal mechanism of carcinogenesis, no doubt, a way will be found to exclude the development of malignant tumors, which means a real victory over the disease.
Therefore, in this text, delving into the description of various theories does not make practical sense. Let us dwell on the simple and understandable moments of carcinogenesis, which are not in doubt, are recognized by all scientists, and are of practical use to readers.
Why does cancer occur?
The human body is made up of a huge number of cells, about 1013 – 1014, four types of tissue: epithelial, connective tissue, muscle, nervous, which are formed from more than 200 types of specialized cells. In a normal organism, all cells act in concert according to a single genetic program.
The lifespan of cells is programmed. For each type of cell, an individual limit of existence is set, for example, a platelet exists for 4 days, and an erythrocyte – 125 days. The human body is constantly updated with new cells.
Stages of a healthy body cell:
The origin and division of stem cells of the body.
Maturation. Genetically determined desire of the cell to morphological and physiological specialization.
Specialization. Acquisition by a cell of morphological, histological, physiological characteristics of a mature one, for example: only similar cells are obtained from an epithelial cell, an erythrocyte, a lymphocyte.
Activity. The full functioning of cells in commonwealth and comprehensive subordination to the macroorganism.
Aging. The period of withering of physiological functions, morphological decrepitude.
Programmed death (apoptosis). The main difference from pathological death – necrosis, is that there is no inflammatory edema around the cell in the state of apoptosis.
Pathological mutations occur every second, however, as a result of multi-stage regulation, altered cells in a healthy body, “bad” cells are destroyed.
Under the influence of internal and / or external pathogenic factors (genetic, physical, chemical, biological), regulation fails, altered cells do not die, but continue to multiply at the place of formation, but according to their own program, not associated with the body.
The essential difference is that mutated cells do not reach the stage of specialization and the stages following it, respectively, their programmed death (apoptosis) does not obey the unified laws of a healthy organism.
Stages of a tumor in the body.
Hyperplasia or excess formation of immature cells;
Formation of a benign tumor
This stage may:
absent in some forms of cancer, the stage of hyperplasia immediately passes into the stage of dysplasia;
be the final stage, without further continuation of pathogenesis.
A benign tumor grows slowly, does not have metastases, and is dangerous in case of compression of the surrounding nerve fibers and blood vessels.
Dysplasia. Fixation and continuation of the pathological growth of altered cells. The transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant one is called malignancy.
A precancerous condition is a borderline condition when a tumor is present, but regression is possible. Another important feature of cells in this state is their localization in a limited space.
invasive cancer. The development of pathogenesis is accompanied by the appearance of metastases, the development of inflammatory reactions in the areas of tumor growth. The prognosis of the outcome of the disease is considered unfavorable if metastases are detected in distant organs.
Carcinogens as a cause of cancer
The main cause of cancer is the main property of the disease – damage to the DNA structure. And damage it carcinogens. Naturally, a person has a natural defense against this.
The body is able to repair itself and destroy carcinogens and even malignant tumors themselves. But with age, this function of the body weakens. Therefore, the chance of getting cancer will depend not only on the work of the body, but also on the amount of incoming carcinogens. Therefore, reducing the intake of carcinogens in the body gives a significant prevention of cancer.
Action of carcinogens
Different carcinogens affect the structure of DNA in different ways. For example, physical damage is caused by carcinogens that produce large amounts of free radicals. These include ultraviolet and x-rays. There are also chemical carcinogens that cause damage by creating chemical bonds. Viruses are classified as biological carcinogens. Viruses usually insert themselves into the very structure of DNA and destroy it.
But the emergence of carcinogens can also contribute to the medicine itself – for example, the use of ionizing radiation and certain variations of hormone therapy and cancer therapy.
Heredity and cancer
Heredity also affects the risk of cancer. A person either has a hereditary predisposition to cancer from birth, associated with weak immunity, or your body has a reduced ability to repair DNA.
cancer and smoking
Tobacco smoking is the best source of two risk factors at once: in addition to physical poisoning, the smoker also receives chemical exposure. It has been proven that about 8 microsieverts comes out of one pack of cigarettes, which is equal to 800 microroentgens. This amount of exposure creates a whole radiation background in 24 hours! And if the smoker smokes much more than one pack? In other words, an active smoker receives a huge amount of toxic substances from which the lungs and stomach suffer, and in addition, he receives a triple dose of radiation! And why don’t these poor people even try to quit smoking?
Currently, 80% of all lung cancer cases are due to smoking and only 10% each to radon and other factors. Every year, 600 people die of cancer!
cancer risk factors statistics
In 95% of cases, cancer occurs due to poor environment and lifestyle:
tobacco smoking – 30% of pathologies;
nutrition – 35% of pathologies;
infections – 10%;
occupational carcinogens – 5%;
ionizing and ultraviolet radiation – 6%;
alcoholism – 2%;
polluted air – 1%;
sexual infections – 4%;
low physical activity – 4%.
It should be noted that the highest percentage shows malnutrition! The reasons are a high-calorie diet, obesity, the presence of carcinogens in foods, a small amount of fiber. Is it time to change your diet and start eating right?









