Contents
Heel spur – what is it?
A heel spur is an overgrowth of the heel bone in the region of the tubercle on the plantar side or in the area of attachment of the Achilles tendon. The growth is in the form of a spike or wedge. Heel spurs are also called plantar fasciitis.
The disease is widespread, its share among the total mass of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system is 10%. Most often, spurs are diagnosed in women who have crossed the line of 40 years, although aseptic inflammation of the calcaneal fascia is not excluded at any age, in any person with predisposing factors.
Causes of a heel spur
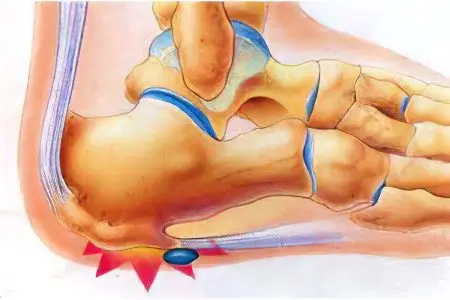
The causes of heel spurs lie in the impact on the heel fascia of various factors, primarily high loads. The fascia is of great importance in the formation and maintenance of the arch of the foot; during walking, it bears the entire weight of a person. Throughout life, it is subjected to various stresses, and by old age, a heel spur is formed in every fourth person.
The causes of the formation of a heel spur are considered to be:
Foot injuries, heel injuries: fractures, bruises, sprains, etc.
Diseases accompanied by circulatory disorders, failures of metabolic processes.
Overweight, diabetes.
Excessive physical activity during sports. Professional athletes often suffer from heel spurs, as grueling workouts can lead to sprains and increase the risk of injury. Sports training causes the formation of spurs at a young age.
Regular wearing of high heels. The condition of the fascia is negatively affected by wearing uncomfortable shoes, the absence of shock-absorbing insoles in it, a thin and hard sole.
Longitudinal flat foot. A heel spur is formed in 90% of people with this pathology. This is due to the fact that the distribution of the load on the foot is uneven, the tendons suffer from excessive tension, and the likelihood of injury increases.
Diseases of the joints and spine. Such pathologies include: gout, arthritis, osteoarthritis. Strengthening of symptoms is observed with exacerbation of bursitis, periostitis.
Connective tissue diseases can provoke the development of heel spurs – these are pathologies such as Bechterew’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis.
Thinning of the fat pad in the heel area due to age-related changes in the body.
Gout. (read also: causes, symptoms and treatment of gout on the legs)
Symptoms of the heel spur
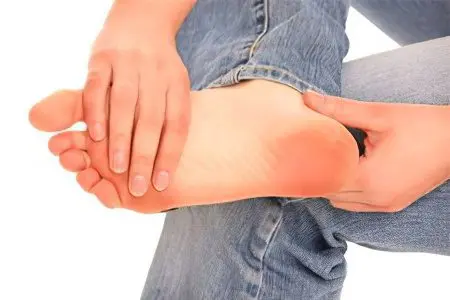
Symptoms of a heel spur cannot go unnoticed by a person, as they are always accompanied by severe pain.
The clinical picture of the disease is as follows:
First, pain occurs while walking or when performing other movements (running, jumping). As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies, causing suffering at the slightest support on the heel. Patients themselves compare pain with the presence of a nail in the heel. The nature of the pain is burning, sharp. The pain does not depend on the size of the growth itself, although it is provoked by the pressure of the overgrown bone on the heel tissue. For example, patients with small flat spurs may experience severe pain, while people with large growths experience only minor discomfort. The strength of the pain depends mainly on the location of the spur. The closer it is to the nerve endings, the stronger the pain.
Sharp pain occurs after a night’s rest. When a person begins to move, it weakens somewhat, but in the evening it rises again. Such cyclicity is due to the fact that during sleep, the microfractures of the fascia have grown together with shortening. The patient lay for a long time, and the angle of inclination of his foot in relation to the lower leg was not straight. When a person wakes up, a micro-rupture reappears, which is the reason for the sharp pain. As the fascia moves, it stretches, the pain becomes somewhat dull, but in the evening it intensifies due to stress and the formation of new microscopic tears.
As calcium compounds begin to accumulate in the scar tissue that forms around the heel spur, a person’s condition worsens. Pain that occurs during rest indicates that the process of calcification provoked the growth of osteophytes.
The patient’s gait changes. This is due to the natural desire of a person to unload a sore spot, namely the heel. Prolonged transfer of the center of gravity from the heel to the forefoot will lead to the fact that a person will have transverse flat feet. It is especially difficult for people to move if they have heel spurs on both legs. Such patients are often unable to do without improvised means, so they begin to use a cane or crutches.
Pain can become stable and disrupt the quality of a person’s life, making him incapacitated for a long time.
External pathological changes in the heel area are not observed. Sometimes you can find a mild swelling of the heel region and its callosity.
Diagnosis of a heel spur
Diagnosis of heel spurs is usually not difficult. The doctor is able to make a preliminary diagnosis based on the patient’s complaints of pain in the heel after waking up, after a long walk or run. During the examination, the doctor will press on the base of the heel, as well as from the sides. These manipulations will provoke the occurrence of pain in a patient with a spur. Also, the specialist evaluates the restrictions in the mobility of the foot, if any.
To verify the presence of a formed heel spur, the patient is sent for an X-ray examination. It allows you to estimate the size of the formation and the exact location of its location. Occasionally, a growth on the bone may be discovered by chance when the patient is being examined for a different purpose. At the same time, the spur does not cause any discomfort to its owner, and he does not even suspect its presence.
The picture will show a spike localized on the surface of the calcaneal tubercle. The spike is curved towards the fingers. In the early stages of the development of the disease, the formation is round, but even in this case, it can cause discomfort. The spike can reach a length of up to 12 mm, forming in the form of a bird’s beak.
Sometimes doctors send the patient not only for an x-ray of the foot, but also for an MRI, which allows you to assess the condition of the soft tissues surrounding the spur. Ultrasound is used less often, since it is less informative in this regard. An ultrasound of the foot is recommended to monitor the ongoing treatment, since ultrasound can be performed more often than MRI and x-rays.
What is the difference between a heel spur and spikes?
Heel spurs should not be confused with spikes (or spikes) on the feet. The heel spur is a process that forms on the heel bone under the soft tissues.
A spike is a type of wart that is localized on the sole or on the palms. Spike occurs due to human infection with a certain strain of the human papillomavirus. It is perfectly visible to the naked eye and looks like a small papilla or nodule on the skin. The danger of the spine is that it can eventually transform into cancer.
The differences between spurs and spikes are obvious. They have a different etiology and clinical course, so it is not correct to compare these two diseases.
How is heel spur treated?
A specialist who will clarify the diagnosis based on the results of the examination will tell you in detail about how the heel spur on the heel is treated.
Methods with proven effectiveness are considered to be:
Reducing the physical load on the foot, but at the same time it is necessary to perform exercise therapy with subsequent taping.
The use of specialized orthoses or brace.
Wearing insoles with arch supports.
The use of shock wave therapy.
Laser therapy
Local injections with glucocorticoids.
Limb immobilization.
Surgical intervention.
Ultrasound treatment.
X-ray therapy.
Cryodestruction.
Unloading the diseased limb and eliminating excessive pressure on the heel should precede any therapeutic measure.
Therefore, patients are given the following recommendations:
Compliance with bed rest;
Decreased walking and standing time;
Use of orthoses during night rest;
Use of orthopedic insoles while walking;
Use of specialized devices (crutches, canes, sticks).
Conservative therapy is reduced to the use of external ointments of the NSAID group. Ointments are used up to 4 times a day for 2 weeks.
In order to relieve pain, improve metabolic processes, and relieve inflammation, such agents as: Dimexide gel, Medical bile, external plant-based patches can be recommended.
Blockade (heel shot)
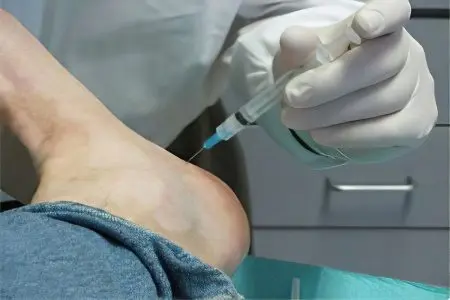
If conservative methods do not bring the expected effect, in many cases, drug blockade of the spur on the heel is recommended. This operation is performed by an orthopedic surgeon, who injects an anesthetic and anti-inflammatory drug directly into the area of inflammation of the plantar fascia.
These are hormonal agents from the group of glucocorticosteroids or have gluco- and mineralocorticosteroid activity. Due to direct administration, they very quickly stop the inflammatory process in the connective tissues of the foot and completely eliminate pain.
The main disadvantages of this procedure:
Elimination of pain occurs temporarily, and it is not known exactly when it can return, in some cases two or even three injections in the heel are required;
If there is an error in the technology of the procedure, there is a risk of complications: purulent inflammation, osteoporosis, necrosis or destruction of the plantar fascia.
Because of these risks, heel spur injection is not considered a first-line treatment for plantar fasciitis.
Orthopedic Insoles
Orthopedic insoles are one of the mandatory measures when plantar fasciitis is detected, since, technically, the cause of permanent micro-ruptures of the ligaments is the incorrect distribution of the load on the foot or its complete overload. In any case, specially shaped insoles will significantly relieve pain and allow the patient to move normally.
Insoles must be selected or ordered together with an orthopedist, as it is necessary to take into account the weight, size, anatomical nuances and severity of the disease. With a spur on the heel, shoes with a small heel are used for the insole, since the pressure needs to be redistributed to the forefoot. For this, a heel pad can be used additionally. The lining of the longitudinal arch of the foot absorbs sharp steps and kneads the muscles and ligaments.
Insoles and heel pads can be made of different materials – synthetic (gel, silicone, artificial leather) or natural (felt, cork). Natural orthopedic insoles are usually more expensive, as they allow the foot to breathe and adapt better to its shape.
Physiotherapy, balneotherapy
Various hot baths: radon, mud, mineral, paraffin. Improve the nutrition of cells and the speed of their recovery (10-20 minutes 7-10 procedures).
Massage. Develops muscles and ligaments, promotes the removal of salts and accelerates blood flow (20-30 minutes 10-14 procedures).
Electrophoresis of anesthetic drugs. It has an analgesic effect (5-10 procedures).
Taping
When all the exercises for the development of ligaments are completed, it is recommended to fix the stretched plantar fascia in an extended position with a heel spur. This can be done quickly and easily with the help of a special sports elastic tape – teip, from which the procedure is called “taping”.
For taping, a regular adhesive plaster can also be used, although it requires ether to pretreat the skin and special blunt-ended scissors to remove it.
One of the common taping methods is presented in the table:
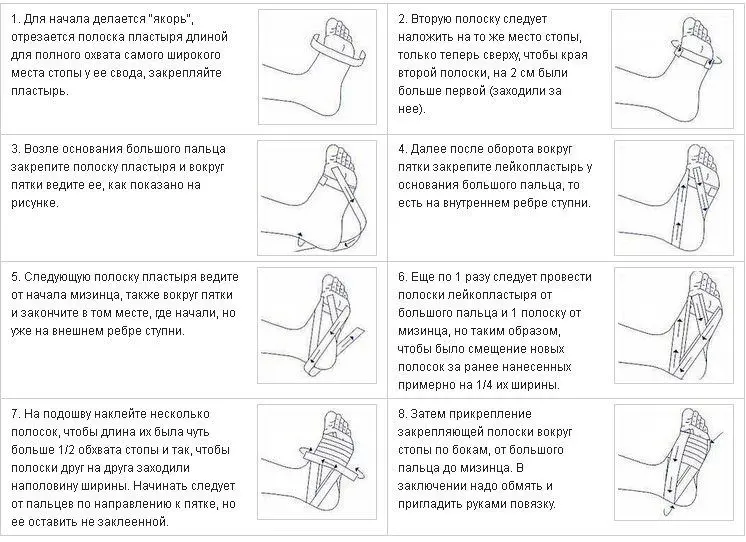
Night orthoses
In order to prevent daily ruptures of ligaments fused during the night, it is necessary to ensure the position of the foot at a right angle during the night. Since, in the absence of any fixators, the foot flexes during sleep, the plantar fascia is in a reduced position, which means it fuses with shortening, which provokes new tears when trying to restore full mobility of the limb.
An orthosis, or brace, is a kind of hard cover that fixes the foot exactly at an angle of 90 ° C relative to the lower leg. When using it, the morning pain is significantly reduced until the complete disappearance, since the ligaments grow together correctly.
If it is not possible to purchase night orthoses, you can tie the toe of the foot to the ankle with a strap, or put on solid fixing shoes (felt boots) at night.
Surgery
If conservative methods do not help get rid of the problem, then it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment. During the operation, an incision is made in the region of the spur, the existing growth is removed, and the tissues are sutured.
A modern surgical method for getting rid of heel spurs is endoscopic dissection of the fascia. The procedure is performed using endoscopic equipment, due to which the incision will be small – no more than 5 mm each. An endoscope is inserted into one incision, and a surgical instrument is inserted into the other. The doctor cuts the fascia of the sole, relieving tension from it, and then removes the spur itself. In addition, it is possible to remove the heel spur under the control of the X-ray machine. It is worth noting that doctors rarely resort to surgical intervention.
Shockwave therapy
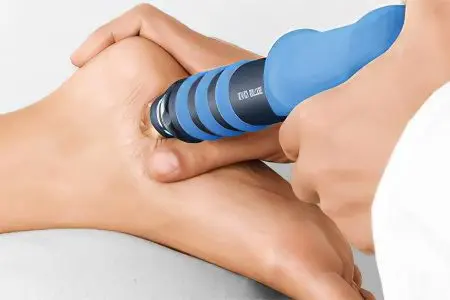
Shock wave therapy for the treatment of heel spurs is recognized as a highly effective method to cope with the problem. For the session, special equipment is used that emits shock sound waves. They have an effect on the affected area, reducing the susceptibility of pain receptors.
In addition, thanks to shock wave therapy, it is possible to loosen calcifications, relieve swelling, and speed up metabolic processes. This method significantly speeds up the recovery of the patient. The duration of one session does not exceed 30 minutes. Between each procedure should pass from 3 to 20 days. For one course, 5 to 7 procedures are recommended.
Benefits of shockwave therapy for heel spurs:
The procedure does not give side effects;
The therapy is highly effective;
There is an opportunity to avoid surgical intervention;
Absence of pain;
Gradual breakdown of calcifications;
Possibility of outpatient treatment;
Short duration of the procedure.
The disadvantages of the shock wave procedure in the treatment of spurs are only some contraindications. So, the session can not be performed for people under 18 years of age, during pregnancy, with hypotension, thrombophlebitis of the veins of the lower extremities, with exacerbation of any infectious diseases.
The effectiveness of the treatment of heel spurs with this method reaches 90%. Shock wave therapy can act as an independent method of treating a disease. However, if desired, it can be combined with conservative therapy and other physiotherapy.
Laser
Laser treatment is used in the absence of the effect of ongoing conservative therapy. Due to the effect of the laser beam, it is possible to reduce swelling, relieve inflammation and pain, and restore damaged tissues faster. However, it will not be possible to remove the bone growth with the use of a laser.
Treatment is carried out in courses, no more than 10 procedures are prescribed for the first course. They need to be done daily. After 2 weeks, the course can be repeated.
Benefits of laser treatment for heel spurs:
If the patient takes medications, then their therapeutic effect will be enhanced;
There are no side effects;
The healing process will be accelerated;
The effect persists for a long time;
There is no likelihood of developing an allergic reaction;
The procedure does not require hospitalization of the patient.
Disadvantages of heel spur treatment with laser:
It will not be possible to get rid of the bone growth;
The presence of contraindications (tumors, diabetes mellitus, heart and lung failure, thyrotoxicosis).
Ultrasound
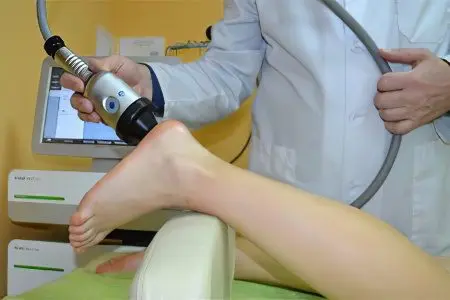
Ultrasound treatment involves exposure to the heel spur using ultrasonic waves emanating from a special device. Such therapy allows you to remove swelling and inflammation, as well as crush salt deposits.
The session is short in time and does not take more than half an hour. During the course, it is necessary to undergo from 5 to 7 procedures, the interval between them should be at least a week.
Benefits of treating heel spurs with ultrasound:
Absence of pain;
Possibility of getting rid of bone growth;
Short duration of the procedure;
No need for hospitalization.
Disadvantages of heel spur treatment with ultrasound:
The high price of the procedure, due to the need to purchase specialized equipment;
The presence of contraindications: violations of the heart, hypotension, the period of childbearing, thrombophlebitis of the veins of the lower extremities, disorders of the nervous system.
X-ray therapy
X-ray therapy for heel spurs is carried out by exposing the problem area with the help of x-rays. The spur has such a location that therapy can be carried out without harm to the whole organism.
X-ray therapy is prescribed when other methods are ineffective. The doctor, using an X-ray machine, directs an X-ray beam to the heel, to the place where the bone growth is located. As a result of this exposure, the nerve endings are blocked, so the person will no longer experience pain. The duration of one procedure is on average 10 minutes. The full course consists of 10 sessions.
Advantages of radiotherapy in the treatment of heel spurs:
Painless procedure;
Session duration;
To get rid of pain, 1 course is enough;
The anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect is long-lasting;
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis;
The impact is targeted, only on the affected area.
Disadvantages of radiotherapy in the treatment of heel spurs:
The presence of a potential risk to the health of the patient as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation;
The safety of the method has not been scientifically proven, long-term monitoring of patients who have undergone such therapy has not been carried out;
The presence of contraindications, including: bearing a child, the patient’s age is over 40 years old, exhaustion, any diseases in the stage of decompensation, blood diseases, radiation sickness.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction is a modern technique for the treatment of superficial formations, therefore this method is not suitable for the treatment of heel spurs. However, it can be successfully used to eliminate spikes on the heel. As a result, the patient will not have scars, the procedure itself is carried out quickly, the risk of recurrence of the disease is reduced.
In conclusion, we can add that the development of the disease can be prevented if you get rid of flat feet and diseases of the spine in a timely manner. Shoes worn by a person should be comfortable and orthopedically well-chosen. If symptoms of the disease occur, you should immediately seek the advice of a specialist.
Spurs exercises
Among the methods of first-line treatment of plantar fasciitis (that is, recognized as effective and mandatory), physiotherapy exercises take first place along with night orthoses and taping.
Special exercises are aimed primarily at stretching the ligaments of the longitudinal arch of the foot. With gradual and regular exercise, this helps to strengthen the plantar fascia, which acquires better elasticity, which reduces pain on a daily basis and reduces the possibility of inflammation in the future.
Exercise 1. Lean against the wall with your palms and place your feet in line with each other, placing the foot with the heel spur behind the healthy one. Slowly lower yourself down without lifting your heels off the floor until a painful stretch occurs in the area of the Achilles tendon of the sore leg. In this position, you should freeze for a few seconds, then rise to the starting position. Repeat 5-10 times.
Exercise 2. It is even easier to warm up the muscles without squats with the help of an elevation – a stand or a step. You also need to rest your palms on the wall or on the railing, stand on a raised platform so that your heels hang down, and slowly lean towards the wall until the ligaments of your sore leg are stretched. When the tension reaches the limit beyond which pain begins to be felt, you need to freeze for 15 seconds, and then also slowly push back from the wall.
Exercise 3. Take a tennis ball or other round or cylindrical object with a small diameter. Just put it under the sore foot and roll, lightly pressing down, along the entire longitudinal arch of the foot. If pain is felt, a small bottle of cold water can be used to achieve an anesthetic effect by cooling.
Exercise 4. A very fun and useful exercise for developing the muscles of the foot. It is known that inward heels can lead to plantar fasciitis, which can be seen in the way the heels or backs of the shoes are worn down. This fairly common phenomenon increases the tension of the fascia, which increases the risk of microtrauma of the ligaments. Therefore, do not be too lazy to do such an exercise every day: scatter a bunch of different small items on a small area – keys, coins, balls, pens and other little things; then collect them with your toes and put them in a pre-prepared jar. In the same plan, an exercise on the motor skills of the toes: put a piece of fabric (towel, T-shirt) on the floor and fold it as neatly as possible with the help of the legs alone.
Exercise 5. To complete the plantar fascia workout, you need to exercise the extreme forward bending of the foot. In a sitting position, take the sore leg with both hands or a strong sports tape and pull it to the body, bending the foot with the toe towards you as much as possible. In the extreme position, freeze for 15 seconds, then relax. After ten repetitions, you can finish the workout.
Prevention
It is worth noting that, subject to preventive measures aimed at preventing the disease of plantar fasciitis, this disease is treated in the early stages, even if it was not previously detected.
The necessary conditions for the prevention of heel spurs are:
Regular training of the muscular-ligamentous apparatus;
Development of joints and prevention of salt deposits;
Refusal of uncomfortable shoes, if necessary – lining of orthopedic insoles;
Cautious behavior in terms of stress on the feet – do not walk too much if overweight, give up extreme sports, travel with overcoming obstacles;
A visit to preventive massage and various physiotherapy;
In the presence of diseases of the musculoskeletal system (flat feet, rheumatoid arthritis, problems with the spine, etc.) – their speedy cure.









