Contents
Several decades ago, the exact cause of the development of stomach and intestinal ulcers was unknown to medicine. Almost half a century ago, scientists discovered the negative effect of Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium that lives in the human digestive tract. The immune system keeps its concentration within acceptable limits, but under favorable conditions, the bacterium multiplies, damaging the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Helicobacter pylori is a unique harmful bacterium that causes the serious disease Helicobacter pylori. Such a dangerous disease of the stomach is also characteristic of the duodenum. This unusual bacterium lives in a special pyloric section of the stomach, due to which it became so called. It has been proven to easily resist the powerful destructive action of the typical acidic environment of the stomach. With the help of its flagella, this bacterium easily moves in the mucous walls of the stomach, and can also be fixed on them.
Helicobacter pylori causes numerous diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. When multiplying, these microorganisms have a detrimental effect on all cells of the stomach, which leads to various inflammatory processes. These include not only gastritis and ulcers, but also cancer. To date, the destruction of such dangerous bacteria can prevent the inevitable development of many pathologies.
What does Helicobacter pylori mean?
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is widespread in the human population. There are statistics from which it follows that 60% of people have it. The acidity of the gastric juice, which is aggressive for other microorganisms, does not pose any danger to it. This is the usual habitat for the bacterium, in which it exists for many years, destroying the lining of the digestive tract. Such an impact becomes a factor in the development of stomach and small intestine ulcers, gastritis, duodenitis, in complicated cases combining these diseases. A long-term ulceration can transform into a cancerous tumor.
Not all infected carriers of this disease require antibiotic therapy. The minimum number of bacteria cannot harm the human body, as they are held back by the immune system. In some cases, immunity weakens.
Defense Weakening Factors:
excessive physical stress;
psycho-emotional overload;
infection;
abuse of bad habits;
sedentary lifestyle;
unhealthy diet: the inclusion in the diet of smoked meats, marinades, spices, sour foods that irritate the mucous membrane and create defects on it;
violation of the diet: rare meals in large volumes, dry food.
In the initial stages of the disease, gastritis develops, which subsequently develops into an ulcer. Peptic ulcer threatens with perforation of the wall of the stomach and intestines, the development of bleeding or oncological pathology. These transformations entail structural changes in other organs of the gastrointestinal tract: in the liver, in the pancreas.
Until 1970, it was believed that inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal mucosa and stomach ulcers were caused by stress factors and eating disorders. To prove what causes Helicobacter pylori infection, its researcher, Australian scientist B. Marshall, drank a concentrate of this culture. During the study, it was found that after a few days he developed gastritis. For their work, Barry Marshall and his team were awarded the Nobel Prize in 2005.
When diagnosing diseases of the stomach and intestines, the gastroenterologist directs the patient for a diagnostic study. The purpose of diagnostics is to find the causative agent of the infection and assess the damage caused by it.
Diagnostic methods:
analysis of gastric juice;
biopsy of the gastric mucosa;
blood test for biochemistry;
PCR test for the detection of antibodies to helicobacter pylori in blood serum.
Polymerase chain reaction will help to detect infection even at minimal concentrations of bacteria in the human body.
Symptoms of Helicobacter

The main warning symptoms that directly indicate infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori are often recurring severe pain in the stomach. Often the pain is localized on an empty stomach, decreasing after eating. Such symptoms indicate the formation of ulcers and erosions on the walls.
It should be mentioned that with helicobacteriosis, patients often complain of heartburn and heaviness in the stomach, and poor digestibility of fatty meat foods can also be observed. In advanced conditions, nausea and, in rare cases, vomiting can be noted. To determine the presence of bacteria, a special test is used, which, using biochemical reactions, determines the content of immunoglobulins in the blood serum. In addition, endoscopy and a breath test are indicated.
Even if the causative agent of the infection has not yet been found during the diagnosis, a person infected with the bacterium notices short-term signs of dyspepsia.
How the clinic of the disease manifests itself:
Hungry pains of low intensity, decreasing after eating;
Nausea, rarely vomiting;
Burping;
Flatulence, bloating.
It is quite possible that the intensity of these manifestations will decrease, and for many years a person will be sure that the tone is healthy, but if the risk factors coincide, the colony of bacteria activates its destructive work. These are smoking, alcohol abuse, infectious infection, and other reasons that reduce immunity.
After the discovery of the leading role of Helicobacter pylori in the development of gastroenterological diseases, the frequency of recurrence of gastritis and peptic ulcer decreased by 10-12 times. Currently, without diagnosis, the presence of a bacterium in the patient’s body does not begin the treatment of these diseases.
Causes of Helicobacter pylori infection

Bacteria absolutely cannot live in the open air. As a rule, it is transmitted through the saliva and mucus of a person through contact. Usually, infection occurs through the household route through dishes and standard personal hygiene products, as well as through kissing. It is known that the family and friends who often come into contact with the patient always fall into the risk group.
When it enters the human stomach through the esophagus, such a bacterium does not die, despite the action of hydrochloric acid. Bacteria easily penetrate the mucous membranes, destroying tissues, which causes disruption of normal functioning. At the same time, the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed, and then erosion, gastritis and ulcers develop. It is believed that if left untreated, the risk of stomach cancer increases significantly.
Since the most likely route for the bacterium to enter the human body is contact with the saliva and mucus of the patient, there are the following causes of infection:
kisses;
Use of common utensils, personal hygiene items;
Transfer of bacteria from mother to child.
Most often, relatives, friends, family members of the carrier of the infection are at risk of infection. The transition of bacteria from one carrier to another increases when basic hygiene standards are not observed, and the level of culture is low. At risk are residents of communal apartments, hostels, social institutions, as well as doctors. In developed countries, the risk of developing heliobacteriosis is much less than in countries with a low standard of living. In Russia, the social map of the distribution of Helicobacter pylori is paradoxical – cases of ulcers and gastritis due to infection with this bacterium are often found in wealthy families.
What does Helicobacter pylori look like?
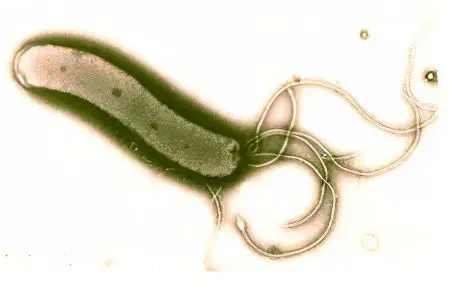
With such a prevalence of the disease, it is quite natural to ask what is helicobacter pylori? Here is a brief description of the microorganism: it is a spiral-shaped bacterium with flagella at one end. These flagella help Helicobacter to move in the digestive system, to be fixed on the gastric mucosa. The bacterium is able to transform its shape from spiral to oval or round.
The term helicobacter pylori comes from the name of the place of its localization – the pyloric part of the stomach. Bacteria are adapted to exist in the acidic environment of gastric juice, they exist without oxygen. So that the hydrochloric acid of the stomach does not damage Helicobacter pylori, it secretes special enzymes, surrounding itself with it, neutralizing the gastric juice. The flagella of the microorganism penetrate through the mucous membrane to the cells of the parietal layer, violating the integrity of the protective environment.
The characterization of the activity of the bacterium would be incomplete without a description of the pathogenesis of helicobacter pylori. It is the cells of the parietal layer of the stomach and intestines that are the source of nutrition for the bacteria. It destroys them, simultaneously releasing ammonia and toxic substances, poisoning the body with the products of its vital activity. The body’s defense system in the form of neutrophils seeks to destroy pathogenic microbes, but it also directs its energy to the cells of the mucous membrane with which the bacterium has already interacted.
Penetrating through the defects of the mucosa, hydrochloric acid actively acts on unsuitable tissues, causing ulceration. How long does Helicobacter pylori live? The bacterium can exist in the pyloric section of the stomach and in its bulb for several decades, until the patient undergoes a course of antibiotic therapy. Outside the human body, she lives a very short time, dies very quickly.
How is Helicobacter pylori transmitted?

Infection with helicobacter pylori occurs by contact, through the saliva of the carrier of the infection. It is quite possible, although much less common, by another alimentary route of infection: through food or liquid. This infection is not transmitted by airborne droplets. The contact-household route of infection makes it possible to consider Helicobacter as a “family microbe”, when, if it is found in one family member, it can be assumed with a high degree of probability (in 95% of cases) that Heliobacteriosis is also present in the rest.
The most likely modes of transmission of the bacterium are:
iatrogenic – in diagnostic procedures that involve insufficiently well-processed instruments, during endoscopy;
fecal-oral – when contaminated food, water that has come into contact with the feces of the infection carrier enters the human body;
oral-oral – with kisses, when using someone else’s toothbrush, unwashed cutlery in canteens and cafes.
There is a theoretical possibility of transmission of the bacterium from domestic animals: pigs, cows, cats and dogs, as well as from monkeys.
Why is the bacterium dangerous?
There are two mechanisms of the pathogenic effect of Helicobacter pylori on the human body.
What is dangerous bacterium:
helicobacter pylori endotoxins have a negative effect on tissues, damaging the endothelium lining the vessels from the inside, affecting smooth muscle muscles;
when exposed to it, immune-inflammatory reactions are activated, associated pathologies arise.
With the influence of bacteria, the digestive system becomes functionally imperfect, since the protective function of the gastric mucosa is disrupted and substances are absorbed into the blood that had not previously entered it. With prolonged existence in the stomach of Helicobacter pylori, the motility of the gastrointestinal tract is disturbed, the synthesis of hormones that stimulate the peristalsis of the stomach and intestines is disrupted.
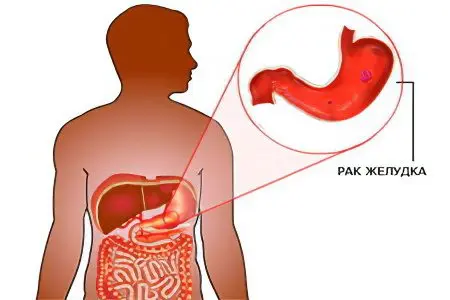
Colonies of bacteria displace beneficial microorganisms of the digestive system, provoking the development of dysbacteriosis. The long course of chronic gastritis caused by it leads to atrophy of the mucosa and the formation of foci of metaplasia on it, when the typical covering of the wall of the stomach and intestines is transformed into atypical cells. In addition to these changes, the secretion of gastric juice, which performs a protective function that prevents the development of neoplasms, decreases. All these factors stimulate the development of stomach cancer, less often – intestines.
The danger of this condition lies in the fact that the patient may not feel severe pain, especially if the cancer occurs against the background of atrophic gastritis. Much more often he feels disgust for protein foods, weakness, irritability, depression, loses interest in the environment.
Diagnostics

In some patients with Helicobacteriosis, certain symptoms may not be observed. Special tests are used to determine the presence of bacteria. Shown histological and special urease analysis to detect Helicobacter pylori.
A cytological study is based on obtaining smears-prints, which are taken during endoscopy, and this procedure also requires biopsy specimens of the mucous membrane of a special antrum of the stomach. As a rule, a biopsy specimen is taken aimingly from those areas where deviations from the norms are visually most pronounced. A specialist in such areas can observe hyperemia and edema. Often spiral-shaped Helicobacteria are located in the center of the mucus.
Such a cytological study determines the three main degrees of contamination of mucous membranes with bacteria. In the presence of less than 20 microbial bodies, a weak contamination is diagnosed, which does not cause concern for human health. Cellular infiltration is also detected when microorganisms are detected in imprint smears and plasma cells.
Depending on the number of certain cellular elements, one can indirectly judge the pronounced degree of activity and the inflammatory process. In addition, such a study reveals proliferative processes in the mucous membranes, dysplasia and metaplasia, as well as various malignant tumors. However, the cytological method does not give an idea of the structure of the mucous membranes.
A special urease test is considered an effective rapid method, which is mainly based on the activity of the microorganisms presented. It is made using a special carrier gel containing urea, a special bacteriostatic agent and a special phenol-rol as a necessary indicator. Such a pH indicator allows you to draw accurate conclusions about the specific state of the gastric mucosa. A mucosal biopsy obtained from endoscopy is also included in this test.
In extremely rare cases, the test shows false negative results, which is possible with a weak Helicobacter pylori infection. To increase the reliability, specialists usually use histological and urease methods. After the antibiotic treatment, they should be repeated. If necessary, a second course of combined therapy of the anti-Helicobacter type can be prescribed, which will avoid early relapses of the disease.
The special breath test is non-invasive and safe. It allows you to easily determine the level of colonization of the population of mucous membranes by these microorganisms. Such an analysis is considered optimal for the full control of eradication therapy. This study should be done on an empty stomach. First, special samples of background exhaled air are taken, and then, after a light breakfast, a test substrate is used.
Various histological methods are designed to quickly detect Helicobacter pylori in biopsy specimens, allowing simultaneous study of morphological changes. Giemsa’s bright coloring method is the most accessible and simplest. With this test, microorganisms are clearly visible on the surface of the epithelium and in the depths of the pits. Another histological method for precise DNA hybridization is sensitive and highly specific. It allows identification of numerous strains of Helicobacter pylori.
Other methods are also used for diagnosis. These include immunological and microbiological methods, polymerase chain reaction, as well as the determination of antigen in feces. As a rule, blood and endoscopy results are taken for analysis, as well as breathing and feces are examined.
Treatment and prevention of helicobacteriosis
The main treatment of helicobacteriosis mainly involves the long-term conduct of the necessary complex therapy, which is aimed at the destruction of harmful microorganisms in the human stomach (more about the treatment regimen).
It is this condition that is necessary for the full healing of all erosions and ulcers on the mucous membranes. Even if the symptoms of the disease do not appear, this is not a complete cure. Bacteria are capable of not manifesting themselves for a long time, while they remain on the walls of the stomach in a passive state.
It should be noted that the development of this disease is directly affected by the lifestyle of a particular person. With smoking and alcohol abuse, with improper nutrition and constant nervous strain, the risk of infection increases significantly. For the treatment of the patient, complex therapy is indicated, including the use of modern antibiotics and special drugs for the restoration of mucous membranes.
Compulsory treatment is indicated for gastric maltoma, atrophic gastritis, gastric resection in oncological formations, as well as for ulcerative conditions of the stomach and duodenum. It can be used not only during the period of exacerbation, but also during remission of the disease.
All treatment regimens for this Helicobacter pylori infection must include at least three drugs. Typically, these include two carefully selected antibiotics and a special proton pump inhibitor. With a dual regimen, treatment in most cases will be ineffective. Therefore, experienced specialists always select a triple eradication scheme. The duration of this treatment is seven days. One of the fastest acting antisecretory and antibacterial drugs is Pariet. It is included in complex therapy, prescribed at least twice a day. Already in the first day of such treatment, a reliable antisecretory effect is noticeable. There is also no need to use this drug before starting antibiotics, which is a definite plus.
Compliance with strict hygiene rules is also considered an equally important step. Always wash your hands before every meal, do not use dirty dishes and towels. Do not use other people’s personal hygiene products. If helicobacteriosis is detected in one family member, all other family members are subject to mandatory examination.
[Video] Dr. Evdokimenko – how to treat Helicobacter pylori, and is it necessary to drink antibiotics?
Consequences of no treatment
It is important to know what leads to self-treatment of heliobacteriosis or ignoring its symptoms. Only an accurate diagnosis, carried out under the guidance of a gastroenterologist, will make it possible to differentiate heliobacteriosis from other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or other somatic pathologies. Only a doctor can determine the duration of the course of treatment, select drugs taking into account contraindications and side effects based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis.
Neglect of one’s health threatens with the formation of malignant tumors of the stomach and duodenum, perforation of the ulcer, and the development of sepsis.
The connection of heliobacteriosis with the following diseases has been proven:
atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels and the brain;
vascular form of migraine;
Raynaud’s disease;
autoimmune diseases: atopic dermatitis, rosacea, alopecia areata (alopecia), iron deficiency anemia.
The connection between heliobacteriosis and the development of diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, and rheumatoid arthritis is questionable.
Since the bacterium is the cause of serious pathologies, you should not be irresponsible even for minimal symptoms of trouble.









