Contents
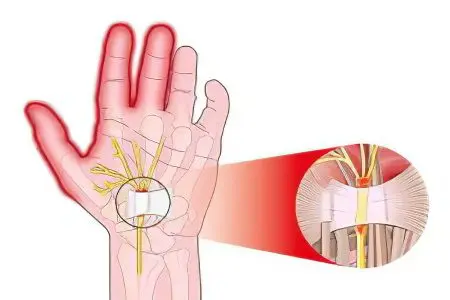
Tenosynovitis of the wrist joint is an inflammation of the inner lining of the tendons responsible for the mobility of the largest joint of the hand. This joint is a movable connection of the bones of the forearm and hand of a person. Pathology can develop as a result of an injury, against the background of constant excessive strain on the muscles responsible for the work of the joint, with infectious and rheumatic diseases.
Tendovaginitis can manifest itself acutely, or it can turn into a chronic form with frequent relapses of the disease. The main manifestations of inflammation are pain, swelling of the tissues and limitation of motor activity of the hand. Since the pathology is capable of adding to the complete loss of the functionality of the limb, the treatment should be timely and complete. If the patient seeks medical help on time, then therapy most often comes down to medication correction. The operation is carried out in exceptional cases.
Statistics indicate that in the general structure of tendovaginitis, inflammation of the hand is observed in 32% of cases, which is the most common indicator.
Causes of tendovaginitis of the wrist joint

Tenosynovitis of the wrist joint can develop due to a variety of reasons, including:
Tendovaginitis, as a result of a person’s professional activity. It is the features of the work that most often lead to inflammation of the synovial membranes of the tendon of the hand. Those people suffer who, by virtue of their duties, perform the same type of repetitive movements with the brush, excessively straining its muscles. At risk for tendovaginitis of the wrist are people working at a computer (operators, machinists), pianists, locksmiths, carpenters, blacksmiths, packers, milkmaids, ironers, seamstresses, etc. The disease most often develops acutely, and later becomes a chronic pathology .
Rheumatic diseases can provoke tendovaginitis of the wrist joint, as well as inflammation of the synovial sheaths of tendons of other localization. In this regard, pathologies such as Reiter’s syndrome, Bechterew’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic scleroderma, and rheumatism pose a danger. The disease most often has an acute course.
The penetration of bacteria into the cavity of the synovial sheath of the tendons of the wrist joint leads to violent inflammation. The infection can get into the specified area with the flow of blood or lymph, as well as during injury. The danger is represented by various injuries (injections, cuts, abrasions, open abscesses). If the infection gets to the tendon by the hematogenous route, then its focus can be located in almost any organ.
In terms of the development of tendovaginitis of the hand, infections such as brucellosis, tuberculosis, syphilis and gonorrhea can be dangerous. This cause of inflammation is rare, but no less dangerous. In this case, tendovaginitis will act as a complication of the underlying disease.
In connection with the etiological factor that underlies inflammation, infectious and aseptic tendovaginitis are distinguished. With aseptic tendovaginitis, the pathogenic flora does not take part in the development of the disease. Inflammation occurs against the background of irritation of the internal structures of the tendon sheath.
Infectious tendovaginitis is a consequence of the vital activity of the pathogenic flora, which enters the synovial sheath of the tendon from the external environment, or from within the body itself. In this case, inflammation is almost always accompanied by the release of pus and a severe course.
In turn, infectious tendovaginitis is divided into specific (provocateurs – gonococcus, Koch’s bacillus, treponema) and non-specific (causative agents of infection – staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci).
Symptoms of tendovaginitis of the wrist

Common symptoms of tendovaginitis of the wrist are as follows:
Pain in the upper limb of varying intensity.
Swelling of tissues. The stronger the inflammation, the more swelling will be.
Redness of the skin in the area of the inflamed tendon.
Local or general increase in body temperature.
Violations in the work of the brush.
With nonspecific acute tendovaginitis of the hand, a person suffers from severe pain, swelling grows rapidly. There may also be signs of general intoxication of the body with fever, chills and headache. If purulent inflammation joins, then the pains become pulsating, as if “pulling” the tendon from the inside.
With nonspecific tendovaginitis of the hand, the symptoms of the underlying disease will come to the fore. The intensity of pain and swelling of the hand is similar to that observed in acute nonspecific tendovaginitis.
Tendovaginitis of the wrist joint, which was provoked by aseptic inflammation, most often manifests acutely. A person begins to experience severe pain in the arm, which intensifies when trying to make a particular movement. The hand swells, it becomes impossible to move it. Reddening of the limb and a local increase in temperature are not excluded. Harbingers of the development of tendovaginitis of the aseptic hand can be the feeling that the muscles are cramping. If the disease becomes chronic, then the pain subsides, disturbing the person from time to time. Edema is not observed, but when you try to move the limb, a soft crunch is heard.
Stenosing tendovaginitis is a separate form of tendovaginitis of the hand. It most often affects women between the ages of 40 and 50. The disease is characterized by the appearance of edema, the muscles at the site of inflammation become denser. Pain occurs after a load on the arm. In the future, the movements of the fingers begin to suffer, which will be problematic to unbend or bend. When trying to overcome resistance, a person will hear a click. The formation of contracture is the most severe complication of stenosing tendovaginitis.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is another pathology caused by stenosing tendovaginitis. The syndrome develops with a narrowing of the carpal tunnel, which runs in the wrist joint from the side of the palm. The sensitivity of 1, 2 and 4 fingers is reduced, the patient cannot perform movements with them. The brush becomes powerless.
De Quervain’s disease, in which, against the background of stenosing tendovaginitis, the work of the short extensor and the long abductor muscle of the first finger on the hand is disrupted. In addition to the fact that a person will no longer be able to perform a full range of movements with a brush, swelling and pain are observed during an exacerbation of the disease.
Diagnosis of tendovaginitis of the wrist joint
Diagnosis of tendovaginitis of the wrist joint is not difficult. It is enough for the doctor to examine the patient to make the correct diagnosis. The main criteria on which the doctor relies are the characteristic symptoms of the disease. It is important to find out the nature of tendovaginitis, for which the patient is interviewed in detail.
An x-ray of the hand and an x-ray of the wrist joint can help clarify the diagnosis. These techniques will provide information about the condition of the joint and bones, which will make it possible to distinguish tendovaginitis from arthritis and osteomyelitis.
If the doctor suspects that tendovaginitis is the result of infection of the body with tuberculosis, syphilis or brucellosis, then he is prescribed the appropriate tests.
Treatment of tendovaginitis of the wrist joint
The treatment of tendovaginitis of the wrist joint is carried out by such specialists as: orthopedists, surgeons, traumatologists, rheumatologists.
Treatment of aseptic tendovaginitis cysts. If the patient has aseptic tendovaginitis of the hand in the acute stage, then the limb must be immobilized. Well, if it is possible to maintain an elevated position for the hand.
To reduce pain and relieve inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, including: Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Butadione, etc. In parallel, the patient will undergo UHF sessions. When it is possible to get rid of acute inflammation, the patient is shown electrophoresis with novocaine and hormonal drugs. Such procedures as have a good effect: treatment with ultraviolet rays, microwave therapy, ultrasound treatment. In order to prevent chronicization of the process, it is necessary to protect the limb from loads as much as possible. If due to professional activity it is impossible to do this, then the job should be changed.
When the disease nevertheless passed into a chronic form, a person will have to receive a course of treatment. To do this, for the duration of the exacerbation, the limb is necessarily immobilized, after which symptomatic therapy is carried out. In order for relapses to occur as rarely as possible, you need to visit the office of a professional massage therapist, perform gymnastic complexes. Applications with paraffin and ozocerite, electrophoresis with lidase have a good effect.
If the patient has stenosing tendovaginitis, then blockades with hormonal drugs are indicated for his treatment. When the ongoing therapy is ineffective, the patient is prepared for surgery to remove the tendon, or to dissect it.
Treatment of specific and nonspecific tendovaginitis of the hand. If the disease is caused by a nonspecific infectious flora, then the patient must be prescribed antibacterial drugs. Analgesics are prescribed to reduce pain. To speed up recovery, the doctor selects immunostimulating drugs for the patient.
When the inflammatory process is accompanied by suppuration, the focus should be opened and the cavity of the synovial sheath of the tendon should be drained.
Provided that tendovaginitis was caused by a specific flora, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease, depending on the sensitivity of the particular pathogen.
A complex of therapeutic exercises for tendovaginitis of the wrist joint
After acute inflammation has been removed, you can speed up recovery by performing a simple set of exercises.
They will also be useful to those people who have had an episode of tendovaginitis in history:
Put your hand on a flat surface, raise your palm and try to touch the tip of your thumb, the tip of your little finger. Then the palm is lowered. Repeat the exercise 6-10 times.
The patient’s hand lies on a flat surface. The palm is raised and, with the help of a healthy hand, is pulled back, pressing on the fingers. This tension should be maintained for 10 seconds, then the hand is lowered. Repeat the exercise 3 times.
A small object is taken into the hand, raised above the head and rotated in the wrist 3 times clockwise and three times counterclockwise. Then the hand is lowered. The exercise is repeated 3 times. As you train, the weight of the subject can be increased.
Squeeze the expander in your hand for 5 seconds with a break of 2 seconds. Repeat the exercise at least 5 times.
Pull the elastic band over the thumb of the affected hand and the thumb of the healthy hand. Then you need to stretch the elastic band with springy movements, overcoming its resistance. Exercise is performed at least 15 times.
Prognosis and prevention
When the patient does not hesitate to seek medical help, the prognosis for a full recovery is most often favorable. It is possible to get rid of the disease, on average, in 2 weeks. About 14 more days the patient will need to fully recover.
Provided that tendovaginitis of the hand is a consequence of professional activity, it is necessary to think about changing jobs. Otherwise, the inflammation will constantly recur, which will lead to severe disorders in the functioning of the limb.
The worst prognosis is observed when an infection becomes the cause of tendovaginitis. With purulent inflammation, a person can develop a permanent impairment of the hand, even after the first episode of tendovaginitis. When the patient ignores pathological symptoms, this can lead to blood poisoning and death.
Preventive measures aimed at preventing tendovaginitis of the wrist joint:
During work associated with an increased load on the arm, it is imperative to take breaks, stretching the limb.
Avoid performing the same movements for a long time.
At home, you can perform massage and gymnastic complexes.
Injuries to the upper extremities and joints should be avoided.
All infectious processes in the body must be treated.
Compliance with these simple recommendations will prevent the development of tendovaginitis of the wrist joint.









