Contents
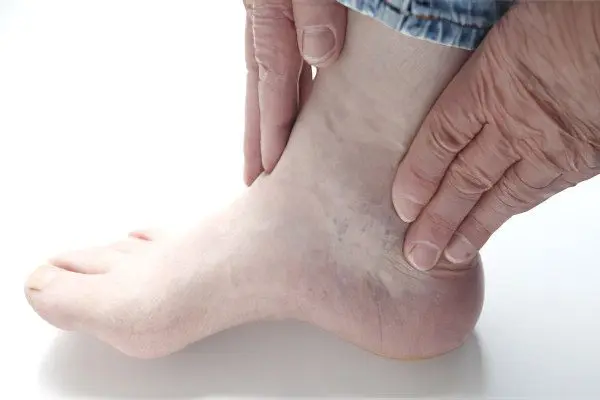
Tenosynovitis of the ankle joint is an inflammation of the synovial membrane of the vagina covering the tendon and is responsible for the movement of the foot. The inflammatory process can have an acute and chronic course, accompanied by the occurrence of symptoms such as pain, swelling, limitation of limb movement, etc.
The causes of tendovaginitis of the ankle joint are diverse, most often the pathology manifests itself as a result of injury, or against the background of infection in the tendon sheaths. If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner, then most often it is possible to cope with the disease with the help of medical correction.
The synovial sheaths that surround the tendons of the foot can be located on the back or plantar part of it. The consequences of untreated inflammation can be the saddest, up to the complete loss of limb functionality. As a result, a person can become disabled. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, you should consult a doctor.
Causes of tendovaginitis of the ankle joint
Causes of tendovaginitis of the ankle joint can be as follows:
Received microtrauma tendon sheaths of the foot. This occurs against the background of pronounced loads, or with an anatomical violation of the ratio of the structures of the foot. At risk for the development of tendovaginitis of this localization are athletes, skaters, tap dancers, ballerinas.
Flat feet can lead to tendovaginitis of the foot. This also includes congenital and acquired deformities of the lower extremities (heel, horse, hollow foot, clubfoot, etc.).
Therefore, additional risk factors for the development of inflammation of synovial bags can be considered:
Rickets;
Poliomyelitis;
Wearing shoes with high heels;
Obesity;
standing work;
Aging of the body;
Hereditary weakness of the ligamentous apparatus;
Insufficient physical activity.
The presence of a focus of purulent infection in the body. In this case, the pathogenic flora enters the tendon with blood flow, or through direct contact with tissues, and begins to multiply in the synovial bags. They constantly produce liquid, which is a favorable environment for an increase in the number of bacteria.
In this regard, pathologies such as:
Felon;
Purulent arthritis.
Injury to the foot with the penetration of infection into it;
Osteomyelitis;
Phlegmon;
Abscess, etc.
Inflammation of the tendons of the foot can develop with the following diseases: influenza, gonorrhea, tuberculosis, brucellosis. In this case, the infectious agents penetrate into the synovial sheaths of the foot with a blood stream.
Diseases of a rheumatic nature are another risk factor in terms of the development of tendovaginitis of the foot. Such pathologies include Bechterew’s disease, systemic scleroderma, Reiter’s syndrome, rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis.
Injuries to the bones and soft tissues of the foot are dangerous because pathogenic flora can get into them, which can cause inflammation. This happens with deep burns, with a splinter in the leg, with stab and lacerations, with fractures and ruptures of tendons with a violation of the integrity of the skin.
Performing a pedicure with non-sterile instruments should be noted separately, since it is this reason that often leads to the development of tendovaginitis in women. During truncation of the cuticle with non-compliance with the rules of sterility, the infection can get under the nail. In the place where the skin is in contact with the nail plate, sweat and sebum accumulate, which is a favorable environment for the development of bacterial flora. As a result, a purulent focus is formed in the finger, which in the future can lead to the development of tendovaginitis of the foot.
Symptoms of tendovaginitis of the ankle joint
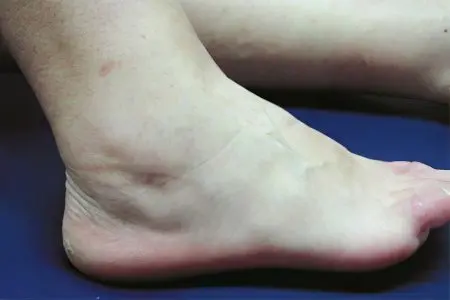
Symptoms of tendovaginitis of the ankle joint can be distinguished as follows:
Pain. Pain increases during any movement of the foot, including when walking. The pain is acute, localized in a strictly designated place, namely, in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe inflamed tendon. The farther the muscles are located from the focus of inflammation, the less intense the pain will be. If tendovaginitis is accompanied by an accumulation of purulent masses, then the pain will be pulsating, pulling from the inside.
Puffiness. As the blood vessels become overfilled with blood, they become permeable. The fluid from them is released into the tissue of the foot, thereby forming edema. Puffiness increases rapidly, literally a few hours after the manifestation of pain, the limb can double in size. Sometimes, due to the strong stretching of the tissues, the skin in the affected area is covered with small cracks.
Hyperemia of the skin. Redness is located clearly above the inflamed tendon, which is caused by the expansion of blood vessels.
A crunch can occur with pressure on inflamed synovial bags.
local hyperthermia. The temperature of the skin rises in the area of inflammation, which is explained by a sharp rush of blood.
Limitation of mobility of the ankle joint.
If the inflammation is purulent, then the patient has intoxication of the body as a whole, his body temperature rises, weakness and malaise are observed.
It cannot be ruled out that the acute form of tendovaginitis will turn into a chronic one. In this case, the person will suffer from pain and limited movement of the limb. During the examination of the patient, the doctor visualizes the formation located under the skin, which has the shape of a cord. Sometimes you can palpate small grains, which are a symptom of tuberculous tendovaginitis.
Diagnostics
To clarify their suspicions about tendovaginitis of the foot, a person can seek advice from a general practitioner or orthopedist. In the future, he may be referred to a rheumatologist or surgeon.
To determine the diagnosis, the doctor performs the following activities:
Visual examination of the patient. In addition, the doctor performs palpation of the affected area, checks reflexes.
Interrogation of the patient.
Blood sampling for general analysis. In acute inflammation, accompanied by suppuration, an increase in ESR and the number of neutrophils will be observed in the blood.
Bacterioscopic and bacteriological examination of exudate from inflamed synovial bags. Fluid sampling is performed during the puncture.
X-ray examination, CT and MRI. These studies provide an opportunity to clarify the absence of bone or articular pathology.
Treatment
Treatment of tendovaginitis of the ankle joint is determined by the form of the disease. First of all, it is necessary to stop acute inflammation and relieve pain in order to alleviate the condition of a person.
So, in the acute phase of tendovaginitis, the following activities are shown:
The limb must be in absolute rest. The leg should be placed in an elevated position using immobilization devices. It can be a plaster splint or an elastic bandage.
Prescribing antibacterial drugs. The doctor chooses the drug empirically, if bacteriological examination of exudate from synovial bags has not been carried out before.
NSAIDs: relieve pain and help eliminate the inflammatory response.
If tendovaginitis develops against the background of infection of the body with tuberculosis, then treatment is carried out aimed at eliminating the underlying infection. The same statement is true for syphilis and brucellosis.
Acute purulent inflammation with a wide distribution requires emergency surgery. In this case, the wound is opened, drained and sanitized. The doctor should carefully examine the wound surface to make sure that there are no fistulas and purulent pockets.
After the acute phase is eliminated, the patient is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapy.
Patients with tendovaginitis are shown the following measures:
UHF;
Electrophoresis with analgesics and hormonal drugs (hydrocortisone + novocaine);
Electrophoresis with lidase;
Massage;
Performing a complex of physiotherapy exercises;
Applications with paraffin and ozocerite;
Mud treatment.
Provided that therapy does not bring the desired results, and relapses occur frequently, it is necessary to prepare the patient for surgery. It is being carried out as planned. During surgery, the tendon is excised, and the wound and dissected tissues are sutured. The recovery period lasts 14 days. At this time, the patient receives antibiotic therapy, performs gymnastic complexes, attends physiotherapy sessions. If the operation is successful, the patient can fully recover.
Physiotherapy

Therapeutic exercises for tendovaginitis are performed in order to strengthen the tendons and relieve tension from them.
To do this, you can practice the following exercises:
Walking on toes, on the outer and inner side of the foot, on the heels. The time of therapeutic walking can be equal to 10-15 minutes.
With the help of a rubber band, they tie the feet and try to spread them in different directions, stretching the elastic as much as possible. At this time, a person should sit on a chair with a back.
Performing circular movements with the feet clockwise and against it. You need to perform 15 rotations in one direction and 15 rotations in the other direction.
Rope jumping. To maximize the load on the ankle tendons, you need to bounce without bending your knees.
Picking up small objects with your toes.
Before exercising, you should consult your doctor. This is especially true for people who have suffered an injury or surgery on the lower limb.
Prognosis and possible complications

The prognosis for tendovaginitis of the foot is most often favorable. If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner, he will recover as soon as possible. Provided that the inflammation is due to professional characteristics, then you should think about changing jobs. Otherwise, relapses of the disease cannot be avoided.
In severe tendovaginitis, as well as in its advanced stage, the following complications may develop:
Formation of contractures and fistulas.
Ligament stenosis.
abscess formation.
The growth of connective tissue.
Sepsis.
If the disease is not treated, then you can completely lose the functionality of the foot.
Meanwhile, preventive measures are not at all complicated. They boil down to avoiding excessive stress on the tendons of the ankle, for which you need to take at least short breaks in work. At home, you can also perform massage and therapeutic exercises. If you get a foot injury, you should take care of its high-quality disinfection. When performing a pedicure, you need to monitor compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards and remember about sterility.









