Contents
What is glomerulonephritis?
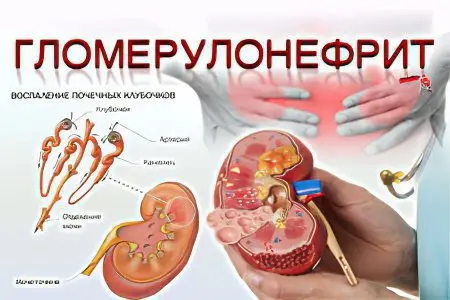
glomerulonephritis is a disease of the kidneys, otherwise known as glomerular nephritis. It is characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli. The disease affects the glomeruli, affecting the tubules of the interstitial (interstitial) tissue.
According to its development, glomerulonephritis refers to infectious-allergic diseases. This combination of words suggests that the disease combines the formation of an infectious allergy and non-immune damage to the organ. However, there are also autoimmune forms of the disease, in which the kidney tissue is damaged by antibodies to its own organ.
The glomerulonephritis proceeds for 15 years. At the same time, there are no edema, arterial pressure is low. For 10–25 years, kidney function is preserved, while the disease continues to progress and invariably leads to chronic insufficiency. Glomerulonephritis occurs with different periods, exacerbations are replaced by remission. During remissions, the patient does not complain about anything, only hypertension and urinalysis can speak of the disease, which constantly signals the presence of glomerulonephritis, only a little less during remission. The disease is aggravated from hypothermia, from infections, from the use of alcoholic beverages. During the period of exacerbation, the symptoms are the same as in acute glomerulonephritis. The skin of a person with glomerulonephritis is usually dry.
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis

Given the different forms of glomerular damage, one or other symptoms of glomerulonephritis begin to predominate:
The presence of blood in the urine (urine has the color of “meat slops”);
Swelling of the face (mainly swollen eyelids), feet and lower legs;
High blood pressure;
Scanty urine, thirst;
Body temperature rises (rarely);
Appetite disappears, nausea, vomiting, headache, weakness appear;
Body weight increases;
There is shortness of breath
Often, after suffering a streptococcal infection (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever), acute glomerulonephritis may develop 6–12 days later. Skin infections (pyoderma, impetigo) also contribute to the development of this disease.
However, the disease can also develop from other infections – bacterial, viral, parasitic – or after antigenic effects (sera, vaccines, drugs).
Causes of glomerulonephritis
There are the following causes of glomerulonephritis:
Infections (tonsillitis, scarlet fever, infective endocarditis, sepsis, pneumococcal pneumonia, typhoid fever, meningococcal infection, viral hepatitis B, infectious mononucleosis, mumps, chickenpox, infections caused by Coxsackie viruses, etc.);
Systemic diseases: systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, Schonlein’s disease, Henoch’s disease, hereditary pulmonary-renal syndrome;
Introduction of vaccines, sera;
Toxic substances (organic solvents, alcohol, mercury, lead, etc.);
Irradiation
Glomerulonephritis manifests itself 1-4 weeks after the negative impact of the provoking factor.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis
Mode
Patients with acute glomerulonephritis are subject to mandatory hospitalization. The patient is shown bed or strict bed rest. It all depends on how he feels. This is due to the fact that the patient’s body must be evenly warmed up. Maintaining a stable temperature regime allows you to optimize the work of the kidneys.
You will have to stay in the hospital for about 14 days or even more. Sometimes patients are hospitalized for a month, or until the symptoms of the disease can be completely stopped. What matters is how the patient’s body reacts to therapy.
Diet
All patients with glomerulonephritis are shown table No. 7a. It involves limiting protein foods and salt. This will avoid the formation of persistent edema and prevent an increase in blood pressure.
Inflamed kidneys can react sharply to foods that are potential allergens. The menu should be dominated by dishes rich in potassium and fiber. This is especially true for patients receiving corticosteroid therapy.
Elimination of the symptoms of the disease
If a person with glomerulonephritis has high blood pressure and edema is formed, then he is prescribed diuretics. They are taken for a short time.
Patients are prescribed drugs that strengthen blood vessels, drugs that nourish the kidneys and antioxidants.
Phytopreparations help to cope with edema with glomerulonephritis. Herbal treatment can reduce the drug burden on the body.
Antibiotics
If the disease was caused by a bacterial flora and this was confirmed during the diagnosis, then the patient is prescribed antibiotics. Most often, antimicrobial therapy is required for patients who have had a sore throat or other infection, the causative agent of which was beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Inflammation of the kidneys in this case will act as a complication
The drugs of choice are: Ampicillin, Ampiox, Penicillin or Oxacillin. They are prescribed 250000 or 500000 units 4 times a day. Drugs are administered intramuscularly. With glomerulonephritis, which is characterized by rapid progression, interferon is prescribed.
Immunosuppressive Therapy
In acute glomerulonephritis, the glomeruli of the kidneys are attacked by their own antibodies. They are produced by the immune system. Thus, it may respond to infection with beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Sometimes the kidneys themselves become an object of attack by antibodies. Therefore, the treatment of glomerulonephritis involves the suppression of the activity of the immune system with the help of immunosuppressants. They are included in various therapeutic schemes.
Reactive glomerulonephritis is treated according to the pulse therapy scheme. The patient during the day intravenously administered high doses of the selected drug. Then it is reduced, bringing to standard values.
The drug of choice is Prednisolone. The daily dose is calculated based on the weight of the patient (1 mg/kg). Then it is reduced to 20 mg per day. When the patient’s health stabilizes, the drug is smoothly canceled.
If therapy is carried out with cytostatics, then doctors most often use Cyclophosphamide (2 mg / kg) and Chlorambucil (0,1 mg / kg of body weight). After achieving remission, drugs that suppress the immune system are canceled. Further treatment is reduced to taking phytopreparations.
Multicomponent regimens for the treatment of glomerulonephritis
Steinberg scheme. The patient is administered 1 mg of Cyclophosphamide intravenously for a year once a month. Over the next 1000 years, the drug is administered once every 2 months. On the 3th and 4th year of treatment, the drug is administered once every 5 months.
The Ponticelli scheme. The patient is given pulse therapy with the use of Prednisolone (1000 mg 1 time per day). High dose therapy is continued for 3 days. Then for another 27 days the patient is offered 30 mg of the drug per knock. Over the next month, Prednisolone is alternated with Chlorambucil at 0,2 mg / kg per day.
four-component treatment regimen. Prednisolone 60 mg per day is prescribed for 30 days. Then the dose of glucocorticosteroids is gradually reduced until a stable remission is achieved. In parallel, a cytostatic agent chosen by the doctor is prescribed. The third component is Heparin (5000 IU 4 times a day). He is appointed for a month. In the future, the patient is transferred to Aspirin. The fourth component is Dipyridamole at a dosage of 400 mg per day. This scheme is prescribed to patients with glomerulonephritis, characterized by rapid progression.
Normalization of the blood coagulation process
Inflammation of the kidneys is accompanied by a violation of the process of blood clotting. Platelets begin to stick together, forming clots. They lead to a deterioration in the nutrition of internal organs. To prevent their hypoxia, patients are prescribed antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants. The most commonly used are Heparin (20 IU per day), Dipyridamole and Pentoxifylline.
Video: answers to questions from surgeon Alexander Malko:










саламатсыздарбы менинда куйом ушул оору мн ооруйт 😞😞 чындыгында корком жаш уй булобуз бир балабыз бар храничиский болуптур умутубуз чон бирок куйомдун ден соолугу уже даарыларды ичсе да анча тасир этпей атат суранам ушул оорунун даарысын тапсаныздар раазы болот элем 🥺🥺😫😫 куйом да раса кыйналып кетти