Contents
- What is herpes?
- Symptoms of herpes on the lips
- Stages of herpes on the lips
- Причины герпеса на губах
- Как передаётся герпес на губах?
- Herpes in children on the lips
- Is herpes permanent?
- Treatment of herpes on the lips
- Prophylaxis of herpes on the lips
The cold sore on the lips that many people know is caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-XNUMX). The official name of this disease is labial (labial) herpes. The disease is characterized by a latent course and periods of exacerbation with vesicular rashes on the mucous membranes of the lips and / or skin of the nasolabial triangle. There may be rashes on other parts of the mucous membranes and skin, as well as systemic lesions involving internal organs and systems in the pathogenesis.
What is herpes?
Herpes is an ailment, popularly known as a fever, when small bubbling rashes appear in the nose or on the lips. Activation of herpes indicates that the immune system is weakened. And the frequent appearance of herpes – for example, 2-3 times a year – indicates a significant decline in protective forces. It is believed that this virus always lives in the human body, but the external symptoms occur only in the activation of herpes. The latter, in turn, is provoked by a decrease in the body’s resistance. This can be severe hypothermia or overheating, a serious illness (for example, pneumonia), as well as stress.
Herpes simplex virus type XNUMX (HSV-I) and herpes virus type XNUMX (HSV-II) are combined into the group of herpes simplex. Virions (formed viruses) of the first and second types are morphologically indistinguishable. Symptoms of diseases are manifested by similar vesicular rashes. Differences in the localization of the rash, the severity of pathogenesis, the frequency of relapses and the antigenic species specificity of viruses.
Each type of herpes virus has its own localization of vesicular rashes on the mucous membranes and skin:
HSV-I – on the lips and nasolabial triangle;
HSV-II – on the anogenital part of the body (in the area of the anus and genitals).
В отдельных случаях локализация высыпаний вирусов I и II типа может меняться. Поэтому при диагностике лабиального герпеса проводят видовую дифференциацию на специфические IgM, чаще IgG к ВПГ-I и ВПГ-II.
It has been proven that:
A lesion on the lips caused by HSV-II is possible after direct contact of a susceptible person with an affected area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe skin (mucous membranes) of the genitals of a patient with this type of herpes, for example, during oral sex;
Type XNUMX virus causes a more aggressive cold sore on the lips, with frequent periods of flare-ups;
Persons who have antibodies to the first type of herpes virus do not have them to the second type.
The latter is important when planning a pregnancy. Herpes simplex virus type II is characterized by severe pathogenesis with serious complications.
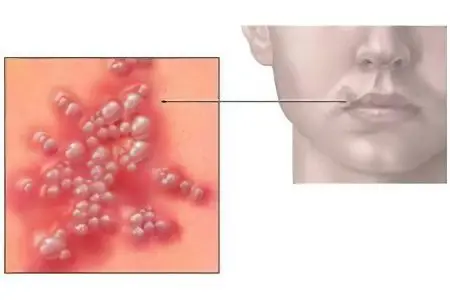
A person after initial contact with the herpes virus of the first type may not feel symptoms of the disease for a long time – this is an inapparent (asymptomatic) stage. The virus is invisible to a healthy person with a well-balanced immune system, but the disease always causes a state of unstable equilibrium. A distinctive feature of all herpes viruses, as well as pathogens of other sluggish viral infections, is the latent (latent or persistent) presence of the pathogen in the body.
Latent infection is when the virus is periodically in two states:
Defective (DNA transcript) – remission;
Active – manifestation of symptoms.
The stage of exacerbation of a latent infection occurs under the influence of other pathogens, as well as hypothermia, overheating, insolation, stress and other negative factors. A persistent infection is when traces of a virus (antibody) are found in the body in the absence of the pathogen itself. Such diseases are accompanied by immunological changes in the body. The clinic is absent, poorly expressed or disguised as another disease.
Инаппарантное (бессимптомное) течение инфекции обеспечивается посредством:
Локализации возбудителя в тканях нервной системы, недоступных для действия иммунных клеток;
Own adaptive mechanisms of the virus, developed in the process of evolution.
В стадии латентной инфекции при нахождении ВПГ-I в клетках нервной ткани они проявляют стойкость к воздействию:
Medicinal (chemical) means;
physical factors;
Protective (protective) properties of the immune system.
Virus carrying continues throughout life, especially with repeated human contact with the virus. In the active phase of HSV-I, like any other viruses, they move from the cells of the nervous tissue into the cells of the blood, lymph, other biological fluids and tissues of the body, where they activate the mechanisms of pathogenesis.
The slow course of viral infections, including herpes, is due to the common properties of all viruses, which are fully characteristic of HSV-I:
Все вирусы – облигатные (обязательные) паразиты клеток организма и бактерий. Вне тела хозяина их активная фаза невозможна;
Кратковременное нахождение активных вирусов вне клетки, например, при заражении соседних клеток, возможно только под защитой оболочки, состоящей из фрагментов клетки, повреждённой вирусом. Вирус, лишенный оболочки из фрагментов клетки и находящийся вне клетки-хозяина, напоминает биополимер без признаков жизни;
Herpes simplex viruses are resistant to sub-zero temperatures and unstable to positive temperatures. At temperatures up to -700They are viable for up to ten years. And at a temperature of +500C – inactivated after thirty minutes. On the skin, herpes viruses survive up to four hours;
Antibiotics that are active in bacterial infections are useless in viral diseases, including herpes. The only group of direct-acting drugs that can suppress the replication of herpes viruses in the clinical course of the disease are acyclic nucleosides, chemically synthesized substances.
Antiviral protection of the body is formed due to:
Nonspecific barriers (skin, mucous membranes, mucous membrane secretions). Interferon is the most powerful factor in nonspecific human immunity;
Humoral barriers (complement, immunoglobulins of five classes and other components);
Cellular immunity (phagocytes, T- and B-lymphocytes, their subpopulations).
A person’s illness with herpes is not accompanied by the acquisition of complete immunity to re-infection. IgG antibodies detected in the blood of recovered people protect to some extent from re-infection, but do not provide total protective immunity.
The mechanism of activation of the virus is not fully understood, in some people herpes often manifests itself (more than six times a year), while in others who are virus carriers, herpes is rarely observed (1-3 per year) or does not occur at all. Probably, in addition to the state of immunity, the sensitivity of the organism to the development of herpetic pathogenesis is influenced by genetic factors and individual characteristics of the organism. It is also possible the influence of acquired factors to counteract the disease (active lifestyle, lack of bad habits, proper diet, etc.).
Symptoms of herpes on the lips
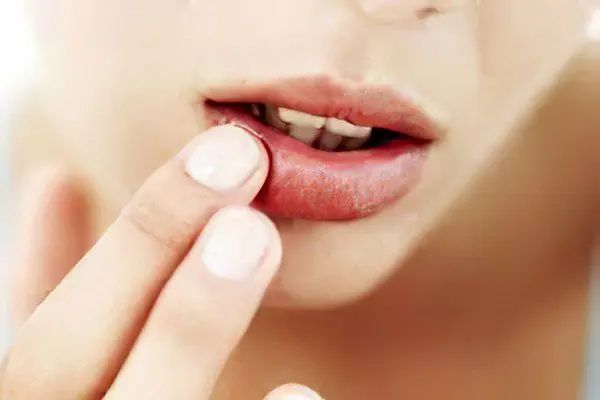

Briefly about the main symptoms
The main symptom of herpes is the appearance of blisters near the mouth, on the cheeks, lips and wings of the nose. Moreover, herpes is accompanied by low health, lack of appetite, fever, irritability and poor sleep.
After the manifestation of primary herpes (the debut of herpes symptoms) has occurred, the external signs disappear, but the virus still remains in your body. It can be activated at any moment and cause characteristic symptoms again. Again there will be clusters of bubbles, turning further into ulcers, in the same places or nearby. Secondary symptoms are more easily tolerated and last less time than those observed during primary herpes. However, rashes always look like bubbles that itch a lot, burst, and in their place there are wounds and crusts.
Details about the symptoms of herpes on the lips
В соответствии c классификацией простых герпесов, предложенной в 1991 году В.А. Исаковым и Д.К. Ермоленко, симптомы ВПГ- I и ВПГ-II не ограничиваются высыпаниями на губах и половых органах. Классические признаки встречаются у лиц с относительно сильным иммунитетом, не имеющих генетической предрасположенности к герпесам. У людей с ослабленным иммунитетом симптоматика характеризуется разнообразными проявлениями.
I. Symptoms of herpes simplex in individuals with no history of immune system depression
Ведущий симптом – зуд, затем одиночные или множественные везикулярные высыпания на границе губ и кожи лица, редко в других участках носогубного треугольника. Визуально симптомы проявляются на второй-третий день, средняя длительность патогенеза – пять-десять дней, в это время снижается качество жизни. Заболевание заканчивается появлением корочек, которые быстро исчезают, не оставляя следов на теле.
Лабиальный герпес служит маркером состояния иммунной системы, которое оценивают по частоте рецидивов герпеса:
Длительное или пожизненное отсутствие симптомов герпеса и его рецидивов – свидетельство гомеостаза организма;
From one to three times a year – a variant of the norm;
От трёх до шести раз в год – проблемы с иммунной системой средней тяжести;
Более шести раз в год – депрессия иммунной системы.
В двух последних случаях рекомендуется пройти обследование с целью изучения состояния гуморального и клеточного иммунитета, определения причин депрессии и путей возможной иммунокоррекции организма.
У лиц, имеющих проблемы с иммунитетом, лабиальный герпес может протекать атипично. В патогенез при этом вовлекаются многие системы и органы человека. Диагностика по клиническим симптомам затруднительна, окончательный диагноз ставится на основании выявления возбудителя заболевания или специфических антител к нему.
II. Herpes simplex symptoms in people with immunosuppression
Спектр клинических проявлений ВПГ-I у лиц с иммунодефицитным статусом (ИДС) очень разнообразен, и зависит от:
The presence of specific antibodies to HSV-I in the human body;
The state of the patient’s defenses;
Вирулентности и патогенности вируса.
The most severe course of the disease is noted after the primary infection, when there are no specific antibodies to the herpes virus.
Possible symptoms of the herpes simplex virus are formulated on the basis of the clinical classification of herpes simplex (according to Isakov and Ermolenko).
Typical forms of lesions caused by herpes simplex
Возможные места локализации пузырчатых высыпаний:
Слизистые оболочки желудочно-кишечного тракта (стоматит, гингивит, фарингит и др.);
Mucous membranes of the eyes (conjunctivitis, keratitis, iridocyclitis, etc.);
Skin areas (herpes of the lips, wings of the nose, face, hands, buttocks, etc.);
Mucous membranes of the penis, vulva, vagina, cervical canal, perineum;
Departments of the nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis);
Internal organs (lungs, liver).
Atypical forms of lesions caused by herpes simplex
Atypical lesions include:
Edematous course, symptoms in the form of limited erythema (redness) and swelling of the subcutaneous tissue. Papules and vesicles are absent, subjective sensations are burning, itching, pain at the site of erythema localization (when pressing on it with a finger, the skin area with erythema does not turn pale, and with hyperemia in a similar situation, a pale area remains under the finger);
Zosteriform herpes simplex (reminiscent of herpes Zoster – herpes zoster) is marked by a small pain syndrome. Localization of vesicles – along the nerve trunks on the trunk, face, arms or legs;
Eczema herpetiformis (Kaposi’s varioliform pustulosis). Characterized by high fever (39-410 C), intoxication syndrome, bullous eruptions and extensive erosions with purulent exudate. More often occurs in children, deaths are recorded;
Ulcerative-necrotic eczema. It is characterized by the formation of skin areas covered with ulcers with necrosis and purulent-hemorrhagic exudate. Moreover, secondary crusts, epithelialization and scarring at the healing stage are formed slowly;
Hemorrhagic eczema. The contents of the vesicles are bloody, in contrast to the usual herpetic vesicles with serous (colorless) contents;
Hemorrhagic-necrotic eczema – the contents of the vesicles are bloody, there are areas of necrosis (necrosis).
What does herpes on the lips look like?
В литературе встречаются описания высыпаний, подразделяемых на локальные, распространённые и генерализованные. При клинической диагностике простых герпесов учитывают локализацию высыпаний на коже.
Three main types of rashes:
Localized. Папулы и везикулы на отдельных небольших участках кожи или слизистых оболочек. Встречаются при герпетических заболеваниях лабиального (носогубного) типа;
Common. Papules, pustules and vesicles localized on a specific area of the body (legs, arms, buttocks, face). Diagnosed usually in individuals with a weakened immune system;
Generalized. Extensive foci of lesions over the entire surface of the body in the form of papules, pustules and vesicles in areas of hyperemic skin. The contents of the vesicles are serous or hemorrhagic; erosions are formed upon opening. They are detected in atypical forms of herpes simplex.
Stages of herpes on the lips
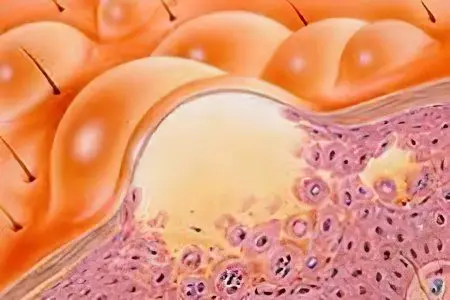
Патогенез заболевания протекает по определённому алгоритму. В развитии ВПГ-I выделяют четыре стадии:
Latent. From infection to the first clinical symptoms. The duration is not regulated, the stage can last for years (this is a feature of herpes). In acute viral infections, the incubation period is from one to two to three weeks. In the latent stage, the herpes simplex virus is localized in the cells of the nervous tissue in an inferior state;
Продромальная. Обычно проявляется зудом в месте будущих высыпаний, иногда гипертермией и снижением работоспособности. Могут быть и иные симптомы, в зависимости от тяжести патогенеза;
Clinical. It is characterized by typical symptoms of the disease, in this case – rashes on the lips or other parts of the body. During this period, the most typical changes at the microlevel are recorded (IgM antibodies are detected, then IgA and IgG, changes occur in the subpopulations of T- and B-lymphocytes and the ratios of suppressors, helpers and killers);
Outcome of the disease. Зависит от тяжести и характера заболевания, статуса иммунной системы и эффективности лечения.
Причины герпеса на губах
Говоря простым языком, вирус начинает свою активную жизнь при перегревании или переохлаждении, а также при менструации, беременности, постоянных стрессах и психических переживаниях, злоупотреблении алкоголем и заболевании инфекционными болезнями. Заражение герпесом происходит половым путём, даже при отсутствии у партнёра симптомов герпетической инфекции, а также через предметы общего пользования. Инфицирование плода герпесом во время родов возможно только при наличии везикулярных элементов на половых органах у матери. Проникнув в организм человека через слизистую оболочку или кожу, вирус герпеса достигает лимфатических узлов и внутренних органов. В дальнейшем возбудитель оседает в чувствительных нервных ганглиях.

Первичный контакт с ВПГ-I, говоря научным языком, вызывает в организме неподготовленного к инфекции человека ответную реакцию с последующей стабилизацией гомеостаза до уровня неустойчивого равновесия. Протективный иммунитет к вирусу не вырабатывается. Максимум чего можно достигнуть при формировании иммунной защиты – это сглаживание клинических проявлений лабиального герпеса.
Repeated contact a person with HSV-I causes a more restrained reaction due to the formation of active non-sterile immunity. A violent symptomatology upon repeated contact indicates defects in the immune system.
The causes of labial herpes are:
General hypothermia or overheating;
Taking immunosuppressants for allergies, chemotherapy and other reasons;
Сопутствующие заболевания (в том числе, вирусные), истощающие иммунную систему;
Nervous tension;
altered physiological state (pregnancy, lactation, menopause).
Why does herpes appear on the lips?
Herpes simplex virus is clinically manifested by primary rashes (papules and vesicles) on the skin and mucous membranes. The reasons for the specific localization of the herpes virus on the lips are not completely clear. The mechanisms of tropism of pathogenic agents of the virus (with an exacerbation of the disease) to the cells of the surface epithelium remain unexplored. There are several hypotheses, one of them is neurogenic.
Undoubtedly, the virus or its DNA is always found in the cells of the nerve ganglia. It has been established that the activation of the virus is associated with a violation of the content of cycloadenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in epithelial cells, a derivative of ATP, which is of great importance in tissue metabolism. In the available literature, there is no complete disclosure of the causes of selective (on the lips) localization of rashes. However, confirmation of this theory is the localization of rashes of certain types of herpes along the large nerve trunks.
Как передаётся герпес на губах?
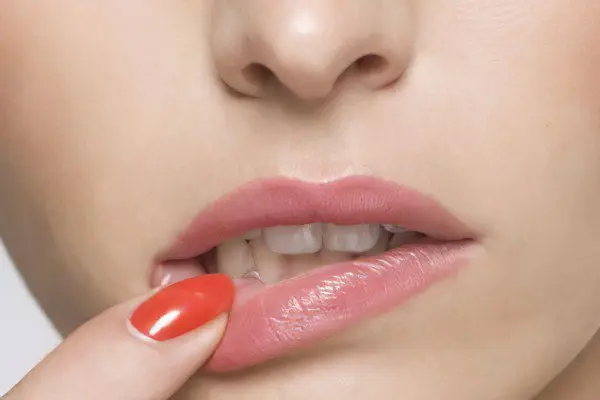

The herpes virus is in the human body for life, can be activated under the influence of adverse factors and cause clinical symptoms of herpes labialis with different pathogenesis.
Primary infection with labial herpes occurs:
Airborne, when the pathogen enters the air with microparticles of exhaled air. The highest concentration of the virus is recorded 2-3 m from the patient. With dust, the virus moves over considerable distances, however, a sufficient dose of the pathogen is required for infection, so infection from a sick person at close range is most likely;
Household contact (unprotected sex, in the case of HSV-I – oral sex and kissing, non-sterile cutlery, medical instruments);
With organ transplantation or transfusion of biological fluids (non-sterility);
Through the placental barrier during pregnancy (in the human body there are several natural barriers through which microorganisms and viruses cannot penetrate, but it has been found that in some cases the herpes virus overcomes this barrier);
When the fetus passes through the birth canal. To prevent infection, a caesarean section is used instead of natural delivery.
Herpes in children on the lips
Лабиальный герпес способен проявляться c первых недель жизни человека. Герпес новорождённых встречается редко, однако имеет тяжёлый патогенез, иногда даже с летальностью на 5-20 день заболевания. Детский герпес развивается на фоне отсутствия материнских антител к вирусу и недостаточности собственного иммунитета у ребёнка. Заражение может произойти в результате случаев, описанных выше (внутриутробное, во время родов), а также как результат госпитальной инфекции или заболевания одного из членов семьи.
Symptoms of labial herpes in newborns:
Skin rash in the form of vesicles filled with liquid;
fluctuations in body temperature;
Drowsiness and convulsions;
Decreased muscle tone.
Unlike herpes in adults, rashes in newborn children are observed at the end of the disease. These symptoms are not always fully manifested. The signs of herpes in children with timely treatment are not bright, in more than fifty percent of cases the clinical picture is limited to rashes. Unfavorable symptoms indicating systemic lesions of the central nervous system are convulsions, liver – decreased muscle tone.
In some cases, a vesicular rash with labial herpes is localized on the skin along the large nerve trunks – this is zosteriform localization. Most often, children from one to three years old suffer from herpetic stomatitis against the background of trauma to the mucous membrane of the jaw during teething. In severe cases, toxicosis, lymphadenitis of the submandibular and cervical nodes with symptoms of tonsillitis are noted, multiple herpetic lesions are found in the oral cavity. Secondary symptoms are profuse salivation (salivation), bleeding gums. In a laboratory blood test, leukopenia (insufficient number of leukocytes) is detected – evidence of exhaustion of the immune system, leukocytosis (active stage of protective reactions) is less often recorded.
In children aged 5-16 years with a normal immune status with recurrent herpes labialis, symptoms are manifested by rashes on the lips, which disappear within 4-7 days and recur 1-3 times a year.
Is herpes permanent?

Herpes is caused by a virus. Or rather, a parasite that lives inside the cell, being in its gene apparatus. Therefore, if a cell with a virus divides, then a secondary cell is born already infected with herpes. Therefore, if a person suddenly decides to completely and forever get rid of herpes, he will spend a lot of time and effort on treatment.
Most carriers of this disease have exacerbations infrequently – 1-2 times a year. However, the manifestations of herpes – those same vesicles on the lips, in intimate places and in other parts of the body where, due to our own carelessness, we can bring the virus – cause a lot of inconvenience due to location: this is a forced rejection of closeness with a loved one, and an unattractive external view, but nothing more. We are constantly intimidated, they say, pregnant women are recommended to have an abortion if antibodies to the herpes virus are detected. And patients “by eye”, without a thorough preliminary examination, are prescribed immunomodulatory drugs and are assured that herpes causes severe damage to internal organs … Due to the incompetence of individual doctors, real herpesophobia develops in society. But in most cases, these fears are greatly exaggerated.
Treatment of herpes on the lips
Herpes is treated with antiviral drugs. One-time topical application to the skin or ingestion of drugs helps to quickly cope with herpes.
Dosage, frequency of use and duration of treatment are indicated on the package or reported by the attending physician. The usual course of therapy takes fourteen days.
In cases of severe course of herpetic disease, complex treatment using specific, symptomatic and pathogenetic means of therapy is advisable.
Состав комплексной терапии зависит от стадии заболевания:
During an exacerbation of infection, etiotropic antiherpetic drugs, immunomodulators of cellular immunity and interferon inducers are indicated;
During the period of remission, the intoxication syndrome is reduced, as well as the body is strengthened with the help of natural antioxidants, adaptogens and prostaglandin inhibitors.
Prophylaxis of herpes on the lips

Specific prophylaxis
In Russia, an inactivated vaccine against HSV-I and HSV-II Vitagerpavak has been registered and is being used. Unfortunately, it does not provide complete protection against the virus, but it reduces the duration of the disease and eliminates the symptoms of the disease. The vaccine is used during the period of remission not earlier than two months after the last case of exacerbation, and combined with an immunostimulant (cycloferon).
Non-specific prophylaxis
Неспецифическая профилактика герпеса заключается в соблюдении простых правил:
Regular meals and a healthy, nutritious diet;
Active lifestyle and giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
Careful handling of rashes during an exacerbation of herpes (do not open the vesicles, do not remove the crusts).









