Contents
What is infertility?
Infertility in women (female infertility) is the impossibility of conception during the year of regular penetration, viable and active spermatozoa, naturally or artificially, into the reproductive organs of a woman of puberty. Infertility is also diagnosed if the pregnancy always ends in miscarriages. Up to 20% of couples are infertile.
Infertility in women should not be confused with non-carrying of a pregnancy, when a mature oocyte is successfully fertilized by a spermatozoon, but the pregnancy ends, at the stage of embryogenesis, in miscarriage or abortion.
A woman is not considered infertile if her partner is found to have non-viable, weak spermatozoa by laboratory methods, or they are completely absent.
The problem of infertility. The problem of infertility is now much more serious than it used to be, several centuries ago. The sexual revolution carries a serious responsibility, if only because it spreads infectious diseases. And young people no longer want to have children, the delay in pregnancy is growing more and more. If we take all infertile couples as 100%, then in 33,3% the man is infertile, in another 33,3% the woman is infertile, and in the remaining couples, both partners are infertile.
The causes of infertility can be malformations in the development of the reproductive system, dysfunction of the genital organs, severe intoxication and general diseases of the body, as well as mental and neurological disorders. Infertility does not belong to the group of independent diseases, it always appears as a result of various diseases of the body. The main cause of female infertility is inflammatory diseases.
Physiology of monthly cycles
Infertility can be with disturbed and normal monthly cycles. The natural monthly cycle of a woman, lasts 21-35 days, consists of three consecutive phases.
1. Follicular phase – egg maturation (at least 7 and not more than 22 days)
2. The ovulatory phase of maturation and release of a mature oocyte, the onset of the fertile period.
3. Luteal – phase of the corpus luteum, catabolism (from 13 to 15 days).
A few days before and after ovulation is called the fertile period (phase) – this is the time of the greatest probability of conception. Up to this point and after pregnancy cannot occur! However, it must be understood that for different women this phase occurs at different periods of menstruation. If the cycle is not resolved by pregnancy, then the body, under the influence of estrogens, prepares for the next cycle.

Classification of infertility
Infertility may be:
primary – pregnancy has never occurred (congenital gynecological anomalies) or (complications on the female genital organs) before or after menarche (first cycle);
secondary, after the first successful pregnancy, the impossibility of re-fertilization, may be absolute (incurable) or relative (curable).
In separate sources devoted to studies of the physiology and pathophysiology of the female genital area, the concept is supplemented by the following types of infertility.
Physiological. The norm is early infertility (before puberty), and postmenopausal infertility (after menopause).
Voluntary. Otherwise, they call consciously chosen infertility – the use of (drug) drugs or physical (spiral, other) means.
Temporary. May be the result of prolonged stress, weakening of the body after or during the period of illness, some authors refer to temporary infertility as lactational amenorrhea – inhibition of ovulation in the early period of regular breastfeeding.
Constant. Removal of the female genital organs, complete or partial, is the result of surgical intervention.
Signs and symptoms of infertility in women

An important sign indicating infertility in a woman is the inability to get pregnant for a year or more, if there are favorable conditions for conception, namely:
regular sexual intercourse;
sexual partner with a good spermogram;
complete, prolonged rejection of contraceptives;
the age of the woman is from 20 to 45 years.
Infertility does not have a pathognomonic (leading) sign, often asymptomatic, or has indirect symptoms. Signs of infertility are established during the collection of anamnesis, examination, physical, laboratory, instrumental studies.
Anamnesis. Establish clear symptoms associated with a violation of regular cycles: long, short, painful, profuse, with extraneous secretions. It is possible to assume infertility on the basis of establishing indirect symptoms characteristic of infectious, non-infectious and surgical diseases.
Physical examination
During physical examinations in the clinic, possible signs of infertility are:
body mass index less than or greater than 20-26;
condition of the skin and derivatives with signs of endocrine disorders;
unsatisfactory degree of development, mammary glands;
signs of soreness, seals in the projection of the female pelvic organs, with bimanual gynecological palpation;
signs of gynecological diseases detected when examining the cervix, using a vaginal mirror, colposcopy.
Laboratory and instrumental methods
Signs, possibly indicating infertility, are established in the process of laboratory and instrumental studies, with:
infectious screening for STIs;
hormonal screening to rule out endocrine infertility;
Ultrasound of the female pelvic organs, thyroid gland – hormonal infertility;
hysterosalpingography (HSG) – X-ray exclusion of symptoms of obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
MRI for brain tumors (turkish saddle) that inhibit the production of hormones – regulators of monthly cycles;
spiral computed tomography (SCT) of the pelvic organs – anatomical causes of infertility;
laparoscopy (visual examination of the abdominal organs) – tubal-peritoneal infertility, adhesions, uterine tumors, ovarian retention cysts;
hysteroscopy (examination of the walls of the uterine cavity) – tumors of the uterus, inflammation, ulceration of the walls of the uterus.
The causes of infertility in women
Women’s infertility is due to many private reasons (factors). The reasons are not always obvious. In some cases, they cannot be diagnosed or are combined with each other, increasing the negative effect on the female body.
If we summarize the known causes (factors) of infertility, there are several large groups – the causes of infertility:
Congenital anomalies of the reproductive organs.
Acquired, caused in the reproductive organs:
anatomical and morphological changes;
functional disorders;
metabolic imbalance.
The above describes most of the private (specific) causes of female infertility. It has been noticed that in women after 35 years, especially those who have not given birth before, the risk of infertility increases.
There are two common causes of reduced fertility that are not associated with previous gynecological diseases:
age-related slowdown of physiological processes;
prolonged use of contraceptives.
Contraceptive infertility
There are conflicting opinions in the literature about the use of hormonal contraceptives. Supporters argue the benefits of contraceptives due to the “rebound effect” after the abolition of hormonal contraceptives. That is, the abolition of factors that inhibit the process of fertilization, stimulates a sharp release of estrogen, increases the likelihood of becoming pregnant. In some cases, this is what happens.
On the other hand, cases of temporary or permanent decrease in fertilization (fertilization) are known after prolonged use of contraceptives. Obviously, the truth is in the middle. The negative impact of hormonal drugs should be avoided, based on the advice of a gynecologist, when planning a personal (marital) life. It is possible to combine different methods of contraception and then they will not be one of the causes of infertility.
Causes of secondary infertility in women
For help in determining the causes of infertility, women who have previously successfully given birth seek help. The inability to get pregnant again for a long time is called secondary female infertility. If we do not take into account the voluntary refusal to conceive and the age factor, the most obvious causes of secondary infertility are previous diseases, including gynecological infectious or non-infectious etiopathogenesis.
Infertility Factors

Infertility almost always has many causes (factors). As a result of research and clinical observations, it has been established that infertility factors are structured (grouped) on the basis of a combination of homogeneous signs, according to:
anatomical localization of the pathogenesis of diseases that caused infertility;
the nature of pathophysiological processes in the body (endocrine disorders, the phenomenon of immunological rejection of germ cells);
genetic abnormalities that prevent fertilization;
the peculiarities of the psychosomatic state of women of childbearing age in different living conditions;
influence of male factor of infertility.
Cervical factor infertility
For successful fertilization, at least 10 million active spermatozoa must enter the uterus of a woman. The vaginal environment of a healthy woman is a barrier to any agents foreign to the female body, including spermatozoa. With vaginitis, the causes of sperm death in the vagina are associated with pathological processes. A normal environment is not an absolute barrier to spermatozoa, active cells move to the cervix, covered with mucus. Mucus on the walls of the cervix is produced by epithelial cells.
The ability of spermatozoa to penetrate cervical mucus depends on:
activity and motility of spermatozoa;
physical and chemical characteristics of cervical mucus.
In pathologies, the properties of mucus change, becoming an insurmountable barrier even for active spermatozoa. The inability of male germ cells to overcome the cervix is called the cervical factor of infertility.
Cervical infertility factor (change in mucus viscosity, other properties) may be the result of:
hormonal failures in the production of female sex hormones;
inflammatory processes in the cervix;
disturbed microflora on cervical mucus.
Tubal factor infertility
The fallopian tubes transport the mature egg from the ovary to the uterine cavity. The mucosa of the fallopian tubes is lined with ciliated epithelium.
The movement of the egg occurs as a result of:
peristaltic movements of the walls of the pipes;
flickering of the cilia of the epithelium, which creates the flow of tubal fluid
Damage to the cilia, provokes pathological fixation of the egg in the tube, creates a risk of ectopic pregnancy. The greatest negative impact is associated with complete or partial obstruction of the tubes for a mature egg – this is the tubal factor of infertility.
Obstruction (obstruction) of the fallopian tubes can be:
in the area of the funnel – the distal (far) department of the fallopian tubes;
in the area of the uterine part of the tubes (proximal or near) of the fallopian tubes;
throughout (obstruction of the infundibulum, ampulla, isthmic and uterine sections) of the tubes.
Diagnostic value is the establishment of types of obstruction:
partial;
complete.
Tube obstruction – a factor infertility can be caused by spasm or blockage of the tube lumen due to inflammatory adhesions, tumor growth, and other reasons. A disease of the fallopian tubes, accompanied by obstruction of the tubes and the accumulation of transudate (fluid) in their lumen, is called hydrosalpinx.
Typical causes of hydrosalpinx are a complicated course of inflammation:
fallopian tubes – salpingitis;
fallopian tubes and ovaries – salpingo-oophoritis;
fallopian tubes, ovaries and ligaments – adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages).
An obstruction in the path of the egg may be accompanied by pain in the abdomen. To diagnose hydrosalpinx, an X-ray examination (hysterosalpingography) and / or laparoscopy (a special type of examination of the abdominal cavity) is used.
Cervical infertility factor
A through hole – a pharynx in the center of the cervix, like a gateway, connects the uterine cavity and the vagina. The function of the gateway, the pharynx of the cervical canal, manifests itself in the form of a periodic:
inaccessibility of the uterus, most of the time, to foreign agents, including spermatozoa;
the availability of the uterus for active spermatozoa seeking to fertilize a mature egg.
The function is provided by the mucus of the cervical canal, which, under the influence of estrogens, changes its physicochemical and rheological (viscosity) properties at different periods of the monthly cycle.
During the period of the greatest probability of fertilization, mucus changes properties, for example, pH from acidic to favorable for spermatozoa – neutral and slightly alkaline and becomes less viscous.
In the inactive phase of the cycle, the pharyngeal mucus provides protection for the woman’s body from disease-causing agents.
If the cervical mucus of the pharynx of the cervix, under the influence of pathological factors, is inaccessible to the penetration of sperm into the fertile phase, this is a cervical infertility factor.
Cervical mucus in the body of a healthy woman performs the following functions:
protection (protection) and temporary depot (storage) of spermatozoa in the reproductive tract;
retention of weak sperm, unable to overcome the physical barriers of viscous cervical mucus;
transfer of the activation factor of spermatozoa, increased their motor activity;
capacitation (ability) and acrosomal reaction (penetration) of spermatozoa i.e. the ability to penetrate the sperm into the oocyte.
External pharynx – visually examined with a vaginal mirror. The internal os is inaccessible to conventional examination methods.
Cervical factor infertility is detected by colposcopy by detecting a “pupil symptom” in the pharynx of the cervical canal. A positive pupillary symptom is clear, watery periovular mucus.
Cervical factor is detected by laboratory methods:
study of rheological and biochemical properties of mucus;
postcoital test (PCT) for the interaction of sperm and mucus after some time after intercourse. The usual time for determining PCT is 9-24 hours;
determination of the periovulatory Kurzrock-Miller test.
Laboratory tests are carried out by experienced laboratory technicians. The results of the research depend on the right time of the research.
tubal peritoneal infertility factor
The abdominal cavity and internal organs are protected by the mesentery from contact and fusion with the abdominal wall and neighboring organs. The mesentery is a serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity from the inside, divided into:
parietal sheet of the mesentery – separates the internal organs from the abdominal wall from the inside.
the visceral sheet of the mesentery suspends all the internal organs of a person.
The abdominal cavity is filled with serous fluid and also serves to protect the organs from mutual fusion and friction. Normally, all internal organs have some degree of spatial mobility.
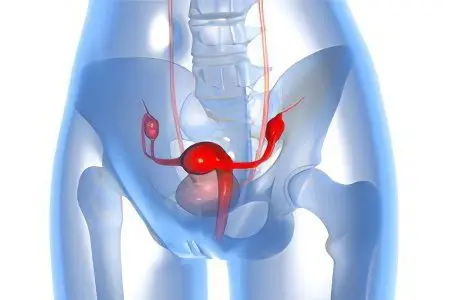
The fallopian tubes and the uterus are suspended on the mesentery. Under the influence of pathogenic factors, adhesions form between the fallopian tubes and the mesentery or a neighboring organ.
As a result, the fallopian tubes, connected to the mesentery, lose:
mobility;
sufficient blood supply
complete innervation;
As a result of adhesions in the abdominal cavity, the fallopian tubes cease to fully perform their functions. The cessation of the functioning of the fallopian tubes under the influence of adhesions of the peritoneum is called the tubal-peritoneal factor of infertility.
Causes of tubal peritoneal infertility factor:
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, which have passed into the chronic stage of fibrinous inflammation (often STIs)
Complications after abortion, operations on the pelvic organs.
Damage to the pipes leads to a violation of the monthly cycles, chronic pain syndrome.
Infertility or decreased fertility of tubal peritoneal origin is manifested by:
impaired patency of the fallopian tubes – tubal infertility factor
adhesive process in the pelvis – peritoneal factor of infertility
combination of tubal and peritoneal infertility
For differential diagnosis of tubal-peritoneal infertility factor, ultrasound, laparoscopy, echography are performed.
Immunological factor of infertility
Normally, the immune system of a woman, when foreign proteins penetrate – in the form of seminal fluid and spermatozoa (antigens), does not react with the production of specific antibodies (ASAT). The reasons for the immunological rejection of sperm are not fully understood.
The appearance of ASAT in women is probably the result of the development of rejection reactions of the type of allergic reactions of type 2. The barrier properties of the mucous membranes can be impaired as a result of a decrease in the amount of mucus on the internal surfaces of the genital organs during degenerative inflammatory processes. Currently, this pathology is treated by methods of immunocorrection, a decrease in the number of circulating antibodies, and stimulation of reparative (restorative) processes on the mucous membranes of the birth canal.
Another immunological pathology is the infertility factor, the production of anti-ovarian antibodies (AOA) by the female body against her own eggs. The reasons for the appearance of immune complexes that destroy their own immune defenses are complex and are within the competence of immunologists. Like all autoimmune diseases in the early stages of pathogenesis, they are treatable. In advanced cases, the prognosis is poor.
endocrine factor infertility
Disturbances in hormonal metabolism lead to irregular cycles or their absence. The main causes of this kind of infertility are dysfunctions:
Consequences of traumatic brain injury, tumors of the hypothalamic-pituitary region of the brain;
An imbalance of androgens over estrogens (hyperandrogenism) in the female body is observed when the ovaries or adrenal glands are damaged, accompanied by polycystic ovary syndrome;
A decrease in the functional activity of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) is the cause of cycle disorders;
Insufficient amount of estrogen, accompanied by a violation of the rhythm of monthly cycles, leads to pathological damage to the mucous membrane of the birth canal;
Lipid metabolism disorders, accompanied by an excess or loss of adipose tissue, provokes a decrease in ovarian function;
Hormonal disorders, accompanied by premature menopause;
Congenital anomalies of the hormonal system, accompanied by underdevelopment of the birth canal.
Endocrine disorders are examined in case of violations of monthly cycles, against the background of external signs of endocrine disorders (obesity, malnutrition, others).
Psychological factor of infertility
Stress is a general adaptive reaction of the body to various stimuli, it has a complex regulation mechanism, including the body’s hormones. It is pointless to look for private causes of stress, like psychological factors of infertility, they are individual for each woman. In a generalized form, the sources of stress are:
excess of negative information;
regular emotional reactions;
physiological or pathophysiological reactions of the body.
In chronic stress, the body’s adaptive defense mechanisms are depleted. The structures of bioregulation (the autonomic nervous system, hormones of the adrenal glands, the pituitary gland, and others) cease to work in the direction of adaptation, causing pathophysiological changes in the body. Behind the psychological factors of infertility are hidden pathophysiological changes in the body (including hormonal disorders). To determine the causes of psychological infertility, you should stop looking for a source of stress, you must:
Change your attitude towards the stress factor. It has been noticed that families with a low level of education do not have problems with the birth of children, in contrast to families where women with a high level of intelligence and social status suffer from obvious and imaginary stresses. Physical education, useful hobbies, relaxation, positive emotions, and so on will restore hormonal and mental balance.
Contact a qualified psychologist. It is not always possible to overcome stress on your own. Find a specialist who will help you stop thinking about imaginary problems, help you understand the true causes of infertility.
Genetic Factors of Infertility
The genetic factors of male infertility are described in detail in the literature. The genetic factors of infertility in women are little studied. There are known private pathologies that cause female infertility, which have genetic roots.
Syndrome of hyperandrogenism of women (an excess of male hormones).
Endometriosis (growth of the walls of the uterus).
Syndrome of premature menopause.
Syndrome of primary amenorrhea (Sherevsky-Turner syndrome).
There are also other diseases accompanied by genetically determined infertility. The causes and probability of exclusion in the future of genetic anomalies is the subject of research by geneticists. Currently, laboratory methods for diagnosing genetic factors of infertility are being developed.
Degrees of infertility

The etymological meaning of the word “degree” in medicine means the magnitude of comparison, pathological processes of different intensity. The use of the term is appropriate when comparing particular (specific) pathological processes in relation to a limited group of patients with a similar diagnosis. More often, in the available literature, infertility is characterized as I and II types of infertility.
1st degree infertility in women. Or infertility I is the absence of pregnancy in a woman who has never given birth before. Usually, the period of infertility is counted after a year of regular sexual activity, without the use of contraceptives. Causes of infertility 1 are listed above in the text (see classification of infertility).
2st degree infertility in women. Or infertility II – this is the impossibility of conception, refers to women who have previously had a pregnancy or have given birth. The term of infertility is counted from the first attempts of repeated pregnancy. Usually also after a year. Causes of infertility II are indicated above in the text (see classification of infertility).
Infertility 3 degrees in women. The term characterizing the degree of inability to conceive is not used in the available literature.
Therapies
The combined use of boron uterus, red brush and sage
Recommendations for suspected infertility
Experts say that in order to achieve the maximum chance of fertilization, it is necessary to conceive from the 11th to the 18th day of the menstrual cycle. We remind you that the first day of menstruation is taken as the first day. Men should not ejaculate more than once every 2 days, as the concentration of sperm is maintained at a maximum, only in this case. Both partners must not apply lubricants. And after sex, a woman should not wash herself. In addition to all this, experts say that you need to have sex during fertilization in the “missionary” position, and after intercourse, the woman should still lie on her back for 15-20 minutes, with her knees bent and raised.
If the presentation methods do not give the desired result, then the couple will be assigned to undergo treatment. In the case when it is impossible to eliminate the causes of infertility, experts recommend modern assisted reproductive methods, such as IVF.
In vitro fertilization is a relatively young method of infertility treatment, the essence of which is the fertilization of eggs with spermatozoa in a test tube and the subsequent transfer of a fertilized developing egg (embryo) to the uterus. This procedure gives good chances of pregnancy, however, it is worth taking a responsible approach to choosing a clinic. The main factors influencing the choice of a clinic are the level of professionalism and experience of fertility doctors, as well as modern equipment.
Among the centers of Russia with the best reputation, we can single out the Moscow Life Line Reproduction Center, which fully complies with the above requirements. The center has the latest innovative equipment that allows you to significantly increase the effectiveness of the procedure. And the personal composition is high-class specialists who are considered one of the best in the field of IVF, including M.E. Potapov, who is at the forefront of domestic reproduction. and member of the Council of the Russian Association of Human Reproduction Kolod Yu.A.
Even if a woman dreaming of a child is diagnosed with infertility, then this is not a reason to despair! Modern medicine not only gives hope for replenishment in the family, but also proves its capabilities as a result of numerous happy families.









