What is scoliosis?
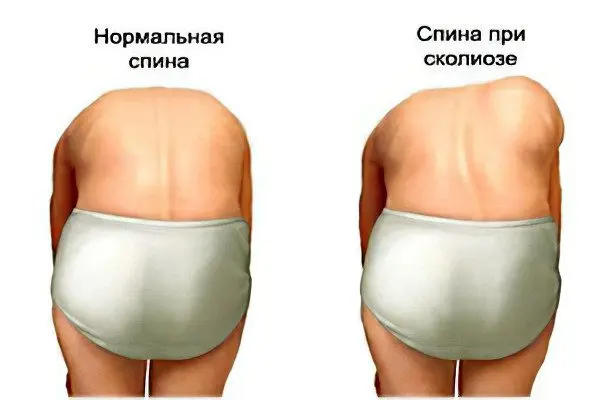
Scoliosis is a persistent deformity of the spine, accompanied by its curvature to the side relative to its axis. All parts of the spinal column are involved in the pathological process, while there is an increase in its physiological bends, as well as twisting. Untreated scoliosis leads to serious consequences, to secondary deformation of the chest, pelvic bones. This entails disturbances in the functioning of internal organs: the heart, lungs, kidneys, intestines, etc.
Scoliosis can develop in childhood or during puberty. The reason for the formation of curvature of the spinal column most often remains unclear. Therapy implies a conservative effect on the body, although in difficult cases the patient is sent for surgery.
It is the periods of active growth of a child at the age of 4-6 years and 10-14 years that are the most dangerous in terms of the development of scoliosis. Parents should pay attention to the posture of a teenager during his puberty. For girls, this is the age of 10-13 years, and for boys – 11-14 years.
Poor posture and scoliosis are two completely different problems. Violations of posture can be corrected by performing physical exercises, and scoliosis requires systematic treatment under the supervision of a doctor throughout the entire period of growth of the child.
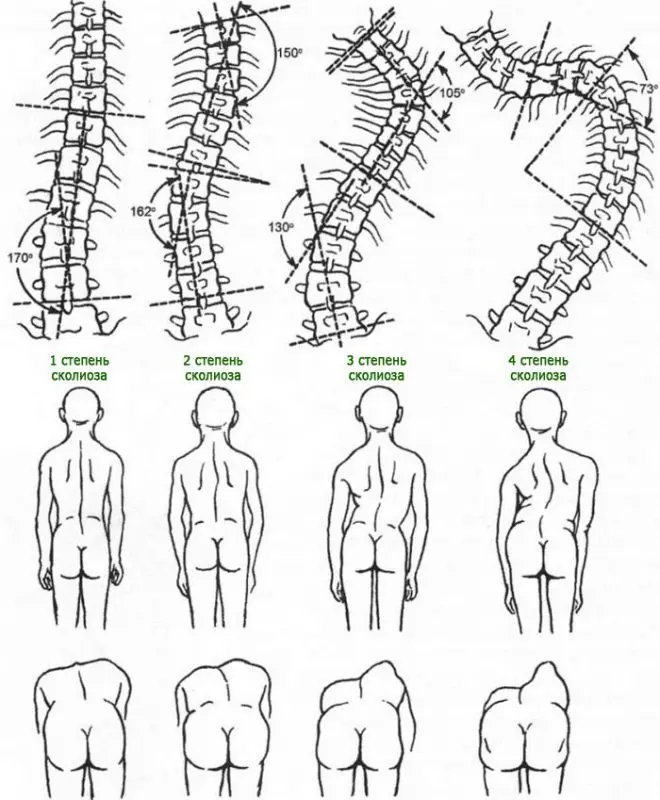
In the general system of orthopedic diseases in children, scoliosis accounts for up to 30% of cases. Although it is impossible to exclude such a situation when scoliosis is formed in adults. It has been found that about 10% of adolescents have scoliosis, but less than 1% of them actually require treatment. Most often, lumbar scoliosis develops, less often the curvature of the spine is observed in the upper or lower back. The severity of the course of scoliosis is determined by the degree of curvature of the spine and the angle of rotation of the body (APT), which is measured in degrees. Approximately 80% of scoliosis cases are considered “mild” and the angle of curvature does not exceed 20°C. If this figure is higher, then the person needs medical attention.
The causes of scoliosis
The spinal column most often consists of 33 vertebrae (in the coccygeal segment, the number of vertebrae may vary). The physiological curves of the spinal column allow it to perform a spring function, that is, while running, jumping, walking and performing other movements, the spine works like a spring.
Anatomical curves of the spinal column:
cervical lordosis. The bend is concentrated in the neck, has the shape of an arc, the top of which is directed forward.
Thoracic kyphosis – the bend is located in the region of the thoracic spine, has the shape of an arc, the top of which is directed backward.
Lumbar lordosis – a bend in the lumbar region, the top of the arc is directed forward.
Sacral kyphosis – resembles thoracic kyphosis, but has a more rigid fixation.
If a person has curvature of the spinal column to the side, then we should talk about scoliosis. Its causes in 80% of cases cannot be established. Then experts talk about idiopathic scoliosis. Girls are 4-7 times more likely to suffer from idiopathic scoliosis than boys.
Of the reasons that are known to doctors today, scoliosis can lead to:
congenital scoliosis is a consequence of the fusion of the vertebrae with each other, or the presence of additional vertebrae that remain underdeveloped. Another cause of congenital scoliosis is the fusion of the ribs with each other. Pathology can also develop if there is a violation in the formation of the arches and processes of the vertebrae. These malformations cause the spinal column to grow asymmetrically. Most often, the diagnosis is made to the child before the moment when he is one year old. Congenital scoliosis progresses slowly.
Dysplastic scoliosis. Pathology is associated with congenital anomalies at the junction of the sacral and lumbar spine. As the reasons for the development of dysplastic congenital scoliosis can be identified:
Non-closure of the arches of the spine.
Underdevelopment of the vertebrae: the last lumbar, or the first sacral.
Lumbarization. In this case, a person will have fewer sacral vertebrae, and more lumbar vertebrae.
Sacralization. This increases the number of sacral vertebrae, and the number of lumbar vertebrae decreases.
Dysplastic scoliosis is most often diagnosed in children aged 3-6 years. Pathology has a severe course and rapid progression, as it is caused by metabolic disorders in the tissues of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs themselves.
“School” scoliosis is called the curvature of the spine, which develops in a child in adolescence. Scoliosis can be caused by past infections that have affected the state of a weak muscular-ligamentous apparatus. The situation is aggravated by prolonged uneven loads on the spine, sitting at the table in the wrong position, carrying a heavy briefcase in one hand, etc.
Neurogenic scoliosis, which is a consequence of disorders in the functioning of the nervous system.
The causes of the formation of neurogenic scoliosis are diseases such as:
Cerebral palsy.
Neurofibromatosis.
Radiculitis.
Spastic paralysis.
Syringomyelia is a degenerative disease of the spinal cord.
Poliomyelitis is a viral infection.
Myopathies are a whole group of diseases that are characterized by dystrophic damage to muscle tissue. Moreover, it is the skeletal muscles that suffer most often.
Rachitic scoliosis. In this case, the curvature of the spinal column is due to rickets. The disease manifests itself in children who experience an acute lack of vitamin D. As a result, muscle tone decreases, and the bones of the skeleton undergo deformation. In addition to scoliosis, a person develops osteoporosis, in which the bone density of the spinal column decreases.
Static scoliosis, which is formed against the background of existing deformities of the lower extremities. If the legs are affected, the pelvis will be out of position when the person is standing. The pelvic bones have stable connections with the sacrum, which entails violations in the region of the spinal column, causing its curvature. The most common cause of static scoliosis is congenital dislocation of the hip.
Acquired scoliosis can develop against the background of a severe injury or after an amputation of a limb.
A significant difference in leg length can cause scoliosis.
The difference between structural and non-structural scoliosis should be understood. Non-structural deformities include those that are a simple lateral deviation of the spine. There are no gross anatomical changes in the spine. There is no fixed rotation. This is the main diagnostic criterion that allows you to distinguish non-structural scoliosis from structural. In the latter case, fixed rotation is always present.
In connection with the etiological factor that leads to the formation of scoliosis, the following non-structural varieties are distinguished:
postural scoliosis, which is a consequence of a violation of posture. It cannot be detected by x-ray of the spinal column in the supine position. It also disappears when the torso is tilted forward. Most often it is diagnosed in children by the age of 10. Predominantly – this is a right-sided curvature.
Reflex scoliosis, which develops as a result of the fact that a person withstands a forced position of the body for a long time against the background of a pain symptom. Experts do not attribute this type of curvature to true scoliosis, calling it a gentle posture. The most common cause of the formation of such a curvature is a herniated disc.
Compensatory scoliosis, which is a consequence of the shortening of one leg. In this case, the pelvis will tilt, which will entail the formation of a bulge in the spine in the direction of shortening.
Hysterical scoliosis, which is rare in medical practice and has a psychological nature. This type of scoliosis gives the impression of a severe disorder, but may spontaneously disappear and recur.
Types of scoliosis
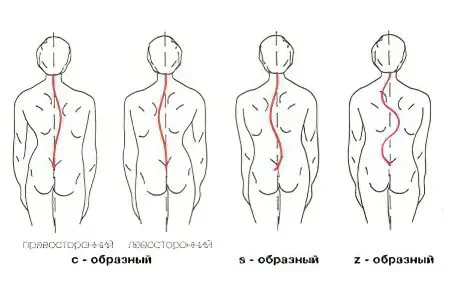
The criteria that underlie the classification of the disease may be different. So, there is a classification according to the location of the curvature in a particular section of the spine. There are lumbosacral, thoracic and cervicothoracic scoliosis. There is also double scoliosis, in which 2 sections of the spinal column suffer at once.
Another criterion for classifying scoliosis is a form of curvature of the spine. In this regard, there are C-shaped scoliosis, S-shaped scoliosis, Z-shaped scoliosis.
There are also 4 degrees of scoliosis. If scoliosis of the first and second degrees of severity can be treated with conservative methods, then a person with degrees 3 and 4 of the severity of the disease needs surgical intervention.
Consequences of scoliosis
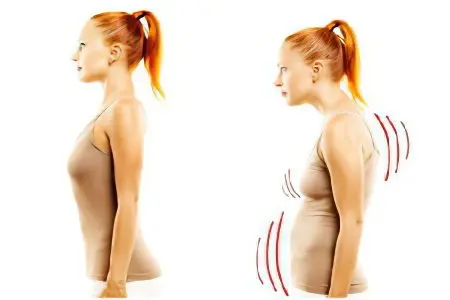
In the early stages of the development of scoliosis, a person will not experience any pronounced health disorders. It is possible that he will notice a slight asymmetry of body parts, stoop, posture disorders. As the disease progresses, deformation of the chest occurs, the formation of an intercostal hump is possible. At this time, pains appear in the affected parts of the spine, which tend to increase after physical exertion, after a long stay in a static position. A person with scoliosis will tire more quickly.
Deformation of the spinal column forces the patient to adjust his lifestyle, refuse to perform sudden movements, lift weights, etc. A person will not be able to engage in certain sports, such as volleyball, basketball, and dancing.
Consequences of scoliosis of the thoracic region:
Pinched nerves.
Syndrome of the vertebral artery.
Displacement of internal organs.
Violations of metabolic processes in the body.
The development of various diseases of internal organs.
In this case, almost all body systems will suffer. Thoracic scoliosis can lead to heart and lung failure. The ribs begin to shift, infringing on the lungs, which affects the volume of inhaled air. Lateral deformation threatens with pathologies of the heart, which are expressed in violations of the work of its right section. Complications grow smoothly, so a person may not notice this for a long period of time. The first signal may be difficulty breathing during exercise. In the future, shortness of breath joins, which begins to bother even during minor physical efforts. In parallel, blood pressure may increase, heart rhythm disturbances appear. Patients with scoliosis often suffer from coronary artery disease.
With scoliosis of the lumbar spine, the following health problems are possible:
Swelling of the lower extremities.
Weakness of the abdominal muscles.
Bloating.
Violations of the stool.
Frequent urination.
Stagnation in the pelvic organs.
Scoliosis provokes the development of osteoporosis, in which the bones become porous and brittle. The most formidable complication of the disease is compression of the spinal cord with paralysis of the legs and complete immobilization.
Special attention should be paid to complications from the nervous system. Patients with scoliosis often have complexes, they have mood swings, they are more irritable and short-tempered compared to healthy people. Also, the disease can lead to visual impairment, muscle paresis, impaired reflexes and sensitivity of the limbs.
In 50% of cases, people with 4 degrees of scoliosis get a disability, as they lose the ability to perform work. Often, they become unable to even take care of themselves.
[Video] Professor Serdyuk V. V. tells the patient’s story, gives specific recommendations:









